Xizhou Bu
Resolving State Ambiguity in Robot Manipulation via Adaptive Working Memory Recoding
Dec 31, 2025Abstract:State ambiguity is common in robotic manipulation. Identical observations may correspond to multiple valid behavior trajectories. The visuomotor policy must correctly extract the appropriate types and levels of information from the history to identify the current task phase. However, naively extending the history window is computationally expensive and may cause severe overfitting. Inspired by the continuous nature of human reasoning and the recoding of working memory, we introduce PAM, a novel visuomotor Policy equipped with Adaptive working Memory. With minimal additional training cost in a two-stage manner, PAM supports a 300-frame history window while maintaining high inference speed. Specifically, a hierarchical frame feature extractor yields two distinct representations for motion primitives and temporal disambiguation. For compact representation, a context router with range-specific queries is employed to produce compact context features across multiple history lengths. And an auxiliary objective of reconstructing historical information is introduced to ensure that the context router acts as an effective bottleneck. We meticulously design 7 tasks and verify that PAM can handle multiple scenarios of state ambiguity simultaneously. With a history window of approximately 10 seconds, PAM still supports stable training and maintains inference speeds above 20Hz. Project website: https://tinda24.github.io/pam/
Learning from Imperfect Demonstrations through Dynamics Evaluation
Dec 18, 2023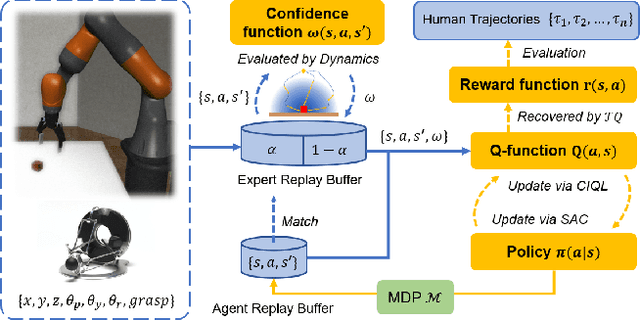
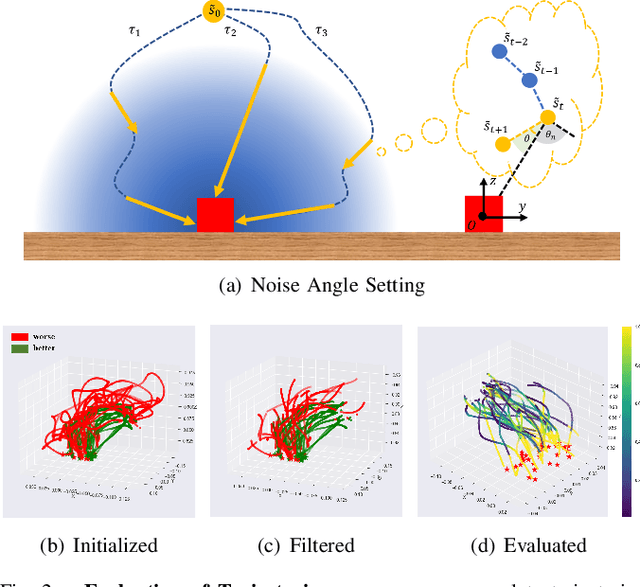
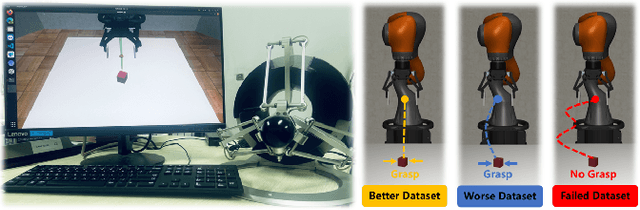
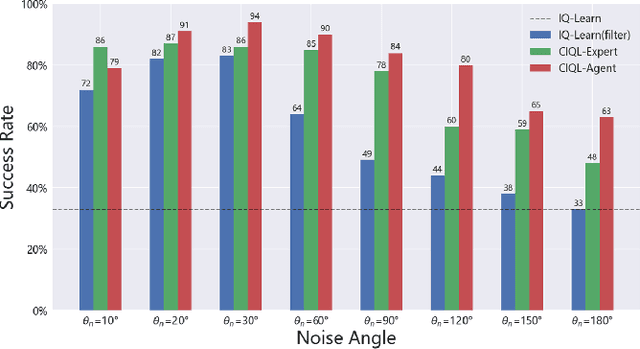
Abstract:Standard imitation learning usually assumes that demonstrations are drawn from an optimal policy distribution. However, in real-world scenarios, every human demonstration may exhibit nearly random behavior and collecting high-quality human datasets can be quite costly. This requires imitation learning can learn from imperfect demonstrations to obtain robotic policies that align human intent. Prior work uses confidence scores to extract useful information from imperfect demonstrations, which relies on access to ground truth rewards or active human supervision. In this paper, we propose a dynamics-based method to evaluate the data confidence scores without above efforts. We develop a generalized confidence-based imitation learning framework called Confidence-based Inverse soft-Q Learning (CIQL), which can employ different optimal policy matching methods by simply changing object functions. Experimental results show that our confidence evaluation method can increase the success rate by $40.3\%$ over the original algorithm and $13.5\%$ over the simple noise filtering.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge