Yongkang Zhou
SpecDiff: Accelerating Diffusion Model Inference with Self-Speculation
Sep 17, 2025Abstract:Feature caching has recently emerged as a promising method for diffusion model acceleration. It effectively alleviates the inefficiency problem caused by high computational requirements by caching similar features in the inference process of the diffusion model. In this paper, we analyze existing feature caching methods from the perspective of information utilization, and point out that relying solely on historical information will lead to constrained accuracy and speed performance. And we propose a novel paradigm that introduces future information via self-speculation based on the information similarity at the same time step across different iteration times. Based on this paradigm, we present \textit{SpecDiff}, a training-free multi-level feature caching strategy including a cached feature selection algorithm and a multi-level feature classification algorithm. (1) Feature selection algorithm based on self-speculative information. \textit{SpecDiff} determines a dynamic importance score for each token based on self-speculative information and historical information, and performs cached feature selection through the importance score. (2) Multi-level feature classification algorithm based on feature importance scores. \textit{SpecDiff} classifies tokens by leveraging the differences in feature importance scores and introduces a multi-level feature calculation strategy. Extensive experiments show that \textit{SpecDiff} achieves average 2.80 \times, 2.74 \times , and 3.17\times speedup with negligible quality loss in Stable Diffusion 3, 3.5, and FLUX compared to RFlow on NVIDIA A800-80GB GPU. By merging speculative and historical information, \textit{SpecDiff} overcomes the speedup-accuracy trade-off bottleneck, pushing the Pareto frontier of speedup and accuracy in the efficient diffusion model inference.
SpecEE: Accelerating Large Language Model Inference with Speculative Early Exiting
Apr 11, 2025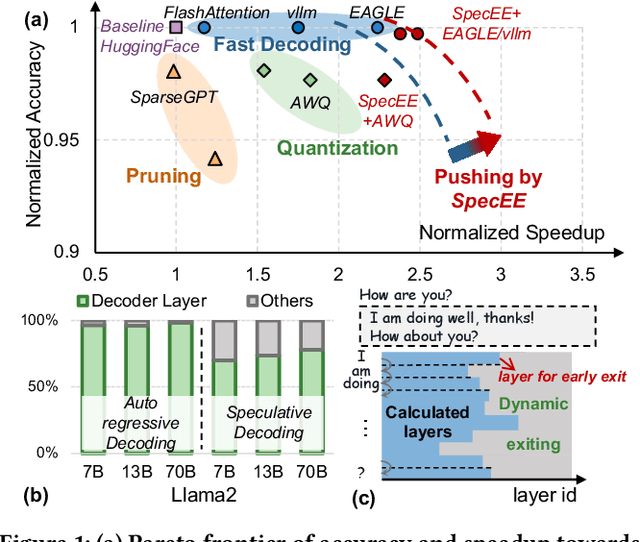
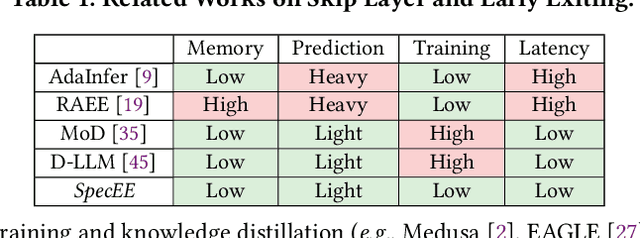
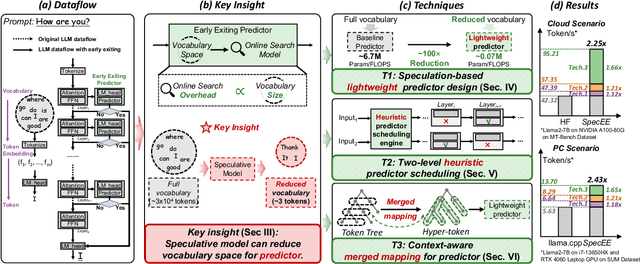
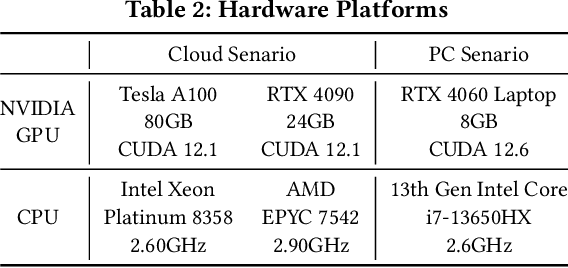
Abstract:Early exiting has recently emerged as a promising technique for accelerating large language models (LLMs) by effectively reducing the hardware computation and memory access. In this paper, we present SpecEE, a fast LLM inference engine with speculative early exiting. (1) At the algorithm level, we propose the speculation-based lightweight predictor design by exploiting the probabilistic correlation between the speculative tokens and the correct results and high parallelism of GPUs. (2) At the system level, we point out that not all layers need a predictor and design the two-level heuristic predictor scheduling engine based on skewed distribution and contextual similarity. (3) At the mapping level, we point out that different decoding methods share the same essential characteristics, and propose the context-aware merged mapping for predictor with efficient GPU implementations to support speculative decoding, and form a framework for various existing orthogonal acceleration techniques (e.g., quantization and sparse activation) on cloud and personal computer (PC) scenarios, successfully pushing the Pareto frontier of accuracy and speedup. It is worth noting that SpecEE can be applied to any LLM by negligible training overhead in advance without affecting the model original parameters. Extensive experiments show that SpecEE achieves 2.25x and 2.43x speedup with Llama2-7B on cloud and PC scenarios respectively.
Are Your Models Still Fair? Fairness Attacks on Graph Neural Networks via Node Injections
Jun 05, 2024



Abstract:Despite the remarkable capabilities demonstrated by Graph Neural Networks (GNNs) in graph-related tasks, recent research has revealed the fairness vulnerabilities in GNNs when facing malicious adversarial attacks. However, all existing fairness attacks require manipulating the connectivity between existing nodes, which may be prohibited in reality. To this end, we introduce a Node Injection-based Fairness Attack (NIFA), exploring the vulnerabilities of GNN fairness in such a more realistic setting. In detail, NIFA first designs two insightful principles for node injection operations, namely the uncertainty-maximization principle and homophily-increase principle, and then optimizes injected nodes' feature matrix to further ensure the effectiveness of fairness attacks. Comprehensive experiments on three real-world datasets consistently demonstrate that NIFA can significantly undermine the fairness of mainstream GNNs, even including fairness-aware GNNs, by injecting merely 1% of nodes. We sincerely hope that our work can stimulate increasing attention from researchers on the vulnerability of GNN fairness, and encourage the development of corresponding defense mechanisms.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge