Xuefeng Cui
SHREC 2021: Classification in cryo-electron tomograms
Mar 18, 2022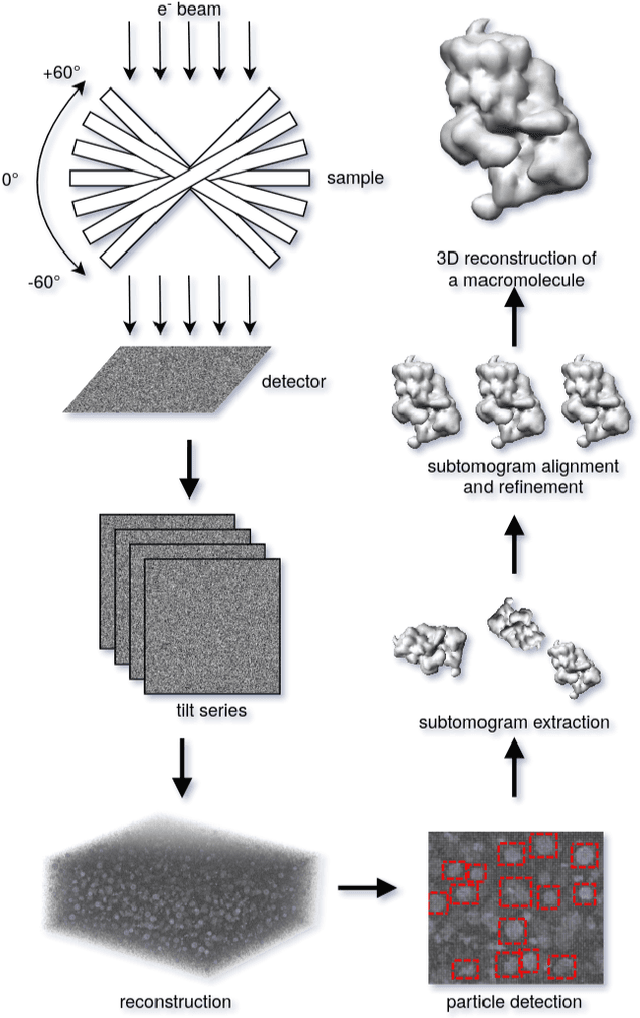
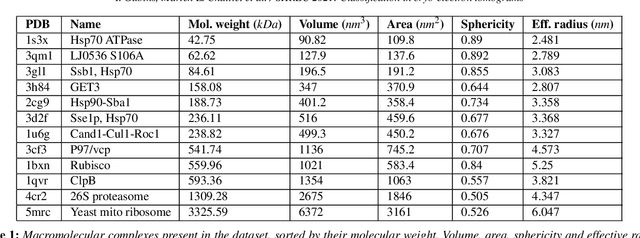
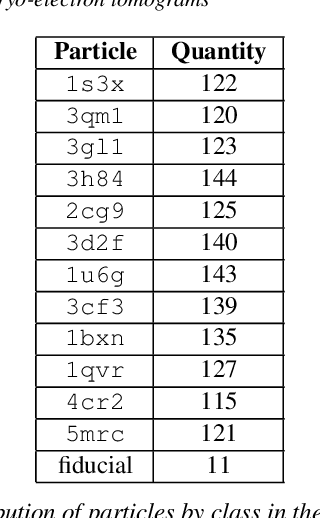
Abstract:Cryo-electron tomography (cryo-ET) is an imaging technique that allows three-dimensional visualization of macro-molecular assemblies under near-native conditions. Cryo-ET comes with a number of challenges, mainly low signal-to-noise and inability to obtain images from all angles. Computational methods are key to analyze cryo-electron tomograms. To promote innovation in computational methods, we generate a novel simulated dataset to benchmark different methods of localization and classification of biological macromolecules in tomograms. Our publicly available dataset contains ten tomographic reconstructions of simulated cell-like volumes. Each volume contains twelve different types of complexes, varying in size, function and structure. In this paper, we have evaluated seven different methods of finding and classifying proteins. Seven research groups present results obtained with learning-based methods and trained on the simulated dataset, as well as a baseline template matching (TM), a traditional method widely used in cryo-ET research. We show that learning-based approaches can achieve notably better localization and classification performance than TM. We also experimentally confirm that there is a negative relationship between particle size and performance for all methods.
When coding meets ranking: A joint framework based on local learning
Nov 02, 2016



Abstract:Sparse coding, which represents a data point as a sparse reconstruction code with regard to a dictionary, has been a popular data representation method. Meanwhile, in database retrieval problems, learning the ranking scores from data points plays an important role. Up to now, these two problems have always been considered separately, assuming that data coding and ranking are two independent and irrelevant problems. However, is there any internal relationship between sparse coding and ranking score learning? If yes, how to explore and make use of this internal relationship? In this paper, we try to answer these questions by developing the first joint sparse coding and ranking score learning algorithm. To explore the local distribution in the sparse code space, and also to bridge coding and ranking problems, we assume that in the neighborhood of each data point, the ranking scores can be approximated from the corresponding sparse codes by a local linear function. By considering the local approximation error of ranking scores, the reconstruction error and sparsity of sparse coding, and the query information provided by the user, we construct a unified objective function for learning of sparse codes, the dictionary and ranking scores. We further develop an iterative algorithm to solve this optimization problem.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge