Yimeng Ren
Addressing Heterogeneity and Heterophily in Graphs: A Heterogeneous Heterophilic Spectral Graph Neural Network
Oct 17, 2024Abstract:Graph Neural Networks (GNNs) have garnered significant scholarly attention for their powerful capabilities in modeling graph structures. Despite this, two primary challenges persist: heterogeneity and heterophily. Existing studies often address heterogeneous and heterophilic graphs separately, leaving a research gap in the understanding of heterogeneous heterophilic graphs-those that feature diverse node or relation types with dissimilar connected nodes. To address this gap, we investigate the application of spectral graph filters within heterogeneous graphs. Specifically, we propose a Heterogeneous Heterophilic Spectral Graph Neural Network (H2SGNN), which employs a dual-module approach: local independent filtering and global hybrid filtering. The local independent filtering module applies polynomial filters to each subgraph independently to adapt to different homophily, while the global hybrid filtering module captures interactions across different subgraphs. Extensive empirical evaluations on four real-world datasets demonstrate the superiority of H2SGNN compared to state-of-the-art methods.
Reinforcement Learning Guided Multi-Objective Exam Paper Generation
Mar 02, 2023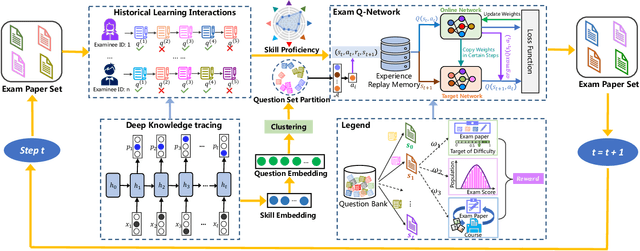

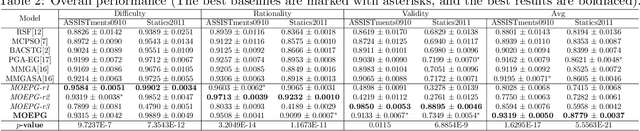
Abstract:To reduce the repetitive and complex work of instructors, exam paper generation (EPG) technique has become a salient topic in the intelligent education field, which targets at generating high-quality exam paper automatically according to instructor-specified assessment criteria. The current advances utilize the ability of heuristic algorithms to optimize several well-known objective constraints, such as difficulty degree, number of questions, etc., for producing optimal solutions. However, in real scenarios, considering other equally relevant objectives (e.g., distribution of exam scores, skill coverage) is extremely important. Besides, how to develop an automatic multi-objective solution that finds an optimal subset of questions from a huge search space of large-sized question datasets and thus composes a high-quality exam paper is urgent but non-trivial. To this end, we skillfully design a reinforcement learning guided Multi-Objective Exam Paper Generation framework, termed MOEPG, to simultaneously optimize three exam domain-specific objectives including difficulty degree, distribution of exam scores, and skill coverage. Specifically, to accurately measure the skill proficiency of the examinee group, we first employ deep knowledge tracing to model the interaction information between examinees and response logs. We then design the flexible Exam Q-Network, a function approximator, which automatically selects the appropriate question to update the exam paper composition process. Later, MOEPG divides the decision space into multiple subspaces to better guide the updated direction of the exam paper. Through extensive experiments on two real-world datasets, we demonstrate that MOEPG is feasible in addressing the multiple dilemmas of exam paper generation scenario.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge