Yarik Menchaca Resendiz
LLM-based Affective Text Generation Quality Based on Different Quantization Values
Jan 31, 2025Abstract:Large language models exhibit a remarkable capacity in language generation and comprehension. These advances enable AI systems to produce more human-like and emotionally engaging text. However, these models rely on a large number of parameters, requiring significant computational resources for training and inference. In some scenarios, accessing these resources can be challenging (e.g., budget or hardware limitations). Techniques like reducing precision bits can make models more memory-efficient, reducing the computational resources needed, at the cost of reduced accuracy. This paper addresses the trade-off between different quantization values, GPU RAM utilization, and text quality in affective text generation (e.g., "I really enjoy running in the snow-covered forest"). To evaluate, we use an emotion classifier and ten seed prompts to generate affective text. We test three setups of precision bits (8, 16, and 32) across five open-weight language models from two different families. Our findings demonstrate that bit reductions lead to memory savings, achieving a reduction of 76%. However, this optimization comes with a trade-off, leading to a decrease of up to 10 pp in F1 score for larger models and an increase of 10 pp for smaller models, along with roughly double the inference time. In terms of text quality, larger models at lower quantization levels generally outperform smaller, higher-precision models -- while requiring similar memory.
MOPO: Multi-Objective Prompt Optimization for Affective Text Generation
Dec 17, 2024Abstract:How emotions are expressed depends on the context and domain. On X (formerly Twitter), for instance, an author might simply use the hashtag #anger, while in a news headline, emotions are typically written in a more polite, indirect manner. To enable conditional text generation models to create emotionally connotated texts that fit a domain, users need to have access to a parameter that allows them to choose the appropriate way to express an emotion. To achieve this, we introduce MOPO, a Multi-Objective Prompt Optimization methodology. MOPO optimizes prompts according to multiple objectives (which correspond here to the output probabilities assigned by emotion classifiers trained for different domains). In contrast to single objective optimization, MOPO outputs a set of prompts, each with a different weighting of the multiple objectives. Users can then choose the most appropriate prompt for their context. We evaluate MOPO using three objectives, determined by various domain-specific emotion classifiers. MOPO improves performance by up to 15 pp across all objectives with a minimal loss (1-2 pp) for any single objective compared to single-objective optimization. These minor performance losses are offset by a broader generalization across multiple objectives - which is not possible with single-objective optimization. Additionally, MOPO reduces computational requirements by simultaneously optimizing for multiple objectives, eliminating separate optimization procedures for each objective.
Which Demographics do LLMs Default to During Annotation?
Oct 11, 2024

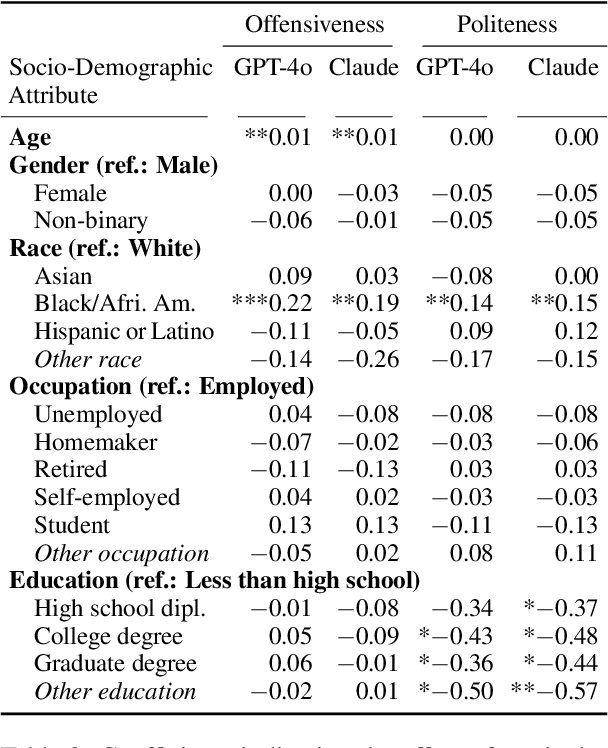
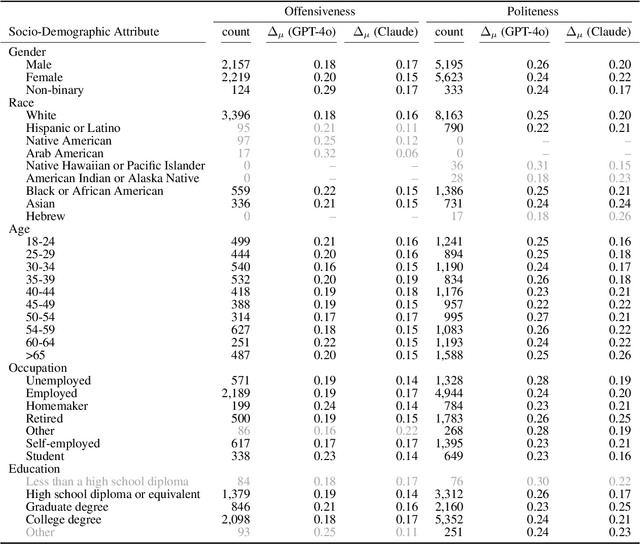
Abstract:Demographics and cultural background of annotators influence the labels they assign in text annotation -- for instance, an elderly woman might find it offensive to read a message addressed to a "bro", but a male teenager might find it appropriate. It is therefore important to acknowledge label variations to not under-represent members of a society. Two research directions developed out of this observation in the context of using large language models (LLM) for data annotations, namely (1) studying biases and inherent knowledge of LLMs and (2) injecting diversity in the output by manipulating the prompt with demographic information. We combine these two strands of research and ask the question to which demographics an LLM resorts to when no demographics is given. To answer this question, we evaluate which attributes of human annotators LLMs inherently mimic. Furthermore, we compare non-demographic conditioned prompts and placebo-conditioned prompts (e.g., "you are an annotator who lives in house number 5") to demographics-conditioned prompts ("You are a 45 year old man and an expert on politeness annotation. How do you rate {instance}"). We study these questions for politeness and offensiveness annotations on the POPQUORN data set, a corpus created in a controlled manner to investigate human label variations based on demographics which has not been used for LLM-based analyses so far. We observe notable influences related to gender, race, and age in demographic prompting, which contrasts with previous studies that found no such effects.
What Makes Medical Claims (Un)Verifiable? Analyzing Entity and Relation Properties for Fact Verification
Feb 02, 2024Abstract:Biomedical claim verification fails if no evidence can be discovered. In these cases, the fact-checking verdict remains unknown and the claim is unverifiable. To improve upon this, we have to understand if there are any claim properties that impact its verifiability. In this work we assume that entities and relations define the core variables in a biomedical claim's anatomy and analyze if their properties help us to differentiate verifiable from unverifiable claims. In a study with trained annotation experts we prompt them to find evidence for biomedical claims, and observe how they refine search queries for their evidence search. This leads to the first corpus for scientific fact verification annotated with subject-relation-object triplets, evidence documents, and fact-checking verdicts (the BEAR-Fact corpus). We find (1) that discovering evidence for negated claims (e.g., X-does-not-cause-Y) is particularly challenging. Further, we see that annotators process queries mostly by adding constraints to the search and by normalizing entities to canonical names. (2) We compare our in-house annotations with a small crowdsourcing setting where we employ medical experts and laypeople. We find that domain expertise does not have a substantial effect on the reliability of annotations. Finally, (3), we demonstrate that it is possible to reliably estimate the success of evidence retrieval purely from the claim text~(.82\F), whereas identifying unverifiable claims proves more challenging (.27\F). The dataset is available at http://www.ims.uni-stuttgart.de/data/bioclaim.
Emotion-Conditioned Text Generation through Automatic Prompt Optimization
Aug 09, 2023Abstract:Conditional natural language generation methods often require either expensive fine-tuning or training a large language model from scratch. Both are unlikely to lead to good results without a substantial amount of data and computational resources. Prompt learning without changing the parameters of a large language model presents a promising alternative. It is a cost-effective approach, while still achieving competitive results. While this procedure is now established for zero- and few-shot text classification and structured prediction, it has received limited attention in conditional text generation. We present the first automatic prompt optimization approach for emotion-conditioned text generation with instruction-fine-tuned models. Our method uses an iterative optimization procedure that changes the prompt by adding, removing, or replacing tokens. As objective function, we only require a text classifier that measures the realization of the conditional variable in the generated text. We evaluate the method on emotion-conditioned text generation with a focus on event reports and compare it to manually designed prompts that also act as the seed for the optimization procedure. The optimized prompts achieve 0.75 macro-average F1 to fulfill the emotion condition in contrast to manually designed seed prompts with only 0.22 macro-average F1.
Affective Natural Language Generation of Event Descriptions through Fine-grained Appraisal Conditions
Jul 26, 2023



Abstract:Models for affective text generation have shown a remarkable progress, but they commonly rely only on basic emotion theories or valance/arousal values as conditions. This is appropriate when the goal is to create explicit emotion statements ("The kid is happy."). Emotions are, however, commonly communicated implicitly. For instance, the emotional interpretation of an event ("Their dog died.") does often not require an explicit emotion statement. In psychology, appraisal theories explain the link between a cognitive evaluation of an event and the potentially developed emotion. They put the assessment of the situation on the spot, for instance regarding the own control or the responsibility for what happens. We hypothesize and subsequently show that including appraisal variables as conditions in a generation framework comes with two advantages. (1) The generation model is informed in greater detail about what makes a specific emotion and what properties it has. This leads to text generation that better fulfills the condition. (2) The variables of appraisal allow a user to perform a more fine-grained control of the generated text, by stating properties of a situation instead of only providing the emotion category. Our Bart and T5-based experiments with 7 emotions (Anger, Disgust, Fear, Guilt, Joy, Sadness, Shame), and 7 appraisals (Attention, Responsibility, Control, Circumstance, Pleasantness, Effort, Certainty) show that (1) adding appraisals during training improves the accurateness of the generated texts by 10 pp in F1. Further, (2) the texts with appraisal variables are longer and contain more details. This exemplifies the greater control for users.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge