Yanchun Zhang
ABG-NAS: Adaptive Bayesian Genetic Neural Architecture Search for Graph Representation Learning
Apr 30, 2025Abstract:Effective and efficient graph representation learning is essential for enabling critical downstream tasks, such as node classification, link prediction, and subgraph search. However, existing graph neural network (GNN) architectures often struggle to adapt to diverse and complex graph structures, limiting their ability to provide robust and generalizable representations. To address this challenge, we propose ABG-NAS, a novel framework for automated graph neural network architecture search tailored for efficient graph representation learning. ABG-NAS encompasses three key components: a Comprehensive Architecture Search Space (CASS), an Adaptive Genetic Optimization Strategy (AGOS), and a Bayesian-Guided Tuning Module (BGTM). CASS systematically explores diverse propagation (P) and transformation (T) operations, enabling the discovery of GNN architectures capable of capturing intricate graph characteristics. AGOS dynamically balances exploration and exploitation, ensuring search efficiency and preserving solution diversity. BGTM further optimizes hyperparameters periodically, enhancing the scalability and robustness of the resulting architectures. Empirical evaluations on benchmark datasets (Cora, PubMed, Citeseer, and CoraFull) demonstrate that ABG-NAS consistently outperforms both manually designed GNNs and state-of-the-art neural architecture search (NAS) methods. These results highlight the potential of ABG-NAS to advance graph representation learning by providing scalable and adaptive solutions for diverse graph structures. Our code is publicly available at https://github.com/sserranw/ABG-NAS.
Pyramid U-Net for Retinal Vessel Segmentation
Apr 06, 2021



Abstract:Retinal blood vessel can assist doctors in diagnosis of eye-related diseases such as diabetes and hypertension, and its segmentation is particularly important for automatic retinal image analysis. However, it is challenging to segment these vessels structures, especially the thin capillaries from the color retinal image due to low contrast and ambiguousness. In this paper, we propose pyramid U-Net for accurate retinal vessel segmentation. In pyramid U-Net, the proposed pyramid-scale aggregation blocks (PSABs) are employed in both the encoder and decoder to aggregate features at higher, current and lower levels. In this way, coarse-to-fine context information is shared and aggregated in each block thus to improve the location of capillaries. To further improve performance, two optimizations including pyramid inputs enhancement and deep pyramid supervision are applied to PSABs in the encoder and decoder, respectively. For PSABs in the encoder, scaled input images are added as extra inputs. While for PSABs in the decoder, scaled intermediate outputs are supervised by the scaled segmentation labels. Extensive evaluations show that our pyramid U-Net outperforms the current state-of-the-art methods on the public DRIVE and CHASE-DB1 datasets.
ObjectAug: Object-level Data Augmentation for Semantic Image Segmentation
Jan 30, 2021



Abstract:Semantic image segmentation aims to obtain object labels with precise boundaries, which usually suffers from overfitting. Recently, various data augmentation strategies like regional dropout and mix strategies have been proposed to address the problem. These strategies have proved to be effective for guiding the model to attend on less discriminative parts. However, current strategies operate at the image level, and objects and the background are coupled. Thus, the boundaries are not well augmented due to the fixed semantic scenario. In this paper, we propose ObjectAug to perform object-level augmentation for semantic image segmentation. ObjectAug first decouples the image into individual objects and the background using the semantic labels. Next, each object is augmented individually with commonly used augmentation methods (e.g., scaling, shifting, and rotation). Then, the black area brought by object augmentation is further restored using image inpainting. Finally, the augmented objects and background are assembled as an augmented image. In this way, the boundaries can be fully explored in the various semantic scenarios. In addition, ObjectAug can support category-aware augmentation that gives various possibilities to objects in each category, and can be easily combined with existing image-level augmentation methods to further boost performance. Comprehensive experiments are conducted on both natural image and medical image datasets. Experiment results demonstrate that our ObjectAug can evidently improve segmentation performance.
Exploiting Review Neighbors for Contextualized Helpfulness Prediction
Jun 17, 2020


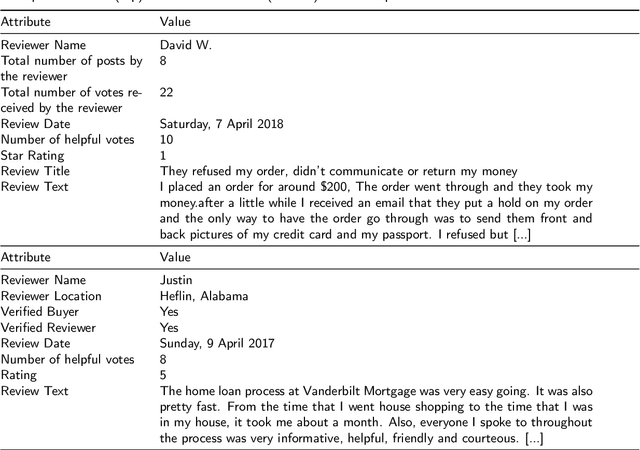
Abstract:Helpfulness prediction techniques have been widely used to identify and recommend high-quality online reviews to customers. Currently, the vast majority of studies assume that a review's helpfulness is self-contained. In practice, however, customers hardly process reviews independently given the sequential nature. The perceived helpfulness of a review is likely to be affected by its sequential neighbors (i.e., context), which has been largely ignored. This paper proposes a new methodology to capture the missing interaction between reviews and their neighbors. The first end-to-end neural architecture is developed for neighbor-aware helpfulness prediction (NAP). For each review, NAP allows for three types of neighbor selection: its preceding, following, and surrounding neighbors. Four weighting schemes are designed to learn context clues from the selected neighbors. A review is then contextualized into the learned clues for neighbor-aware helpfulness prediction. NAP is evaluated on six domains of real-world online reviews against a series of state-of-the-art baselines. Extensive experiments confirm the effectiveness of NAP and the influence of sequential neighbors on a current reviews. Further hyperparameter analysis reveals three main findings. (1) On average, eight neighbors treated with uneven importance are engaged for context construction. (2) The benefit of neighbor-aware prediction mainly results from closer neighbors. (3) Equally considering up to five closest neighbors of a review can usually produce a weaker but tolerable prediction result.
MDU-Net: Multi-scale Densely Connected U-Net for biomedical image segmentation
Dec 04, 2018



Abstract:Radiologist is "doctor's doctor", biomedical image segmentation plays a central role in quantitative analysis, clinical diagnosis, and medical intervention. In the light of the fully convolutional networks (FCN) and U-Net, deep convolutional networks (DNNs) have made significant contributions in biomedical image segmentation applications. In this paper, based on U-Net, we propose MDUnet, a multi-scale densely connected U-net for biomedical image segmentation. we propose three different multi-scale dense connections for U shaped architectures encoder, decoder and across them. The highlights of our architecture is directly fuses the neighboring different scale feature maps from both higher layers and lower layers to strengthen feature propagation in current layer. Which can largely improves the information flow encoder, decoder and across them. Multi-scale dense connections, which means containing shorter connections between layers close to the input and output, also makes much deeper U-net possible. We adopt the optimal model based on the experiment and propose a novel Multi-scale Dense U-Net (MDU-Net) architecture with quantization. Which reduce overfitting in MDU-Net for better accuracy. We evaluate our purpose model on the MICCAI 2015 Gland Segmentation dataset (GlaS). The three multi-scale dense connections improve U-net performance by up to 1.8% on test A and 3.5% on test B in the MICCAI Gland dataset. Meanwhile the MDU-net with quantization achieves the superiority over U-Net performance by up to 3% on test A and 4.1% on test B.
Supervised Anomaly Detection in Uncertain Pseudoperiodic Data Streams
Jul 20, 2016



Abstract:Uncertain data streams have been widely generated in many Web applications. The uncertainty in data streams makes anomaly detection from sensor data streams far more challenging. In this paper, we present a novel framework that supports anomaly detection in uncertain data streams. The proposed framework adopts an efficient uncertainty pre-processing procedure to identify and eliminate uncertainties in data streams. Based on the corrected data streams, we develop effective period pattern recognition and feature extraction techniques to improve the computational efficiency. We use classification methods for anomaly detection in the corrected data stream. We also empirically show that the proposed approach shows a high accuracy of anomaly detection on a number of real datasets.
Refining Adverse Drug Reactions using Association Rule Mining for Electronic Healthcare Data
Feb 20, 2015
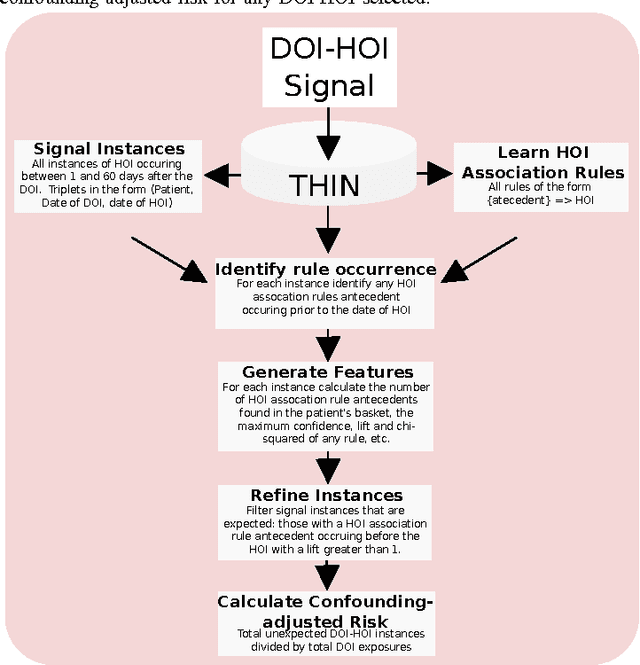
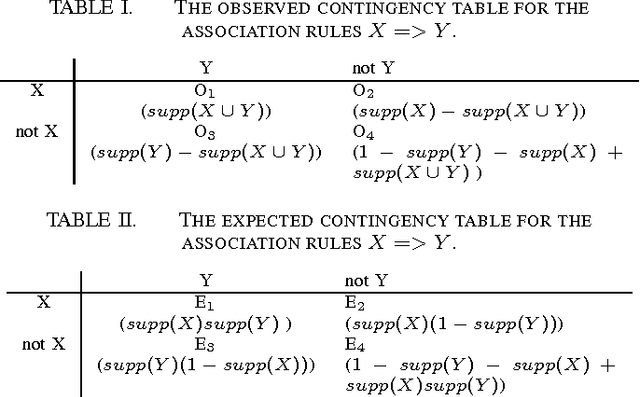

Abstract:Side effects of prescribed medications are a common occurrence. Electronic healthcare databases present the opportunity to identify new side effects efficiently but currently the methods are limited due to confounding (i.e. when an association between two variables is identified due to them both being associated to a third variable). In this paper we propose a proof of concept method that learns common associations and uses this knowledge to automatically refine side effect signals (i.e. exposure-outcome associations) by removing instances of the exposure-outcome associations that are caused by confounding. This leaves the signal instances that are most likely to correspond to true side effect occurrences. We then calculate a novel measure termed the confounding-adjusted risk value, a more accurate absolute risk value of a patient experiencing the outcome within 60 days of the exposure. Tentative results suggest that the method works. For the four signals (i.e. exposure-outcome associations) investigated we are able to correctly filter the majority of exposure-outcome instances that were unlikely to correspond to true side effects. The method is likely to improve when tuning the association rule mining parameters for specific health outcomes. This paper shows that it may be possible to filter signals at a patient level based on association rules learned from considering patients' medical histories. However, additional work is required to develop a way to automate the tuning of the method's parameters.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge