Xuemin Zhu
EMDS-5: Environmental Microorganism Image Dataset Fifth Version for Multiple Image Analysis Tasks
Feb 20, 2021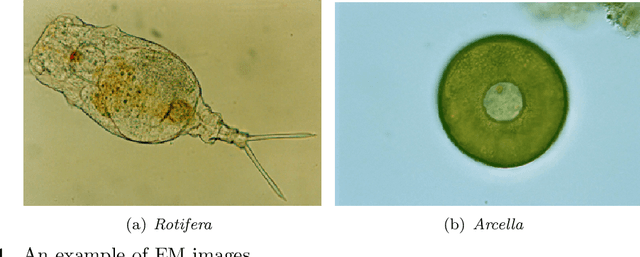
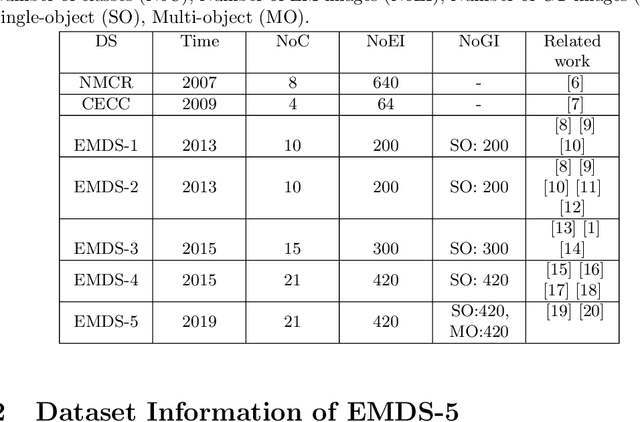
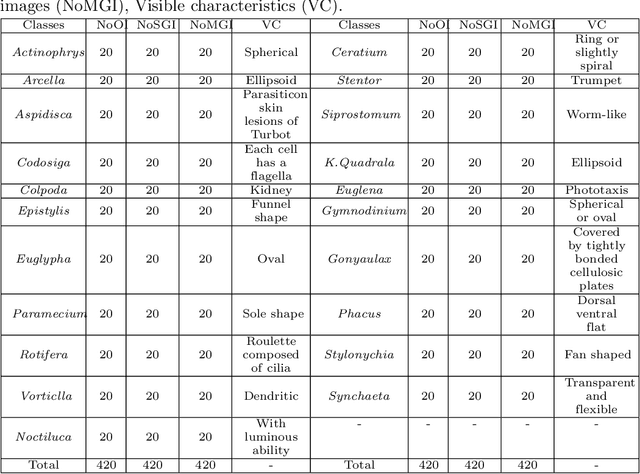

Abstract:Environmental Microorganism Data Set Fifth Version (EMDS-5) is a microscopic image dataset including original Environmental Microorganism (EM) images and two sets of Ground Truth (GT) images. The GT image sets include a single-object GT image set and a multi-object GT image set. The EMDS-5 dataset has 21 types of EMs, each of which contains 20 original EM images, 20 single-object GT images and 20 multi-object GT images. EMDS-5 can realize to evaluate image preprocessing, image segmentation, feature extraction, image classification and image retrieval functions. In order to prove the effectiveness of EMDS-5, for each function, we select the most representative algorithms and price indicators for testing and evaluation. The image preprocessing functions contain two parts: image denoising and image edge detection. Image denoising uses nine kinds of filters to denoise 13 kinds of noises, respectively. In the aspect of edge detection, six edge detection operators are used to detect the edges of the images, and two evaluation indicators, peak-signal to noise ratio and mean structural similarity, are used for evaluation. Image segmentation includes single-object image segmentation and multi-object image segmentation. Six methods are used for single-object image segmentation, while k-means and U-net are used for multi-object segmentation.We extract nine features from the images in EMDS-5 and use the Support Vector Machine classifier for testing. In terms of image classification, we select the VGG16 feature to test different classifiers. We test two types of retrieval approaches: texture feature retrieval and deep learning feature retrieval. We select the last layer of features of these two deep learning networks as feature vectors. We use mean average precision as the evaluation index for retrieval.
SeFM: A Sequential Feature Point Matching Algorithm for Object 3D Reconstruction
Dec 07, 2018
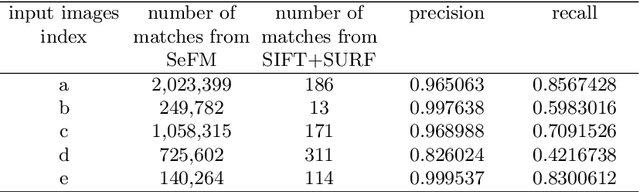
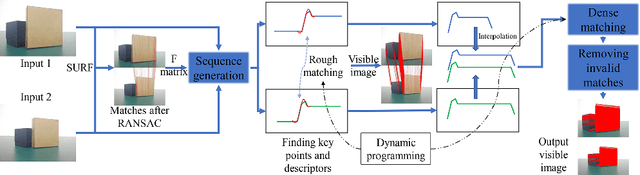

Abstract:3D reconstruction is a fundamental issue in many applications and the feature point matching problem is a key step while reconstructing target objects. Conventional algorithms can only find a small number of feature points from two images which is quite insufficient for reconstruction. To overcome this problem, we propose SeFM a sequential feature point matching algorithm. We first utilize the epipolar geometry to find the epipole of each image. Rotating along the epipole, we generate a set of the epipolar lines and reserve those intersecting with the input image. Next, a rough matching phase, followed by a dense matching phase, is applied to find the matching dot-pairs using dynamic programming. Furthermore, we also remove wrong matching dot-pairs by calculating the validity. Experimental results illustrate that SeFM can achieve around 1,000 to 10,000 times matching dot-pairs, depending on individual image, compared to conventional algorithms and the object reconstruction with only two images is semantically visible. Moreover, it outperforms conventional algorithms, such as SIFT and SURF, regarding precision and recall.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge