Xiongwei Mao
Graph-based Pyramid Global Context Reasoning with a Saliency-aware Projection for COVID-19 Lung Infections Segmentation
Mar 07, 2021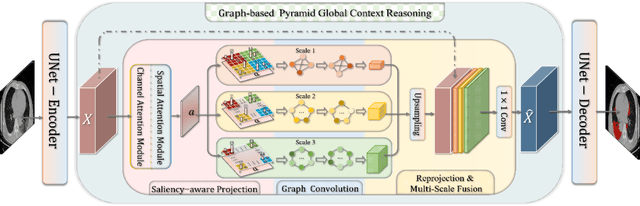
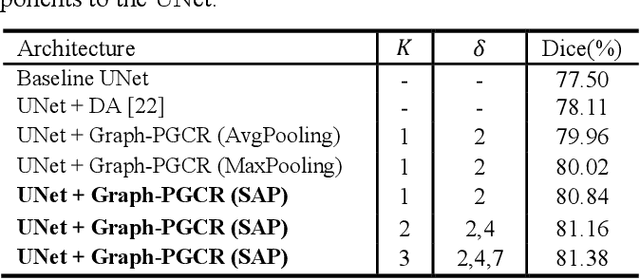
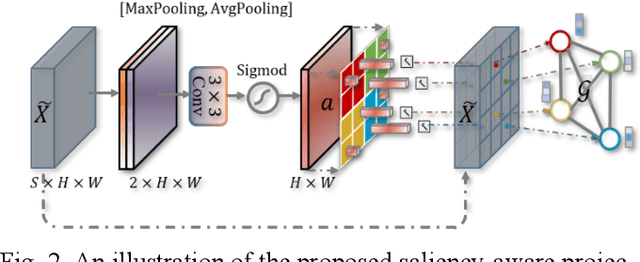
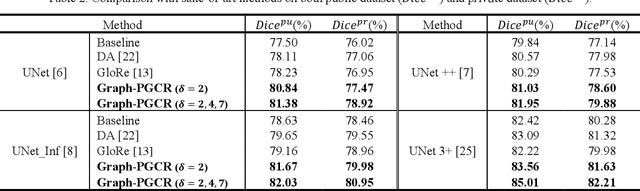
Abstract:Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19) has rapidly spread in 2020, emerging a mass of studies for lung infection segmentation from CT images. Though many methods have been proposed for this issue, it is a challenging task because of infections of various size appearing in different lobe zones. To tackle these issues, we propose a Graph-based Pyramid Global Context Reasoning (Graph-PGCR) module, which is capable of modeling long-range dependencies among disjoint infections as well as adapt size variation. We first incorporate graph convolution to exploit long-term contextual information from multiple lobe zones. Different from previous average pooling or maximum object probability, we propose a saliency-aware projection mechanism to pick up infection-related pixels as a set of graph nodes. After graph reasoning, the relation-aware features are reversed back to the original coordinate space for the down-stream tasks. We further construct multiple graphs with different sampling rates to handle the size variation problem. To this end, distinct multi-scale long-range contextual patterns can be captured. Our Graph-PGCR module is plug-and-play, which can be integrated into any architecture to improve its performance. Experiments demonstrated that the proposed method consistently boost the performance of state-of-the-art backbone architectures on both of public and our private COVID-19 datasets.
PA-ResSeg: A Phase Attention Residual Network for Liver Tumor Segmentation from Multi-phase CT Images
Feb 27, 2021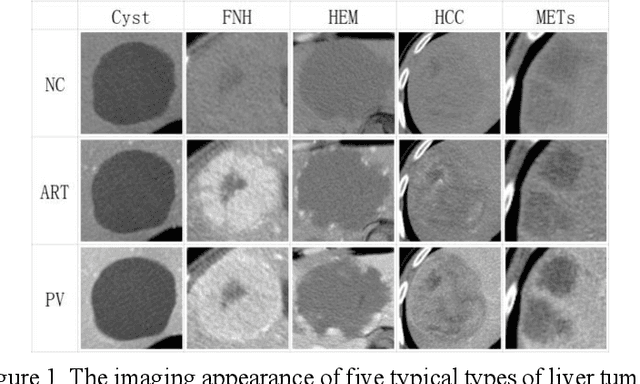
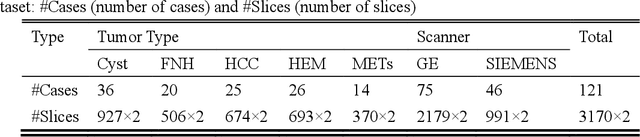
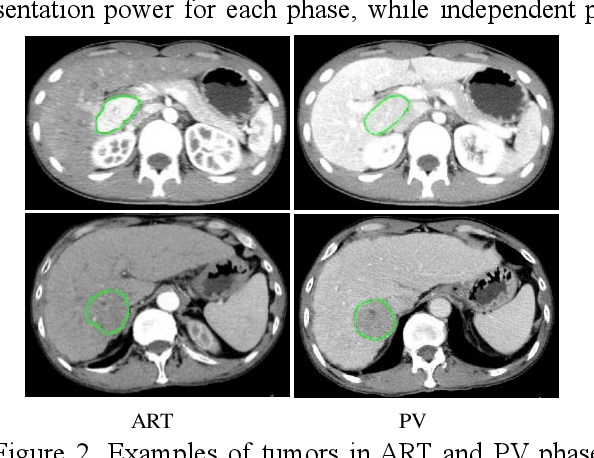
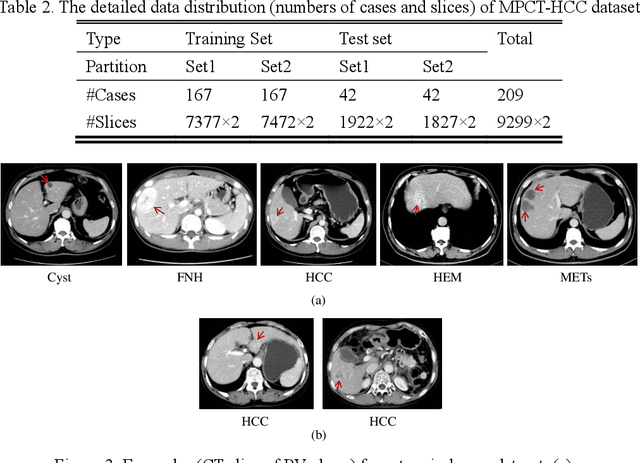
Abstract:In this paper, we propose a phase attention residual network (PA-ResSeg) to model multi-phase features for accurate liver tumor segmentation, in which a phase attention (PA) is newly proposed to additionally exploit the images of arterial (ART) phase to facilitate the segmentation of portal venous (PV) phase. The PA block consists of an intra-phase attention (Intra-PA) module and an inter-phase attention (Inter-PA) module to capture channel-wise self-dependencies and cross-phase interdependencies, respectively. Thus it enables the network to learn more representative multi-phase features by refining the PV features according to the channel dependencies and recalibrating the ART features based on the learned interdependencies between phases. We propose a PA-based multi-scale fusion (MSF) architecture to embed the PA blocks in the network at multiple levels along the encoding path to fuse multi-scale features from multi-phase images. Moreover, a 3D boundary-enhanced loss (BE-loss) is proposed for training to make the network more sensitive to boundaries. To evaluate the performance of our proposed PA-ResSeg, we conducted experiments on a multi-phase CT dataset of focal liver lesions (MPCT-FLLs). Experimental results show the effectiveness of the proposed method by achieving a dice per case (DPC) of 0.77.87, a dice global (DG) of 0.8682, a volumetric overlap error (VOE) of 0.3328 and a relative volume difference (RVD) of 0.0443 on the MPCT-FLLs. Furthermore, to validate the effectiveness and robustness of PA-ResSeg, we conducted extra experiments on another multi-phase liver tumor dataset and obtained a DPC of 0.8290, a DG of 0.9132, a VOE of 0.2637 and a RVD of 0.0163. The proposed method shows its robustness and generalization capability in different datasets and different backbones.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge