Xinyu Liang
Selection of Layers from Self-supervised Learning Models for Predicting Mean-Opinion-Score of Speech
Aug 12, 2025Abstract:Self-supervised learning (SSL) models like Wav2Vec2, HuBERT, and WavLM have been widely used in speech processing. These transformer-based models consist of multiple layers, each capturing different levels of representation. While prior studies explored their layer-wise representations for efficiency and performance, speech quality assessment (SQA) models predominantly rely on last-layer features, leaving intermediate layers underexamined. In this work, we systematically evaluate different layers of multiple SSL models for predicting mean-opinion-score (MOS). Features from each layer are fed into a lightweight regression network to assess effectiveness. Our experiments consistently show early-layers features outperform or match those from the last layer, leading to significant improvements over conventional approaches and state-of-the-art MOS prediction models. These findings highlight the advantages of early-layer selection, offering enhanced performance and reduced system complexity.
Leveraging LLMs for Scalable Non-intrusive Speech Quality Assessment
Aug 08, 2025Abstract:Non-intrusive speech quality assessment (SQA) systems suffer from limited training data and costly human annotations, hindering their generalization to real-time conferencing calls. In this work, we propose leveraging large language models (LLMs) as pseudo-raters for speech quality to address these data bottlenecks. We construct LibriAugmented, a dataset consisting of 101,129 speech clips with simulated degradations labeled by a fine-tuned auditory LLM (Vicuna-7b-v1.5). We compare three training strategies: using human-labeled data, using LLM-labeled data, and a two-stage approach (pretraining on LLM labels, then fine-tuning on human labels), using both DNSMOS Pro and DeePMOS. We test on several datasets across languages and quality degradations. While LLM-labeled training yields mixed results compared to human-labeled training, we provide empirical evidence that the two-stage approach improves the generalization performance (e.g., DNSMOS Pro achieves 0.63 vs. 0.55 PCC on NISQA_TEST_LIVETALK and 0.73 vs. 0.65 PCC on Tencent with reverb). Our findings demonstrate the potential of using LLMs as scalable pseudo-raters for speech quality assessment, offering a cost-effective solution to the data limitation problem.
Multivariate Probabilistic Assessment of Speech Quality
Jun 05, 2025Abstract:The mean opinion score (MOS) is a standard metric for assessing speech quality, but its singular focus fails to identify specific distortions when low scores are observed. The NISQA dataset addresses this limitation by providing ratings across four additional dimensions: noisiness, coloration, discontinuity, and loudness, alongside MOS. In this paper, we extend the explored univariate MOS estimation to a multivariate framework by modeling these dimensions jointly using a multivariate Gaussian distribution. Our approach utilizes Cholesky decomposition to predict covariances without imposing restrictive assumptions and extends probabilistic affine transformations to a multivariate context. Experimental results show that our model performs on par with state-of-the-art methods in point estimation, while uniquely providing uncertainty and correlation estimates across speech quality dimensions. This enables better diagnosis of poor speech quality and informs targeted improvements.
Human-in-the-Loop AI for HVAC Management Enhancing Comfort and Energy Efficiency
May 09, 2025Abstract:Heating, Ventilation, and Air Conditioning (HVAC) systems account for approximately 38% of building energy consumption globally, making them one of the most energy-intensive services. The increasing emphasis on energy efficiency and sustainability, combined with the need for enhanced occupant comfort, presents a significant challenge for traditional HVAC systems. These systems often fail to dynamically adjust to real-time changes in electricity market rates or individual comfort preferences, leading to increased energy costs and reduced comfort. In response, we propose a Human-in-the-Loop (HITL) Artificial Intelligence framework that optimizes HVAC performance by incorporating real-time user feedback and responding to fluctuating electricity prices. Unlike conventional systems that require predefined information about occupancy or comfort levels, our approach learns and adapts based on ongoing user input. By integrating the occupancy prediction model with reinforcement learning, the system improves operational efficiency and reduces energy costs in line with electricity market dynamics, thereby contributing to demand response initiatives. Through simulations, we demonstrate that our method achieves significant cost reductions compared to baseline approaches while maintaining or enhancing occupant comfort. This feedback-driven approach ensures personalized comfort control without the need for predefined settings, offering a scalable solution that balances individual preferences with economic and environmental goals.
Impairments are Clustered in Latents of Deep Neural Network-based Speech Quality Models
Apr 30, 2025Abstract:In this article, we provide an experimental observation: Deep neural network (DNN) based speech quality assessment (SQA) models have inherent latent representations where many types of impairments are clustered. While DNN-based SQA models are not trained for impairment classification, our experiments show good impairment classification results in an appropriate SQA latent representation. We investigate the clustering of impairments using various kinds of audio degradations that include different types of noises, waveform clipping, gain transition, pitch shift, compression, reverberation, etc. To visualize the clusters we perform classification of impairments in the SQA-latent representation domain using a standard k-nearest neighbor (kNN) classifier. We also develop a new DNN-based SQA model, named DNSMOS+, to examine whether an improvement in SQA leads to an improvement in impairment classification. The classification accuracy is 94% for LibriAugmented dataset with 16 types of impairments and 54% for ESC-50 dataset with 50 types of real noises.
Learning and Generating Diverse Residential Load Patterns Using GAN with Weakly-Supervised Training and Weight Selection
Apr 19, 2025



Abstract:The scarcity of high-quality residential load data can pose obstacles for decarbonizing the residential sector as well as effective grid planning and operation. The above challenges have motivated research into generating synthetic load data, but existing methods faced limitations in terms of scalability, diversity, and similarity. This paper proposes a Generative Adversarial Network-based Synthetic Residential Load Pattern (RLP-GAN) generation model, a novel weakly-supervised GAN framework, leveraging an over-complete autoencoder to capture dependencies within complex and diverse load patterns and learn household-level data distribution at scale. We incorporate a model weight selection method to address the mode collapse problem and generate load patterns with high diversity. We develop a holistic evaluation method to validate the effectiveness of RLP-GAN using real-world data of 417 households. The results demonstrate that RLP-GAN outperforms state-of-the-art models in capturing temporal dependencies and generating load patterns with higher similarity to real data. Furthermore, we have publicly released the RLP-GAN generated synthetic dataset, which comprises one million synthetic residential load pattern profiles.
* 12 pages
ER2Score: LLM-based Explainable and Customizable Metric for Assessing Radiology Reports with Reward-Control Loss
Nov 26, 2024



Abstract:Automated radiology report generation (R2Gen) has advanced significantly, introducing challenges in accurate evaluation due to its complexity. Traditional metrics often fall short by relying on rigid word-matching or focusing only on pathological entities, leading to inconsistencies with human assessments. To bridge this gap, we introduce ER2Score, an automatic evaluation metric designed specifically for R2Gen. Our metric utilizes a reward model, guided by our margin-based reward enforcement loss, along with a tailored training data design that enables customization of evaluation criteria to suit user-defined needs. It not only scores reports according to user-specified criteria but also provides detailed sub-scores, enhancing interpretability and allowing users to adjust the criteria between different aspects of reports. Leveraging GPT-4, we designed an easy-to-use data generation pipeline, enabling us to produce extensive training data based on two distinct scoring systems, each containing reports of varying quality along with corresponding scores. These GPT-generated reports are then paired as accepted and rejected samples through our pairing rule to train an LLM towards our fine-grained reward model, which assigns higher rewards to the report with high quality. Our reward-control loss enables this model to simultaneously output multiple individual rewards corresponding to the number of evaluation criteria, with their summation as our final ER2Score. Our experiments demonstrate ER2Score's heightened correlation with human judgments and superior performance in model selection compared to traditional metrics. Notably, our model provides both an overall score and individual scores for each evaluation item, enhancing interpretability. We also demonstrate its flexible training across various evaluation systems.
Synthetic Data Generation for Residential Load Patterns via Recurrent GAN and Ensemble Method
Oct 20, 2024Abstract:Generating synthetic residential load data that can accurately represent actual electricity consumption patterns is crucial for effective power system planning and operation. The necessity for synthetic data is underscored by the inherent challenges associated with using real-world load data, such as privacy considerations and logistical complexities in large-scale data collection. In this work, we tackle the above-mentioned challenges by developing the Ensemble Recurrent Generative Adversarial Network (ERGAN) framework to generate high-fidelity synthetic residential load data. ERGAN leverages an ensemble of recurrent Generative Adversarial Networks, augmented by a loss function that concurrently takes into account adversarial loss and differences between statistical properties. Our developed ERGAN can capture diverse load patterns across various households, thereby enhancing the realism and diversity of the synthetic data generated. Comprehensive evaluations demonstrate that our method consistently outperforms established benchmarks in the synthetic generation of residential load data across various performance metrics including diversity, similarity, and statistical measures. The findings confirm the potential of ERGAN as an effective tool for energy applications requiring synthetic yet realistic load data. We also make the generated synthetic residential load patterns publicly available.
* 12 pages
MRScore: Evaluating Radiology Report Generation with LLM-based Reward System
Apr 27, 2024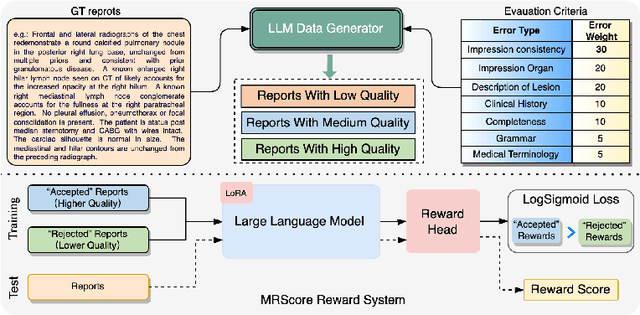
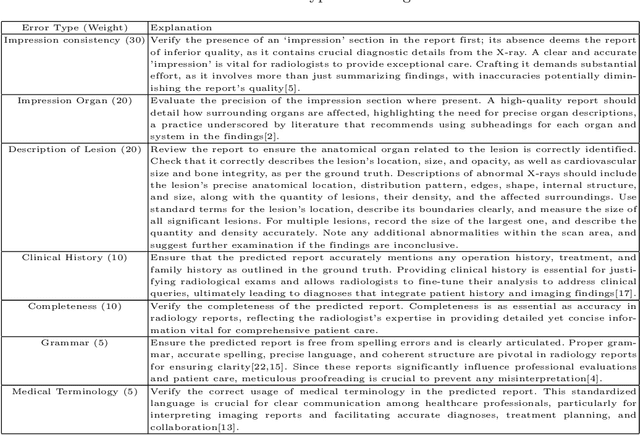
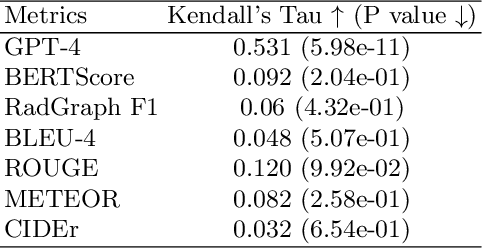
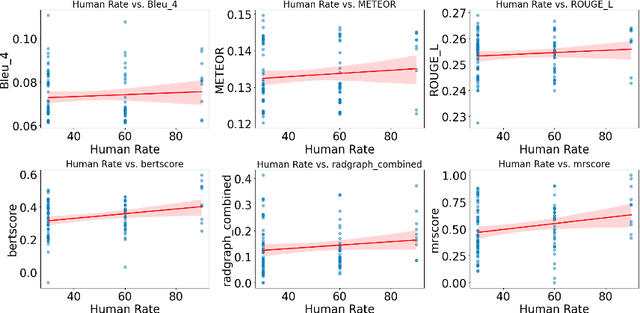
Abstract:In recent years, automated radiology report generation has experienced significant growth. This paper introduces MRScore, an automatic evaluation metric tailored for radiology report generation by leveraging Large Language Models (LLMs). Conventional NLG (natural language generation) metrics like BLEU are inadequate for accurately assessing the generated radiology reports, as systematically demonstrated by our observations within this paper. To address this challenge, we collaborated with radiologists to develop a framework that guides LLMs for radiology report evaluation, ensuring alignment with human analysis. Our framework includes two key components: i) utilizing GPT to generate large amounts of training data, i.e., reports with different qualities, and ii) pairing GPT-generated reports as accepted and rejected samples and training LLMs to produce MRScore as the model reward. Our experiments demonstrate MRScore's higher correlation with human judgments and superior performance in model selection compared to traditional metrics. Our code and datasets will be available on GitHub.
A Comprehensive Study of GPT-4V's Multimodal Capabilities in Medical Imaging
Nov 06, 2023Abstract:This paper presents a comprehensive evaluation of GPT-4V's capabilities across diverse medical imaging tasks, including Radiology Report Generation, Medical Visual Question Answering (VQA), and Visual Grounding. While prior efforts have explored GPT-4V's performance in medical image analysis, to the best of our knowledge, our study represents the first quantitative evaluation on publicly available benchmarks. Our findings highlight GPT-4V's potential in generating descriptive reports for chest X-ray images, particularly when guided by well-structured prompts. Meanwhile, its performance on the MIMIC-CXR dataset benchmark reveals areas for improvement in certain evaluation metrics, such as CIDEr. In the domain of Medical VQA, GPT-4V demonstrates proficiency in distinguishing between question types but falls short of the VQA-RAD benchmark in terms of accuracy. Furthermore, our analysis finds the limitations of conventional evaluation metrics like the BLEU scores, advocating for the development of more semantically robust assessment methods. In the field of Visual Grounding, GPT-4V exhibits preliminary promise in recognizing bounding boxes, but its precision is lacking, especially in identifying specific medical organs and signs. Our evaluation underscores the significant potential of GPT-4V in the medical imaging domain, while also emphasizing the need for targeted refinements to fully unlock its capabilities.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge