Yaojin Lin
Cross-Modality Earth Mover's Distance for Visible Thermal Person Re-Identification
Mar 03, 2022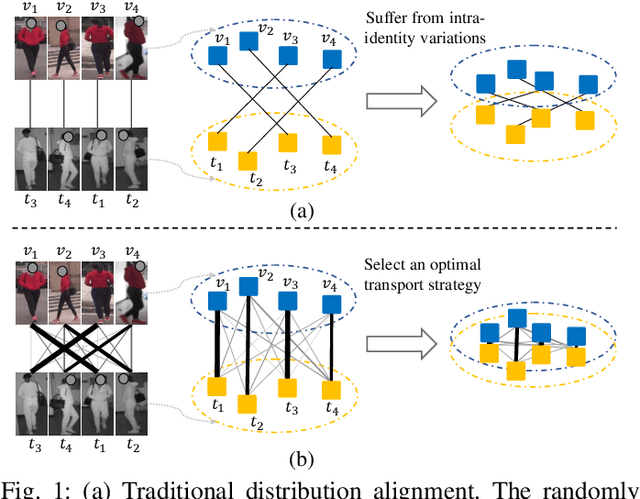
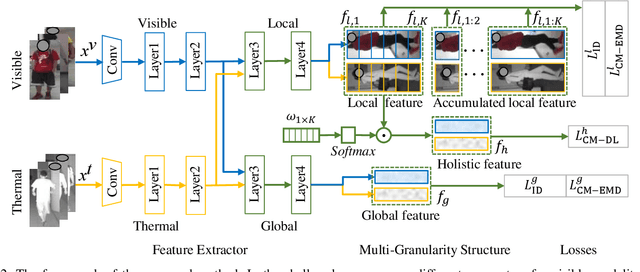
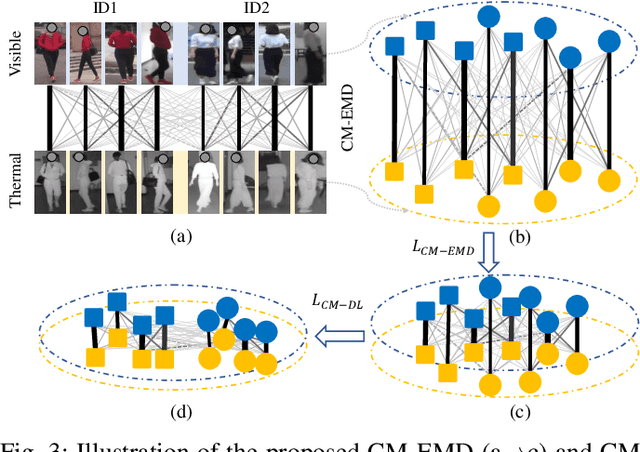

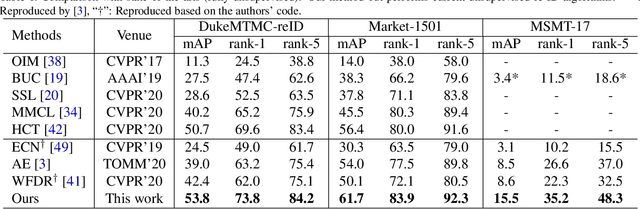
Abstract:Visible thermal person re-identification (VT-ReID) suffers from the inter-modality discrepancy and intra-identity variations. Distribution alignment is a popular solution for VT-ReID, which, however, is usually restricted to the influence of the intra-identity variations. In this paper, we propose the Cross-Modality Earth Mover's Distance (CM-EMD) that can alleviate the impact of the intra-identity variations during modality alignment. CM-EMD selects an optimal transport strategy and assigns high weights to pairs that have a smaller intra-identity variation. In this manner, the model will focus on reducing the inter-modality discrepancy while paying less attention to intra-identity variations, leading to a more effective modality alignment. Moreover, we introduce two techniques to improve the advantage of CM-EMD. First, the Cross-Modality Discrimination Learning (CM-DL) is designed to overcome the discrimination degradation problem caused by modality alignment. By reducing the ratio between intra-identity and inter-identity variances, CM-DL leads the model to learn more discriminative representations. Second, we construct the Multi-Granularity Structure (MGS), enabling us to align modalities from both coarse- and fine-grained levels with the proposed CM-EMD. Extensive experiments show the benefits of the proposed CM-EMD and its auxiliary techniques (CM-DL and MGS). Our method achieves state-of-the-art performance on two VT-ReID benchmarks.
Joint Noise-Tolerant Learning and Meta Camera Shift Adaptation for Unsupervised Person Re-Identification
Mar 08, 2021

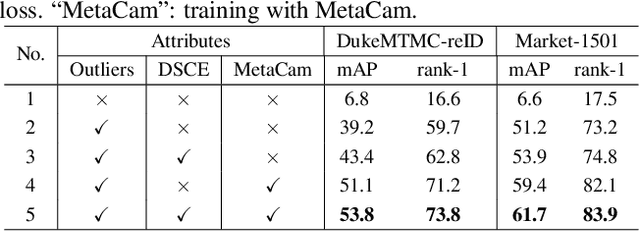
Abstract:This paper considers the problem of unsupervised person re-identification (re-ID), which aims to learn discriminative models with unlabeled data. One popular method is to obtain pseudo-label by clustering and use them to optimize the model. Although this kind of approach has shown promising accuracy, it is hampered by 1) noisy labels produced by clustering and 2) feature variations caused by camera shift. The former will lead to incorrect optimization and thus hinders the model accuracy. The latter will result in assigning the intra-class samples of different cameras to different pseudo-label, making the model sensitive to camera variations. In this paper, we propose a unified framework to solve both problems. Concretely, we propose a Dynamic and Symmetric Cross-Entropy loss (DSCE) to deal with noisy samples and a camera-aware meta-learning algorithm (MetaCam) to adapt camera shift. DSCE can alleviate the negative effects of noisy samples and accommodate the change of clusters after each clustering step. MetaCam simulates cross-camera constraint by splitting the training data into meta-train and meta-test based on camera IDs. With the interacted gradient from meta-train and meta-test, the model is enforced to learn camera-invariant features. Extensive experiments on three re-ID benchmarks show the effectiveness and the complementary of the proposed DSCE and MetaCam. Our method outperforms the state-of-the-art methods on both fully unsupervised re-ID and unsupervised domain adaptive re-ID.
Learning to Generalize Unseen Domains via Memory-based Multi-Source Meta-Learning for Person Re-Identification
Dec 01, 2020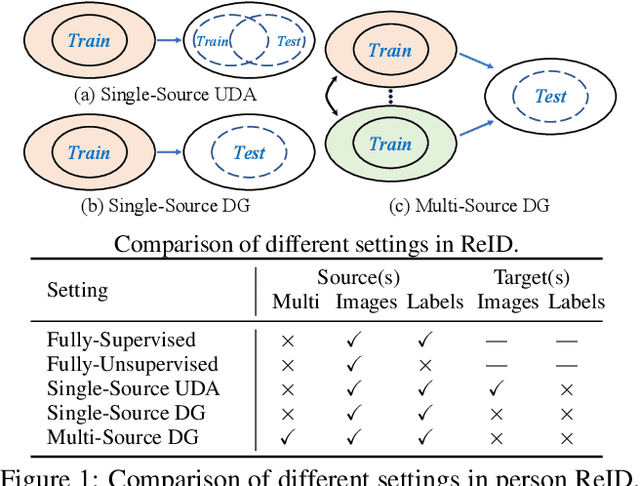
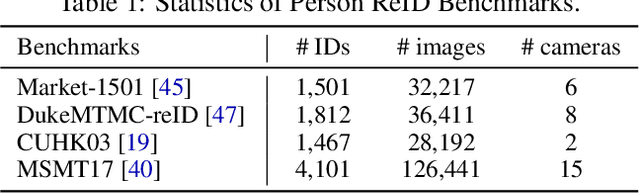
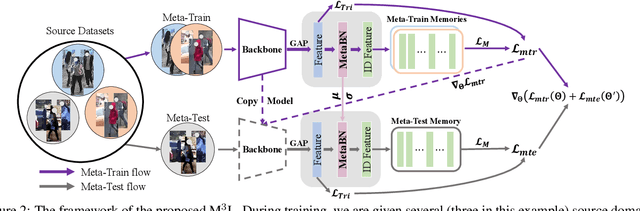
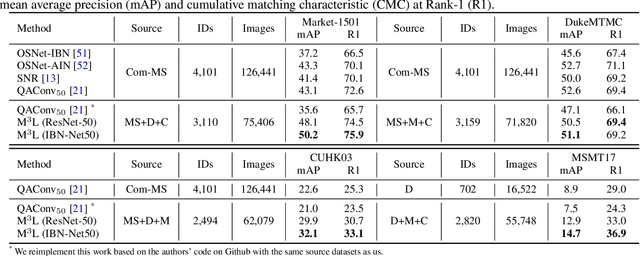
Abstract:Recent advances in person re-identification (ReID) obtain impressive accuracy in the supervised and unsupervised learning settings. However, most of the existing methods need to train a new model for a new domain by accessing data. Due to public privacy, the new domain data are not always accessible, leading to a limited applicability of these methods. In this paper, we study the problem of multi-source domain generalization in ReID, which aims to learn a model that can perform well on unseen domains with only several labeled source domains. To address this problem, we propose the Memory-based Multi-Source Meta-Learning (M$^3$L) framework to train a generalizable model for unseen domains. Specifically, a meta-learning strategy is introduced to simulate the train-test process of domain generalization for learning more generalizable models. To overcome the unstable meta-optimization caused by the parametric classifier, we propose a memory-based identification loss that is non-parametric and harmonizes with meta-learning. We also present a meta batch normalization layer (MetaBN) to diversify meta-test features, further establishing the advantage of meta-learning. Experiments demonstrate that our M$^3$L can effectively enhance the generalization ability of the model for unseen domains and can outperform the state-of-the-art methods on four large-scale ReID datasets.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge