Yongsu Ahn
From Answer Givers to Design Mentors: Guiding LLMs with the Cognitive Apprenticeship Model
Jan 27, 2026Abstract:Design feedback helps practitioners improve their artifacts while also fostering reflection and design reasoning. Large Language Models (LLMs) such as ChatGPT can support design work, but often provide generic, one-off suggestions that limit reflective engagement. We investigate how to guide LLMs to act as design mentors by applying the Cognitive Apprenticeship Model, which emphasizes demonstrating reasoning through six methods: modeling, coaching, scaffolding, articulation, reflection, and exploration. We operationalize these instructional methods through structured prompting and evaluate them in a within-subjects study with data visualization practitioners. Participants interacted with both a baseline LLM and an instructional LLM designed with cognitive apprenticeship prompts. Surveys, interviews, and conversational log analyses compared experiences across conditions. Our findings show that cognitively informed prompts elicit deeper design reasoning and more reflective feedback exchanges, though the baseline is sometimes preferred depending on task types or experience levels. We distill design considerations for AI-assisted feedback systems that foster reflective practice.
Human-centered explanation does not fit all: The interplay of sociotechnical, cognitive, and individual factors in the effect AI explanations in algorithmic decision-making
Feb 17, 2025Abstract:Recent XAI studies have investigated what constitutes a \textit{good} explanation in AI-assisted decision-making. Despite the widely accepted human-friendly properties of explanations, such as contrastive and selective, existing studies have yielded inconsistent findings. To address these gaps, our study focuses on the cognitive dimensions of explanation evaluation, by evaluating six explanations with different contrastive strategies and information selectivity and scrutinizing factors behind their valuation process. Our analysis results find that contrastive explanations are not the most preferable or understandable in general; Rather, different contrastive and selective explanations were appreciated to a different extent based on who they are, when, how, and what to explain -- with different level of cognitive load and engagement and sociotechnical contexts. Given these findings, we call for a nuanced view of explanation strategies, with implications for designing AI interfaces to accommodate individual and contextual differences in AI-assisted decision-making.
Gender Bias in LLM-generated Interview Responses
Oct 28, 2024



Abstract:LLMs have emerged as a promising tool for assisting individuals in diverse text-generation tasks, including job-related texts. However, LLM-generated answers have been increasingly found to exhibit gender bias. This study evaluates three LLMs (GPT-3.5, GPT-4, Claude) to conduct a multifaceted audit of LLM-generated interview responses across models, question types, and jobs, and their alignment with two gender stereotypes. Our findings reveal that gender bias is consistent, and closely aligned with gender stereotypes and the dominance of jobs. Overall, this study contributes to the systematic examination of gender bias in LLM-generated interview responses, highlighting the need for a mindful approach to mitigate such biases in related applications.
Interactive Counterfactual Exploration of Algorithmic Harms in Recommender Systems
Sep 10, 2024Abstract:Recommender systems have become integral to digital experiences, shaping user interactions and preferences across various platforms. Despite their widespread use, these systems often suffer from algorithmic biases that can lead to unfair and unsatisfactory user experiences. This study introduces an interactive tool designed to help users comprehend and explore the impacts of algorithmic harms in recommender systems. By leveraging visualizations, counterfactual explanations, and interactive modules, the tool allows users to investigate how biases such as miscalibration, stereotypes, and filter bubbles affect their recommendations. Informed by in-depth user interviews, this tool benefits both general users and researchers by increasing transparency and offering personalized impact assessments, ultimately fostering a better understanding of algorithmic biases and contributing to more equitable recommendation outcomes. This work provides valuable insights for future research and practical applications in mitigating bias and enhancing fairness in machine learning algorithms.
Exploring Teachers' Perception of Artificial Intelligence: The Socio-emotional Deficiency as Opportunities and Challenges in Human-AI Complementarity in K-12 Education
May 20, 2024

Abstract:In schools, teachers play a multitude of roles, serving as educators, counselors, decision-makers, and members of the school community. With recent advances in artificial intelligence (AI), there is increasing discussion about how AI can assist, complement, and collaborate with teachers. To pave the way for better teacher-AI complementary relationships in schools, our study aims to expand the discourse on teacher-AI complementarity by seeking educators' perspectives on the potential strengths and limitations of AI across a spectrum of responsibilities. Through a mixed method using a survey with 100 elementary school teachers in South Korea and in-depth interviews with 12 teachers, our findings indicate that teachers anticipate AI's potential to complement human teachers by automating administrative tasks and enhancing personalized learning through advanced intelligence. Interestingly, the deficit of AI's socio-emotional capabilities has been perceived as both challenges and opportunities. Overall, our study demonstrates the nuanced perception of teachers and different levels of expectations over their roles, challenging the need for decisions about AI adoption tailored to educators' preferences and concerns.
Break Out of a Pigeonhole: A Unified Framework for Examining Miscalibration, Bias, and Stereotype in Recommender Systems
Dec 29, 2023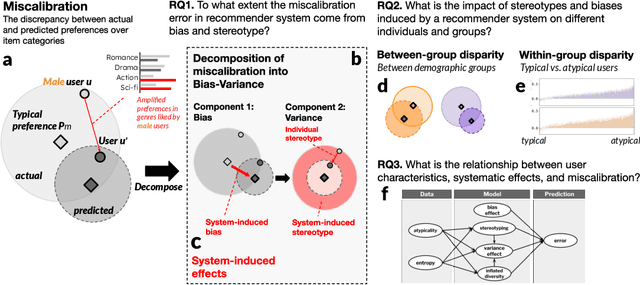
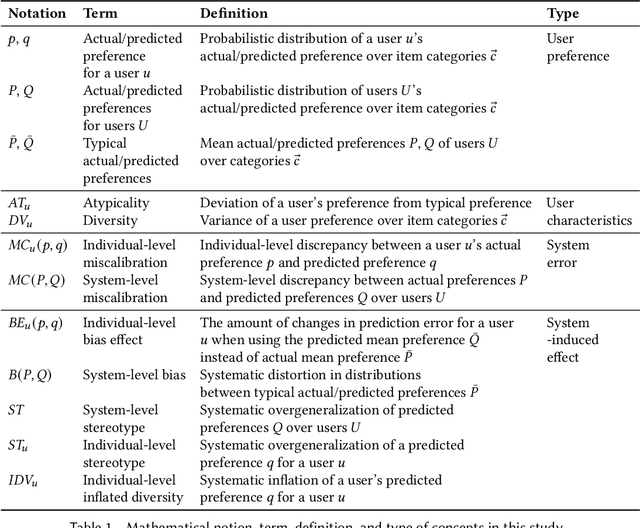
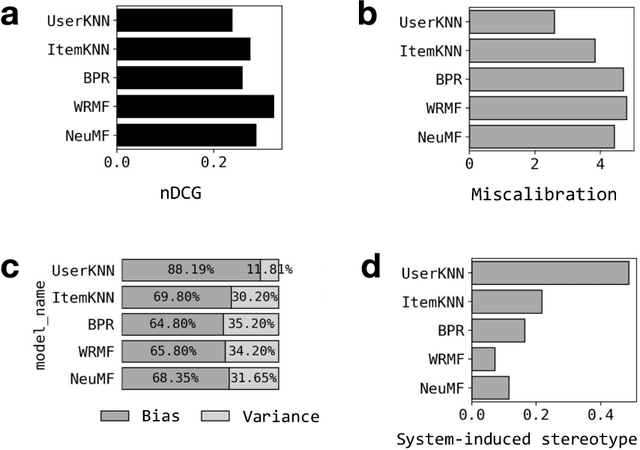
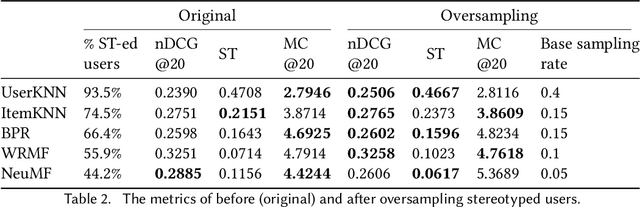
Abstract:Despite the benefits of personalizing items and information tailored to users' needs, it has been found that recommender systems tend to introduce biases that favor popular items or certain categories of items, and dominant user groups. In this study, we aim to characterize the systematic errors of a recommendation system and how they manifest in various accountability issues, such as stereotypes, biases, and miscalibration. We propose a unified framework that distinguishes the sources of prediction errors into a set of key measures that quantify the various types of system-induced effects, both at the individual and collective levels. Based on our measuring framework, we examine the most widely adopted algorithms in the context of movie recommendation. Our research reveals three important findings: (1) Differences between algorithms: recommendations generated by simpler algorithms tend to be more stereotypical but less biased than those generated by more complex algorithms. (2) Disparate impact on groups and individuals: system-induced biases and stereotypes have a disproportionate effect on atypical users and minority groups (e.g., women and older users). (3) Mitigation opportunity: using structural equation modeling, we identify the interactions between user characteristics (typicality and diversity), system-induced effects, and miscalibration. We further investigate the possibility of mitigating system-induced effects by oversampling underrepresented groups and individuals, which was found to be effective in reducing stereotypes and improving recommendation quality. Our research is the first systematic examination of not only system-induced effects and miscalibration but also the stereotyping issue in recommender systems.
HungerGist: An Interpretable Predictive Model for Food Insecurity
Nov 18, 2023Abstract:The escalating food insecurity in Africa, caused by factors such as war, climate change, and poverty, demonstrates the critical need for advanced early warning systems. Traditional methodologies, relying on expert-curated data encompassing climate, geography, and social disturbances, often fall short due to data limitations, hindering comprehensive analysis and potential discovery of new predictive factors. To address this, this paper introduces "HungerGist", a multi-task deep learning model utilizing news texts and NLP techniques. Using a corpus of over 53,000 news articles from nine African countries over four years, we demonstrate that our model, trained solely on news data, outperforms the baseline method trained on both traditional risk factors and human-curated keywords. In addition, our method has the ability to detect critical texts that contain interpretable signals known as "gists." Moreover, our examination of these gists indicates that this approach has the potential to reveal latent factors that would otherwise remain concealed in unstructured texts.
VISPUR: Visual Aids for Identifying and Interpreting Spurious Associations in Data-Driven Decisions
Jul 26, 2023Abstract:Big data and machine learning tools have jointly empowered humans in making data-driven decisions. However, many of them capture empirical associations that might be spurious due to confounding factors and subgroup heterogeneity. The famous Simpson's paradox is such a phenomenon where aggregated and subgroup-level associations contradict with each other, causing cognitive confusions and difficulty in making adequate interpretations and decisions. Existing tools provide little insights for humans to locate, reason about, and prevent pitfalls of spurious association in practice. We propose VISPUR, a visual analytic system that provides a causal analysis framework and a human-centric workflow for tackling spurious associations. These include a CONFOUNDER DASHBOARD, which can automatically identify possible confounding factors, and a SUBGROUP VIEWER, which allows for the visualization and comparison of diverse subgroup patterns that likely or potentially result in a misinterpretation of causality. Additionally, we propose a REASONING STORYBOARD, which uses a flow-based approach to illustrate paradoxical phenomena, as well as an interactive DECISION DIAGNOSIS panel that helps ensure accountable decision-making. Through an expert interview and a controlled user experiment, our qualitative and quantitative results demonstrate that the proposed "de-paradox" workflow and the designed visual analytic system are effective in helping human users to identify and understand spurious associations, as well as to make accountable causal decisions.
Tribe or Not? Critical Inspection of Group Differences Using TribalGram
Mar 16, 2023

Abstract:With the rise of AI and data mining techniques, group profiling and group-level analysis have been increasingly used in many domains including policy making and direct marketing. In some cases, the statistics extracted from data may provide insights to a group's shared characteristics; in others, the group-level analysis can lead to problems including stereotyping and systematic oppression. How can analytic tools facilitate a more conscientious process in group analysis? In this work, we identify a set of accountable group analytics design guidelines to explicate the needs for group differentiation and preventing overgeneralization of a group. Following the design guidelines, we develop TribalGram, a visual analytic suite that leverages interpretable machine learning algorithms and visualization to offer inference assessment, model explanation, data corroboration, and sense-making. Through the interviews with domain experts, we showcase how our design and tools can bring a richer understanding of "groups" mined from the data.
ESCAPE: Countering Systematic Errors from Machine's Blind Spots via Interactive Visual Analysis
Mar 16, 2023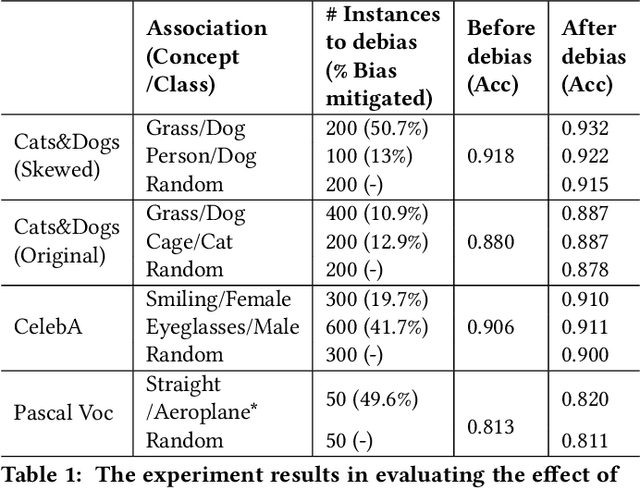
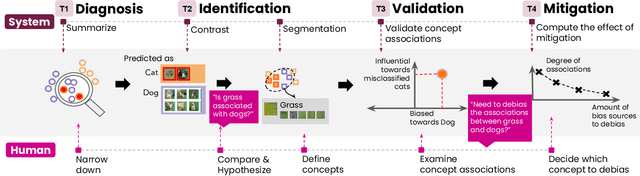
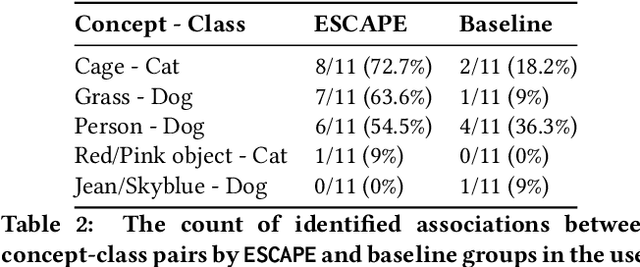
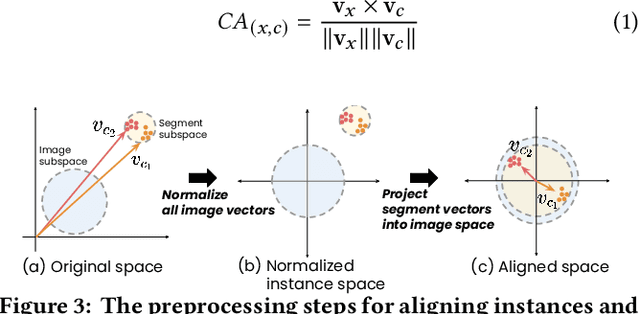
Abstract:Classification models learn to generalize the associations between data samples and their target classes. However, researchers have increasingly observed that machine learning practice easily leads to systematic errors in AI applications, a phenomenon referred to as AI blindspots. Such blindspots arise when a model is trained with training samples (e.g., cat/dog classification) where important patterns (e.g., black cats) are missing or periphery/undesirable patterns (e.g., dogs with grass background) are misleading towards a certain class. Even more sophisticated techniques cannot guarantee to capture, reason about, and prevent the spurious associations. In this work, we propose ESCAPE, a visual analytic system that promotes a human-in-the-loop workflow for countering systematic errors. By allowing human users to easily inspect spurious associations, the system facilitates users to spontaneously recognize concepts associated misclassifications and evaluate mitigation strategies that can reduce biased associations. We also propose two statistical approaches, relative concept association to better quantify the associations between a concept and instances, and debias method to mitigate spurious associations. We demonstrate the utility of our proposed ESCAPE system and statistical measures through extensive evaluation including quantitative experiments, usage scenarios, expert interviews, and controlled user experiments.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge