Yinfeng Liu
MDEval: Evaluating and Enhancing Markdown Awareness in Large Language Models
Jan 25, 2025Abstract:Large language models (LLMs) are expected to offer structured Markdown responses for the sake of readability in web chatbots (e.g., ChatGPT). Although there are a myriad of metrics to evaluate LLMs, they fail to evaluate the readability from the view of output content structure. To this end, we focus on an overlooked yet important metric -- Markdown Awareness, which directly impacts the readability and structure of the content generated by these language models. In this paper, we introduce MDEval, a comprehensive benchmark to assess Markdown Awareness for LLMs, by constructing a dataset with 20K instances covering 10 subjects in English and Chinese. Unlike traditional model-based evaluations, MDEval provides excellent interpretability by combining model-based generation tasks and statistical methods. Our results demonstrate that MDEval achieves a Spearman correlation of 0.791 and an accuracy of 84.1% with human, outperforming existing methods by a large margin. Extensive experimental results also show that through fine-tuning over our proposed dataset, less performant open-source models are able to achieve comparable performance to GPT-4o in terms of Markdown Awareness. To ensure reproducibility and transparency, MDEval is open sourced at https://github.com/SWUFE-DB-Group/MDEval-Benchmark.
HyperDet: Generalizable Detection of Synthesized Images by Generating and Merging A Mixture of Hyper LoRAs
Oct 08, 2024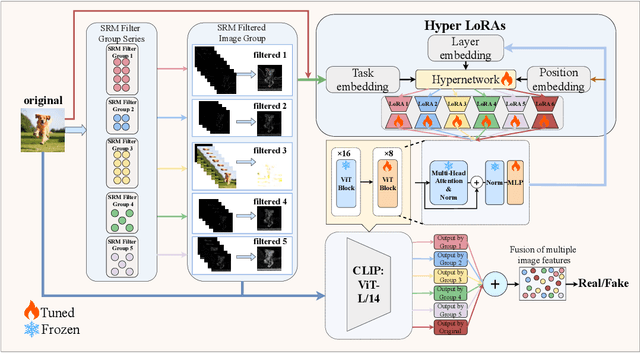



Abstract:The emergence of diverse generative vision models has recently enabled the synthesis of visually realistic images, underscoring the critical need for effectively detecting these generated images from real photos. Despite advances in this field, existing detection approaches often struggle to accurately identify synthesized images generated by different generative models. In this work, we introduce a novel and generalizable detection framework termed HyperDet, which innovatively captures and integrates shared knowledge from a collection of functionally distinct and lightweight expert detectors. HyperDet leverages a large pretrained vision model to extract general detection features while simultaneously capturing and enhancing task-specific features. To achieve this, HyperDet first groups SRM filters into five distinct groups to efficiently capture varying levels of pixel artifacts based on their different functionality and complexity. Then, HyperDet utilizes a hypernetwork to generate LoRA model weights with distinct embedding parameters. Finally, we merge the LoRA networks to form an efficient model ensemble. Also, we propose a novel objective function that balances the pixel and semantic artifacts effectively. Extensive experiments on the UnivFD and Fake2M datasets demonstrate the effectiveness of our approach, achieving state-of-the-art performance. Moreover, our work paves a new way to establish generalizable domain-specific fake image detectors based on pretrained large vision models.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge