Yanwei Zheng
Two-Stage Depth Enhanced Learning with Obstacle Map For Object Navigation
Jun 20, 2024Abstract:The task that requires an agent to navigate to a given object through only visual observation is called visual object navigation (VON). The main bottlenecks of VON are strategies exploration and prior knowledge exploitation. Traditional strategies exploration ignores the differences of searching and navigating stages, using the same reward in two stages, which reduces navigation performance and training efficiency. Our study enables the agent to explore larger area in searching stage and seek the optimal path in navigating stage, improving the success rate of navigation. Traditional prior knowledge exploitation focused on learning and utilizing object association, which ignored the depth and obstacle information in the environment. This paper uses the RGB and depth information of the training scene to pretrain the feature extractor, which improves navigation efficiency. The obstacle information is memorized by the agent during the navigation, reducing the probability of collision and deadlock. Depth, obstacle and other prior knowledge are concatenated and input into the policy network, and navigation actions are output under the training of two-stage rewards. We evaluated our method on AI2-Thor and RoboTHOR and demonstrated that it significantly outperforms state-of-the-art (SOTA) methods on success rate and navigation efficiency.
Federating to Grow Transformers with Constrained Resources without Model Sharing
Jun 19, 2024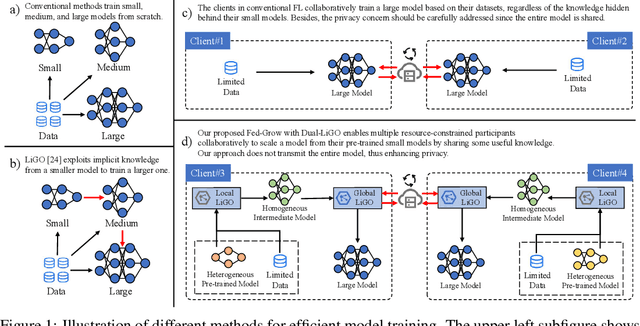
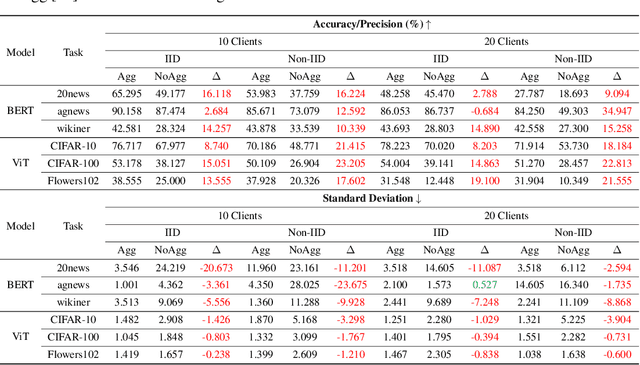
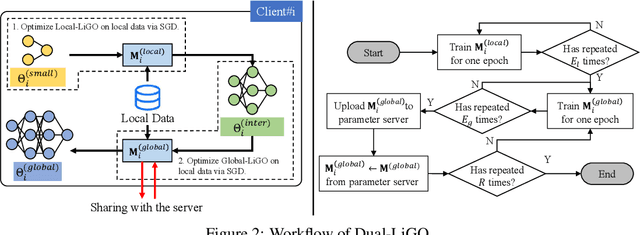
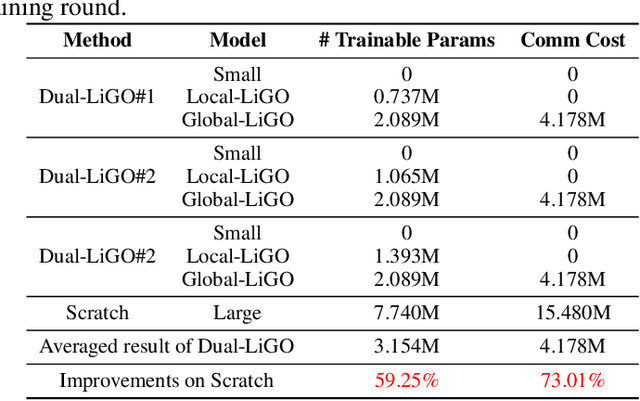
Abstract:The high resource consumption of large-scale models discourages resource-constrained users from developing their customized transformers. To this end, this paper considers a federated framework named Fed-Grow for multiple participants to cooperatively scale a transformer from their pre-trained small models. Under the Fed-Grow, a Dual-LiGO (Dual Linear Growth Operator) architecture is designed to help participants expand their pre-trained small models to a transformer. In Dual-LiGO, the Local-LiGO part is used to address the heterogeneity problem caused by the various pre-trained models, and the Global-LiGO part is shared to exchange the implicit knowledge from the pre-trained models, local data, and training process of participants. Instead of model sharing, only sharing the Global-LiGO strengthens the privacy of our approach. Compared with several state-of-the-art methods in simulation, our approach has higher accuracy, better precision, and lower resource consumption on computations and communications. To the best of our knowledge, most of the previous model-scaling works are centralized, and our work is the first one that cooperatively grows a transformer from multiple pre-trained heterogeneous models with the user privacy protected in terms of local data and models. We hope that our approach can extend the transformers to the broadly distributed scenarios and encourage more resource-constrained users to enjoy the bonus taken by the large-scale transformers.
Leveraging Unknown Objects to Construct Labeled-Unlabeled Meta-Relationships for Zero-Shot Object Navigation
May 27, 2024Abstract:Zero-shot object navigation (ZSON) addresses situation where an agent navigates to an unseen object that does not present in the training set. Previous works mainly train agent using seen objects with known labels, and ignore the seen objects without labels. In this paper, we introduce seen objects without labels, herein termed as ``unknown objects'', into training procedure to enrich the agent's knowledge base with distinguishable but previously overlooked information. Furthermore, we propose the label-wise meta-correlation module (LWMCM) to harness relationships among objects with and without labels, and obtain enhanced objects information. Specially, we propose target feature generator (TFG) to generate the features representation of the unlabeled target objects. Subsequently, the unlabeled object identifier (UOI) module assesses whether the unlabeled target object appears in the current observation frame captured by the camera and produces an adapted target features representation specific to the observed context. In meta contrastive feature modifier (MCFM), the target features is modified via approaching the features of objects within the observation frame while distancing itself from features of unobserved objects. Finally, the meta object-graph learner (MOGL) module is utilized to calculate the relationships among objects based on the features. Experiments conducted on AI2THOR and RoboTHOR platforms demonstrate the effectiveness of our proposed method.
Temporal-Spatial Object Relations Modeling for Vision-and-Language Navigation
Mar 23, 2024Abstract:Vision-and-Language Navigation (VLN) is a challenging task where an agent is required to navigate to a natural language described location via vision observations. The navigation abilities of the agent can be enhanced by the relations between objects, which are usually learned using internal objects or external datasets. The relationships between internal objects are modeled employing graph convolutional network (GCN) in traditional studies. However, GCN tends to be shallow, limiting its modeling ability. To address this issue, we utilize a cross attention mechanism to learn the connections between objects over a trajectory, which takes temporal continuity into account, termed as Temporal Object Relations (TOR). The external datasets have a gap with the navigation environment, leading to inaccurate modeling of relations. To avoid this problem, we construct object connections based on observations from all viewpoints in the navigational environment, which ensures complete spatial coverage and eliminates the gap, called Spatial Object Relations (SOR). Additionally, we observe that agents may repeatedly visit the same location during navigation, significantly hindering their performance. For resolving this matter, we introduce the Turning Back Penalty (TBP) loss function, which penalizes the agent's repetitive visiting behavior, substantially reducing the navigational distance. Experimental results on the REVERIE, SOON, and R2R datasets demonstrate the effectiveness of the proposed method.
CPCL: Cross-Modal Prototypical Contrastive Learning for Weakly Supervised Text-based Person Re-Identification
Jan 18, 2024Abstract:Weakly supervised text-based person re-identification (TPRe-ID) seeks to retrieve images of a target person using textual descriptions, without relying on identity annotations and is more challenging and practical. The primary challenge is the intra-class differences, encompassing intra-modal feature variations and cross-modal semantic gaps. Prior works have focused on instance-level samples and ignored prototypical features of each person which are intrinsic and invariant. Toward this, we propose a Cross-Modal Prototypical Contrastive Learning (CPCL) method. In practice, the CPCL introduces the CLIP model to weakly supervised TPRe-ID for the first time, mapping visual and textual instances into a shared latent space. Subsequently, the proposed Prototypical Multi-modal Memory (PMM) module captures associations between heterogeneous modalities of image-text pairs belonging to the same person through the Hybrid Cross-modal Matching (HCM) module in a many-to-many mapping fashion. Moreover, the Outlier Pseudo Label Mining (OPLM) module further distinguishes valuable outlier samples from each modality, enhancing the creation of more reliable clusters by mining implicit relationships between image-text pairs. Experimental results demonstrate that our proposed CPCL attains state-of-the-art performance on all three public datasets, with a significant improvement of 11.58%, 8.77% and 5.25% in Rank@1 accuracy on CUHK-PEDES, ICFG-PEDES and RSTPReid datasets, respectively. The code is available at https://github.com/codeGallery24/CPCL.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge