Xiyao Jin
A quality assurance framework for real-time monitoring of deep learning segmentation models in radiotherapy
May 19, 2023



Abstract:To safely deploy deep learning models in the clinic, a quality assurance framework is needed for routine or continuous monitoring of input-domain shift and the models' performance without ground truth contours. In this work, cardiac substructure segmentation was used as an example task to establish a QA framework. A benchmark dataset consisting of Computed Tomography (CT) images along with manual cardiac delineations of 241 patients were collected, including one 'common' image domain and five 'uncommon' domains. Segmentation models were tested on the benchmark dataset for an initial evaluation of model capacity and limitations. An image domain shift detector was developed by utilizing a trained Denoising autoencoder (DAE) and two hand-engineered features. Another Variational Autoencoder (VAE) was also trained to estimate the shape quality of the auto-segmentation results. Using the extracted features from the image/segmentation pair as inputs, a regression model was trained to predict the per-patient segmentation accuracy, measured by Dice coefficient similarity (DSC). The framework was tested across 19 segmentation models to evaluate the generalizability of the entire framework. As results, the predicted DSC of regression models achieved a mean absolute error (MAE) ranging from 0.036 to 0.046 with an averaged MAE of 0.041. When tested on the benchmark dataset, the performances of all segmentation models were not significantly affected by scanning parameters: FOV, slice thickness and reconstructions kernels. For input images with Poisson noise, CNN-based segmentation models demonstrated a decreased DSC ranging from 0.07 to 0.41, while the transformer-based model was not significantly affected.
Deep Embedding Convolutional Neural Network for Synthesizing CT Image from T1-Weighted MR Image
Nov 09, 2017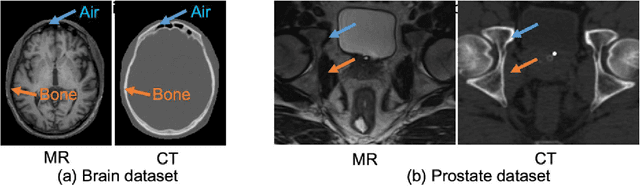
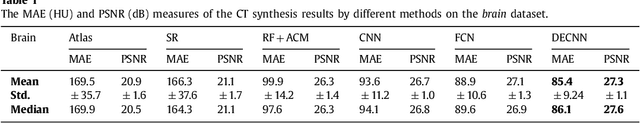
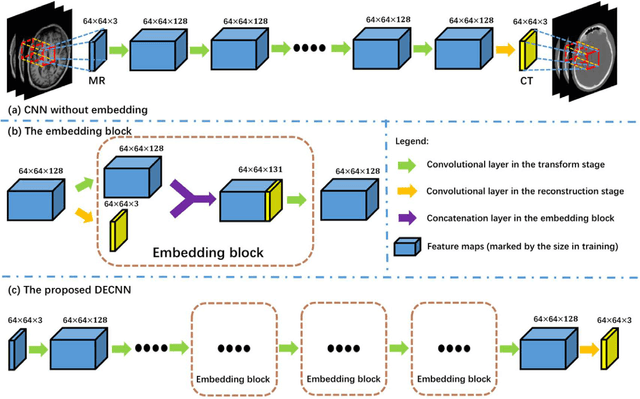
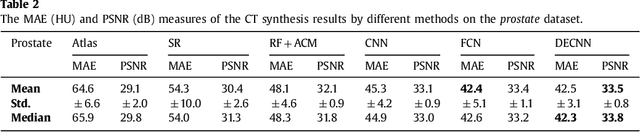
Abstract:Recently, more and more attention is drawn to the field of medical image synthesis across modalities. Among them, the synthesis of computed tomography (CT) image from T1-weighted magnetic resonance (MR) image is of great importance, although the mapping between them is highly complex due to large gaps of appearances of the two modalities. In this work, we aim to tackle this MR-to-CT synthesis by a novel deep embedding convolutional neural network (DECNN). Specifically, we generate the feature maps from MR images, and then transform these feature maps forward through convolutional layers in the network. We can further compute a tentative CT synthesis from the midway of the flow of feature maps, and then embed this tentative CT synthesis back to the feature maps. This embedding operation results in better feature maps, which are further transformed forward in DECNN. After repeat-ing this embedding procedure for several times in the network, we can eventually synthesize a final CT image in the end of the DECNN. We have validated our proposed method on both brain and prostate datasets, by also compar-ing with the state-of-the-art methods. Experimental results suggest that our DECNN (with repeated embedding op-erations) demonstrates its superior performances, in terms of both the perceptive quality of the synthesized CT image and the run-time cost for synthesizing a CT image.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge