Yichao Jin
Multi-Stage Field Extraction of Financial Documents with OCR and Compact Vision-Language Models
Oct 27, 2025
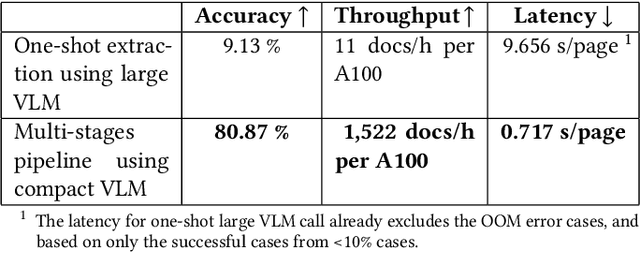


Abstract:Financial documents are essential sources of information for regulators, auditors, and financial institutions, particularly for assessing the wealth and compliance of Small and Medium-sized Businesses. However, SMB documents are often difficult to parse. They are rarely born digital and instead are distributed as scanned images that are none machine readable. The scans themselves are low in resolution, affected by skew or rotation, and often contain noisy backgrounds. These documents also tend to be heterogeneous, mixing narratives, tables, figures, and multilingual content within the same report. Such characteristics pose major challenges for automated information extraction, especially when relying on end to end large Vision Language Models, which are computationally expensive, sensitive to noise, and slow when applied to files with hundreds of pages. We propose a multistage pipeline that leverages traditional image processing models and OCR extraction, together with compact VLMs for structured field extraction of large-scale financial documents. Our approach begins with image pre-processing, including segmentation, orientation detection, and size normalization. Multilingual OCR is then applied to recover page-level text. Upon analyzing the text information, pages are retrieved for coherent sections. Finally, compact VLMs are operated within these narrowed-down scopes to extract structured financial indicators. Our approach is evaluated using an internal corpus of multi-lingual, scanned financial documents. The results demonstrate that compact VLMs, together with a multistage pipeline, achieves 8.8 times higher field level accuracy relative to directly feeding the whole document into large VLMs, only at 0.7 percent of the GPU cost and 92.6 percent less end-to-end service latency.
Modeling and Analysis of Multi-Line Orders in Multi-Tote Storage and Retrieval Autonomous Mobile Robot Systems
Jul 08, 2024



Abstract:As warehouses are emphasizing space utilization and the ability to handle multi-line orders, multi-tote storage and retrieval (MTSR) autonomous mobile robot systems, where robots directly retrieve totes from high shelves, are becoming increasingly popular. This paper presents a novel shared-token, multi-class, semi-open queueing network model to account for multi-line orders with general distribution forms in MTSR systems. The numerical results obtained from solving the SOQN model are validated against discrete-event simulation, with most key performance metrics demonstrating high accuracy. In our experimental setting, results indicate a 12.5% reduction in the minimum number of robots needed to satisfy a specific order arrival rate using the closest retrieval sequence policy compared with the random policy. Increasing the number of tote buffer positions on a robot can greatly reduce the number of robots required in the warehouse.
A Dataset of Images of Public Streetlights with Operational Monitoring using Computer Vision Techniques
Apr 01, 2022



Abstract:A dataset of street light images is presented. Our dataset consists of $\sim350\textrm{k}$ images, taken from 140 UMBRELLA nodes installed in the South Gloucestershire region in the UK. Each UMBRELLA node is installed on the pole of a lamppost and is equipped with a Raspberry Pi Camera Module v1 facing upwards towards the sky and lamppost light bulb. Each node collects an image at hourly intervals for 24h every day. The data collection spans for a period of six months. Each image taken is logged as a single entry in the dataset along with the Global Positioning System (GPS) coordinates of the lamppost. All entries in the dataset have been post-processed and labelled based on the operation of the lamppost, i.e., whether the lamppost is switched ON or OFF. The dataset can be used to train deep neural networks and generate pre-trained models providing feature representations for smart city CCTV applications, smart weather detection algorithms, or street infrastructure monitoring. The dataset can be found at \url{https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.6046758}.
Hysia: Serving DNN-Based Video-to-Retail Applications in Cloud
Jun 09, 2020


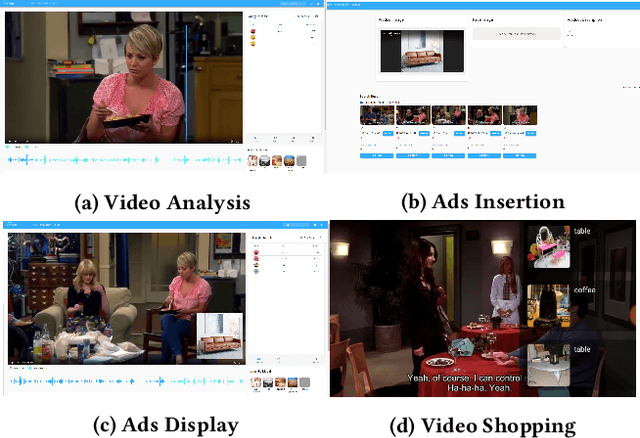
Abstract:Combining \underline{v}ideo streaming and online \underline{r}etailing (V2R) has been a growing trend recently. In this paper, we provide practitioners and researchers in multimedia with a cloud-based platform named Hysia for easy development and deployment of V2R applications. The system consists of: 1) a back-end infrastructure providing optimized V2R related services including data engine, model repository, model serving and content matching; and 2) an application layer which enables rapid V2R application prototyping. Hysia addresses industry and academic needs in large-scale multimedia by: 1) seamlessly integrating state-of-the-art libraries including NVIDIA video SDK, Facebook faiss, and gRPC; 2) efficiently utilizing GPU computation; and 3) allowing developers to bind new models easily to meet the rapidly changing deep learning (DL) techniques. On top of that, we implement an orchestrator for further optimizing DL model serving performance. Hysia has been released as an open source project on GitHub, and attracted considerable attention. We have published Hysia to DockerHub as an official image for seamless integration and deployment in current cloud environments.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge