Xinya Shu
A Simple Aerial Detection Baseline of Multimodal Language Models
Jan 16, 2025



Abstract:The multimodal language models (MLMs) based on generative pre-trained Transformer are considered powerful candidates for unifying various domains and tasks. MLMs developed for remote sensing (RS) have demonstrated outstanding performance in multiple tasks, such as visual question answering and visual grounding. In addition to visual grounding that detects specific objects corresponded to given instruction, aerial detection, which detects all objects of multiple categories, is also a valuable and challenging task for RS foundation models. However, aerial detection has not been explored by existing RS MLMs because the autoregressive prediction mechanism of MLMs differs significantly from the detection outputs. In this paper, we present a simple baseline for applying MLMs to aerial detection for the first time, named LMMRotate. Specifically, we first introduce a normalization method to transform detection outputs into textual outputs to be compatible with the MLM framework. Then, we propose a evaluation method, which ensures a fair comparison between MLMs and conventional object detection models. We construct the baseline by fine-tuning open-source general-purpose MLMs and achieve impressive detection performance comparable to conventional detector. We hope that this baseline will serve as a reference for future MLM development, enabling more comprehensive capabilities for understanding RS images. Code is available at https://github.com/Li-Qingyun/mllm-mmrotate.
Reblurring-Guided Single Image Defocus Deblurring: A Learning Framework with Misaligned Training Pairs
Sep 26, 2024
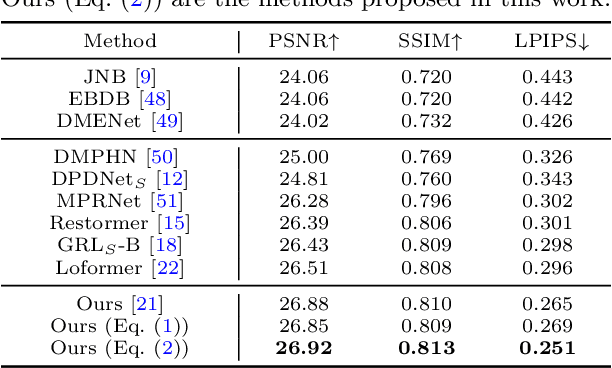
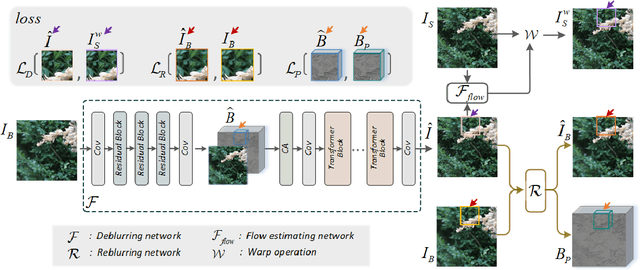
Abstract:For single image defocus deblurring, acquiring well-aligned training pairs (or training triplets), i.e., a defocus blurry image, an all-in-focus sharp image (and a defocus blur map), is an intricate task for the development of deblurring models. Existing image defocus deblurring methods typically rely on training data collected by specialized imaging equipment, presupposing that these pairs or triplets are perfectly aligned. However, in practical scenarios involving the collection of real-world data, direct acquisition of training triplets is infeasible, and training pairs inevitably encounter spatial misalignment issues. In this work, we introduce a reblurring-guided learning framework for single image defocus deblurring, enabling the learning of a deblurring network even with misaligned training pairs. Specifically, we first propose a baseline defocus deblurring network that utilizes spatially varying defocus blur map as degradation prior to enhance the deblurring performance. Then, to effectively learn the baseline defocus deblurring network with misaligned training pairs, our reblurring module ensures spatial consistency between the deblurred image, the reblurred image and the input blurry image by reconstructing spatially variant isotropic blur kernels. Moreover, the spatially variant blur derived from the reblurring module can serve as pseudo supervision for defocus blur map during training, interestingly transforming training pairs into training triplets. Additionally, we have collected a new dataset specifically for single image defocus deblurring (SDD) with typical misalignments, which not only substantiates our proposed method but also serves as a benchmark for future research.
Learning Single Image Defocus Deblurring with Misaligned Training Pairs
Nov 29, 2022



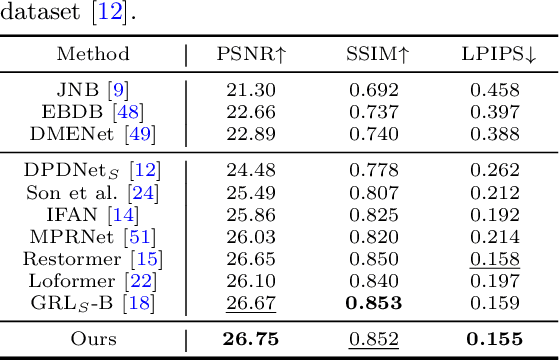
Abstract:By adopting popular pixel-wise loss, existing methods for defocus deblurring heavily rely on well aligned training image pairs. Although training pairs of ground-truth and blurry images are carefully collected, e.g., DPDD dataset, misalignment is inevitable between training pairs, making existing methods possibly suffer from deformation artifacts. In this paper, we propose a joint deblurring and reblurring learning (JDRL) framework for single image defocus deblurring with misaligned training pairs. Generally, JDRL consists of a deblurring module and a spatially invariant reblurring module, by which deblurred result can be adaptively supervised by ground-truth image to recover sharp textures while maintaining spatial consistency with the blurry image. First, in the deblurring module, a bi-directional optical flow-based deformation is introduced to tolerate spatial misalignment between deblurred and ground-truth images. Second, in the reblurring module, deblurred result is reblurred to be spatially aligned with blurry image, by predicting a set of isotropic blur kernels and weighting maps. Moreover, we establish a new single image defocus deblurring (SDD) dataset, further validating our JDRL and also benefiting future research. Our JDRL can be applied to boost defocus deblurring networks in terms of both quantitative metrics and visual quality on DPDD, RealDOF and our SDD datasets.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge