Yahui Fu
Multilingual and Continuous Backchannel Prediction: A Cross-lingual Study
Dec 16, 2025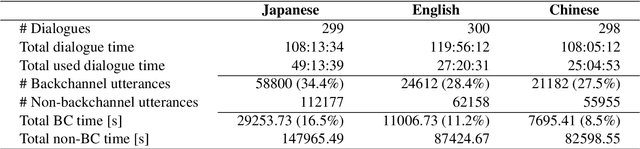
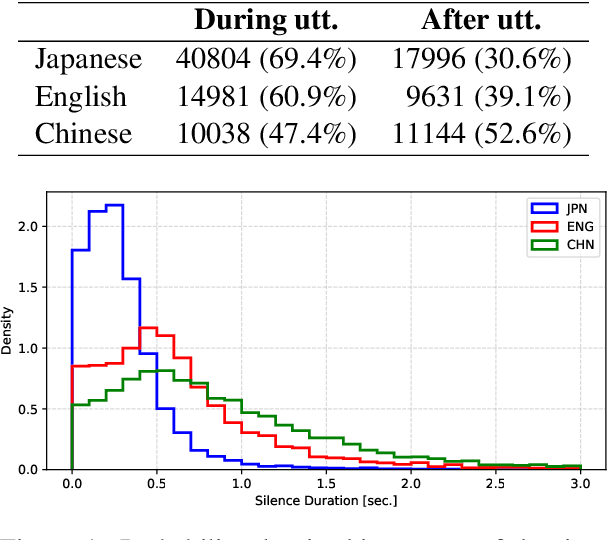
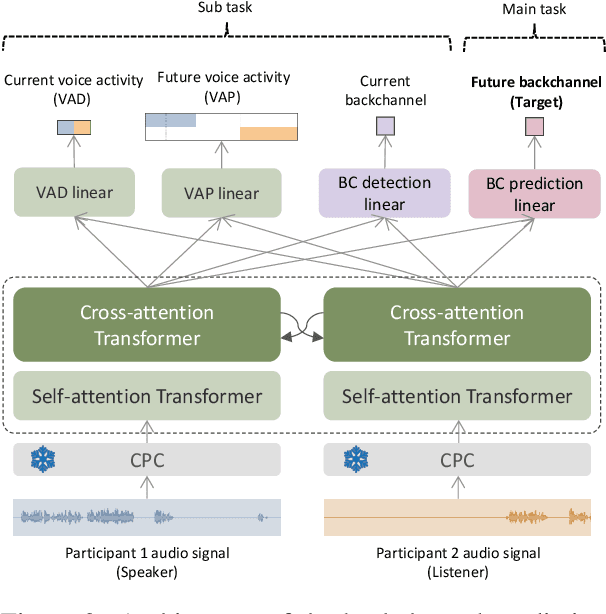
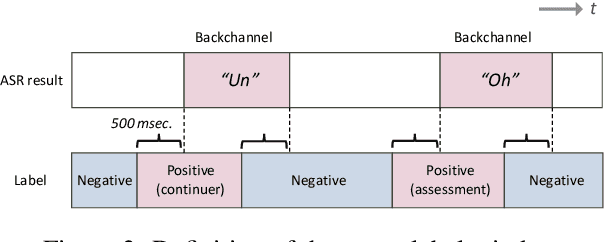
Abstract:We present a multilingual, continuous backchannel prediction model for Japanese, English, and Chinese, and use it to investigate cross-linguistic timing behavior. The model is Transformer-based and operates at the frame level, jointly trained with auxiliary tasks on approximately 300 hours of dyadic conversations. Across all three languages, the multilingual model matches or surpasses monolingual baselines, indicating that it learns both language-universal cues and language-specific timing patterns. Zero-shot transfer with two-language training remains limited, underscoring substantive cross-lingual differences. Perturbation analyses reveal distinct cue usage: Japanese relies more on short-term linguistic information, whereas English and Chinese are more sensitive to silence duration and prosodic variation; multilingual training encourages shared yet adaptable representations and reduces overreliance on pitch in Chinese. A context-length study further shows that Japanese is relatively robust to shorter contexts, while Chinese benefits markedly from longer contexts. Finally, we integrate the trained model into a real-time processing software, demonstrating CPU-only inference. Together, these findings provide a unified model and empirical evidence for how backchannel timing differs across languages, informing the design of more natural, culturally-aware spoken dialogue systems.
Minority-Aware Satisfaction Estimation in Dialogue Systems via Preference-Adaptive Reinforcement Learning
Nov 07, 2025Abstract:User satisfaction in dialogue systems is inherently subjective. When the same response strategy is applied across users, minority users may assign different satisfaction ratings than majority users due to variations in individual intents and preferences. However, existing alignment methods typically train one-size-fits-all models that aim for broad consensus, often overlooking minority perspectives and user-specific adaptation. We propose a unified framework that models both individual- and group-level preferences for user satisfaction estimation. First, we introduce Chain-of-Personalized-Reasoning (CoPeR) to capture individual preferences through interpretable reasoning chains. Second, we propose an expectation-maximization-based Majority-Minority Preference-Aware Clustering (M2PC) algorithm that discovers distinct user groups in an unsupervised manner to learn group-level preferences. Finally, we integrate these components into a preference-adaptive reinforcement learning framework (PAda-PPO) that jointly optimizes alignment with both individual and group preferences. Experiments on the Emotional Support Conversation dataset demonstrate consistent improvements in user satisfaction estimation, particularly for underrepresented user groups.
Bridging Speech Emotion Recognition and Personality: Dataset and Temporal Interaction Condition Network
May 20, 2025Abstract:This study investigates the interaction between personality traits and emotional expression, exploring how personality information can improve speech emotion recognition (SER). We collected personality annotation for the IEMOCAP dataset, and the statistical analysis identified significant correlations between personality traits and emotional expressions. To extract finegrained personality features, we propose a temporal interaction condition network (TICN), in which personality features are integrated with Hubert-based acoustic features for SER. Experiments show that incorporating ground-truth personality traits significantly enhances valence recognition, improving the concordance correlation coefficient (CCC) from 0.698 to 0.785 compared to the baseline without personality information. For practical applications in dialogue systems where personality information about the user is unavailable, we develop a front-end module of automatic personality recognition. Using these automatically predicted traits as inputs to our proposed TICN model, we achieve a CCC of 0.776 for valence recognition, representing an 11.17% relative improvement over the baseline. These findings confirm the effectiveness of personality-aware SER and provide a solid foundation for further exploration in personality-aware speech processing applications.
Does the Appearance of Autonomous Conversational Robots Affect User Spoken Behaviors in Real-World Conference Interactions?
Mar 17, 2025Abstract:We investigate the impact of robot appearance on users' spoken behavior during real-world interactions by comparing a human-like android, ERICA, with a less anthropomorphic humanoid, TELECO. Analyzing data from 42 participants at SIGDIAL 2024, we extracted linguistic features such as disfluencies and syntactic complexity from conversation transcripts. The results showed moderate effect sizes, suggesting that participants produced fewer disfluencies and employed more complex syntax when interacting with ERICA. Further analysis involving training classification models like Na\"ive Bayes, which achieved an F1-score of 71.60\%, and conducting feature importance analysis, highlighted the significant role of disfluencies and syntactic complexity in interactions with robots of varying human-like appearances. Discussing these findings within the frameworks of cognitive load and Communication Accommodation Theory, we conclude that designing robots to elicit more structured and fluent user speech can enhance their communicative alignment with humans.
Human-Like Embodied AI Interviewer: Employing Android ERICA in Real International Conference
Dec 13, 2024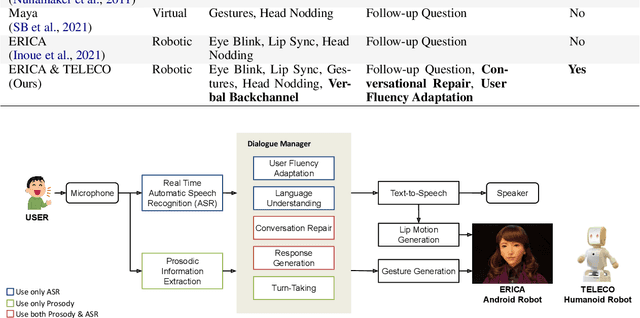
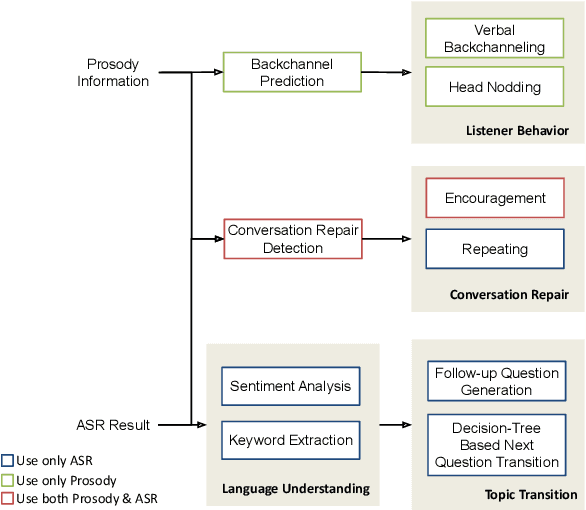

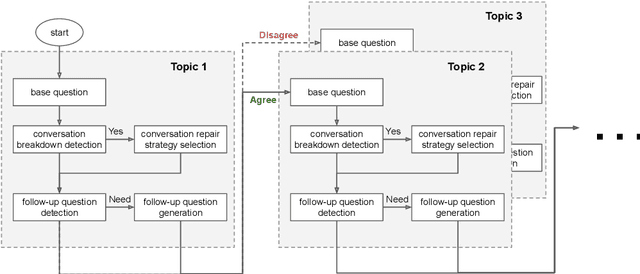
Abstract:This paper introduces the human-like embodied AI interviewer which integrates android robots equipped with advanced conversational capabilities, including attentive listening, conversational repairs, and user fluency adaptation. Moreover, it can analyze and present results post-interview. We conducted a real-world case study at SIGDIAL 2024 with 42 participants, of whom 69% reported positive experiences. This study demonstrated the system's effectiveness in conducting interviews just like a human and marked the first employment of such a system at an international conference. The demonstration video is available at https://youtu.be/jCuw9g99KuE.
StyEmp: Stylizing Empathetic Response Generation via Multi-Grained Prefix Encoder and Personality Reinforcement
Aug 05, 2024



Abstract:Recent approaches for empathetic response generation mainly focus on emotional resonance and user understanding, without considering the system's personality. Consistent personality is evident in real human expression and is important for creating trustworthy systems. To address this problem, we propose StyEmp, which aims to stylize the empathetic response generation with a consistent personality. Specifically, it incorporates a multi-grained prefix mechanism designed to capture the intricate relationship between a system's personality and its empathetic expressions. Furthermore, we introduce a personality reinforcement module that leverages contrastive learning to calibrate the generation model, ensuring that responses are both empathetic and reflective of a distinct personality. Automatic and human evaluations on the EMPATHETICDIALOGUES benchmark show that StyEmp outperforms competitive baselines in terms of both empathy and personality expressions.
Acknowledgment of Emotional States: Generating Validating Responses for Empathetic Dialogue
Feb 20, 2024



Abstract:In the realm of human-AI dialogue, the facilitation of empathetic responses is important. Validation is one of the key communication techniques in psychology, which entails recognizing, understanding, and acknowledging others' emotional states, thoughts, and actions. This study introduces the first framework designed to engender empathetic dialogue with validating responses. Our approach incorporates a tripartite module system: 1) validation timing detection, 2) users' emotional state identification, and 3) validating response generation. Utilizing Japanese EmpatheticDialogues dataset - a textual-based dialogue dataset consisting of 8 emotional categories from Plutchik's wheel of emotions - the Task Adaptive Pre-Training (TAPT) BERT-based model outperforms both random baseline and the ChatGPT performance, in term of F1-score, in all modules. Further validation of our model's efficacy is confirmed in its application to the TUT Emotional Storytelling Corpus (TESC), a speech-based dialogue dataset, by surpassing both random baseline and the ChatGPT. This consistent performance across both textual and speech-based dialogues underscores the effectiveness of our framework in fostering empathetic human-AI communication.
Enhancing Personality Recognition in Dialogue by Data Augmentation and Heterogeneous Conversational Graph Networks
Jan 11, 2024



Abstract:Personality recognition is useful for enhancing robots' ability to tailor user-adaptive responses, thus fostering rich human-robot interactions. One of the challenges in this task is a limited number of speakers in existing dialogue corpora, which hampers the development of robust, speaker-independent personality recognition models. Additionally, accurately modeling both the interdependencies among interlocutors and the intra-dependencies within the speaker in dialogues remains a significant issue. To address the first challenge, we introduce personality trait interpolation for speaker data augmentation. For the second, we propose heterogeneous conversational graph networks to independently capture both contextual influences and inherent personality traits. Evaluations on the RealPersonaChat corpus demonstrate our method's significant improvements over existing baselines.
Reasoning before Responding: Integrating Commonsense-based Causality Explanation for Empathetic Response Generation
Jul 28, 2023Abstract:Recent approaches to empathetic response generation try to incorporate commonsense knowledge or reasoning about the causes of emotions to better understand the user's experiences and feelings. However, these approaches mainly focus on understanding the causalities of context from the user's perspective, ignoring the system's perspective. In this paper, we propose a commonsense-based causality explanation approach for diverse empathetic response generation that considers both the user's perspective (user's desires and reactions) and the system's perspective (system's intentions and reactions). We enhance ChatGPT's ability to reason for the system's perspective by integrating in-context learning with commonsense knowledge. Then, we integrate the commonsense-based causality explanation with both ChatGPT and a T5-based model. Experimental evaluations demonstrate that our method outperforms other comparable methods on both automatic and human evaluations.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge