Xiaoxue Yu
Communications-Incentivized Collaborative Reasoning in NetGPT through Agentic Reinforcement Learning
Jan 31, 2026Abstract:The evolution of next-Generation (xG) wireless networks marks a paradigm shift from connectivity-centric architectures to Artificial Intelligence (AI)-native designs that tightly integrate data, computing, and communication. Yet existing AI deployments in communication systems remain largely siloed, offering isolated optimizations without intrinsic adaptability, dynamic task delegation, or multi-agent collaboration. In this work, we propose a unified agentic NetGPT framework for AI-native xG networks, wherein a NetGPT core can either perform autonomous reasoning or delegate sub-tasks to domain-specialized agents via agentic communication. The framework establishes clear modular responsibilities and interoperable workflows, enabling scalable, distributed intelligence across the network. To support continual refinement of collaborative reasoning strategies, the framework is further enhanced through Agentic reinforcement learning under partially observable conditions and stochastic external states. The training pipeline incorporates masked loss against external agent uncertainty, entropy-guided exploration, and multi-objective rewards that jointly capture task quality, coordination efficiency, and resource constraints. Through this process, NetGPT learns when and how to collaborate, effectively balancing internal reasoning with agent invocation. Overall, this work provides a foundational architecture and training methodology for self-evolving, AI-native xG networks capable of autonomous sensing, reasoning, and action in complex communication environments.
AirLLM: Diffusion Policy-based Adaptive LoRA for Remote Fine-Tuning of LLM over the Air
Jul 15, 2025Abstract:Operating Large Language Models (LLMs) on edge devices is increasingly challenged by limited communication bandwidth and strained computational and memory costs. Thus, cloud-assisted remote fine-tuning becomes indispensable. Nevertheless, existing Low-Rank Adaptation (LoRA) approaches typically employ fixed or heuristic rank configurations, and the subsequent over-the-air transmission of all LoRA parameters could be rather inefficient. To address this limitation, we develop AirLLM, a hierarchical diffusion policy framework for communication-aware LoRA adaptation. Specifically, AirLLM models the rank configuration as a structured action vector that spans all LoRA-inserted projections. To solve the underlying high-dimensional sequential decision-making problem, a Proximal Policy Optimization (PPO) agent generates coarse-grained decisions by jointly observing wireless states and linguistic complexity, which are then refined via Denoising Diffusion Implicit Models (DDIM) to produce high-resolution, task- and channel-adaptive rank vectors. The two modules are optimized alternatively, with the DDIM trained under the Classifier-Free Guidance (CFG) paradigm to maintain alignment with PPO rewards. Experiments under varying signal-to-noise ratios demonstrate that AirLLM consistently enhances fine-tuning performance while significantly reducing transmission costs, highlighting the effectiveness of reinforcement-driven, diffusion-refined rank adaptation for scalable and efficient remote fine-tuning over the air.
Large-Scale AI in Telecom: Charting the Roadmap for Innovation, Scalability, and Enhanced Digital Experiences
Mar 06, 2025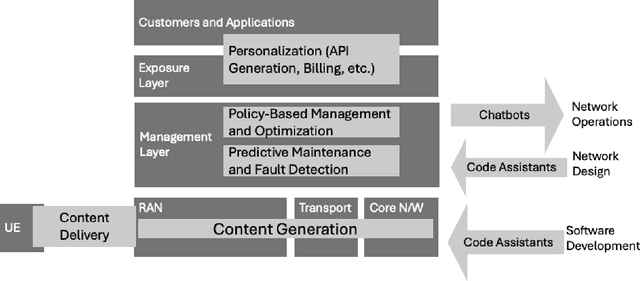
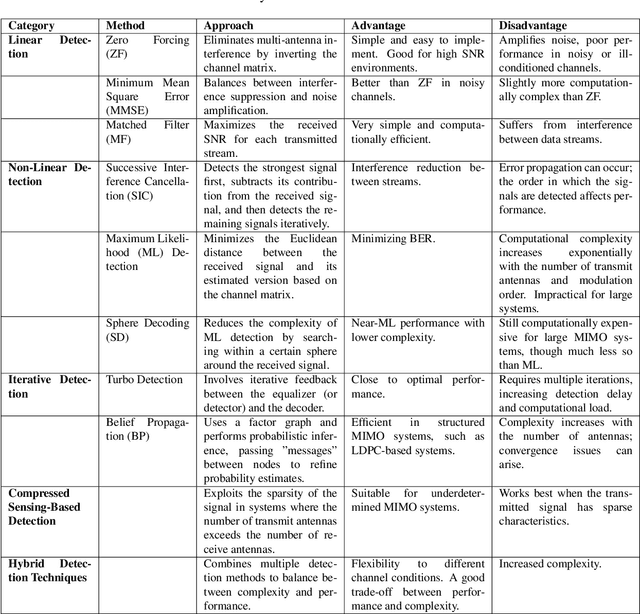
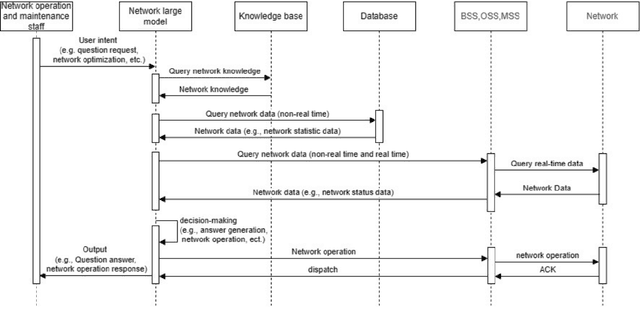
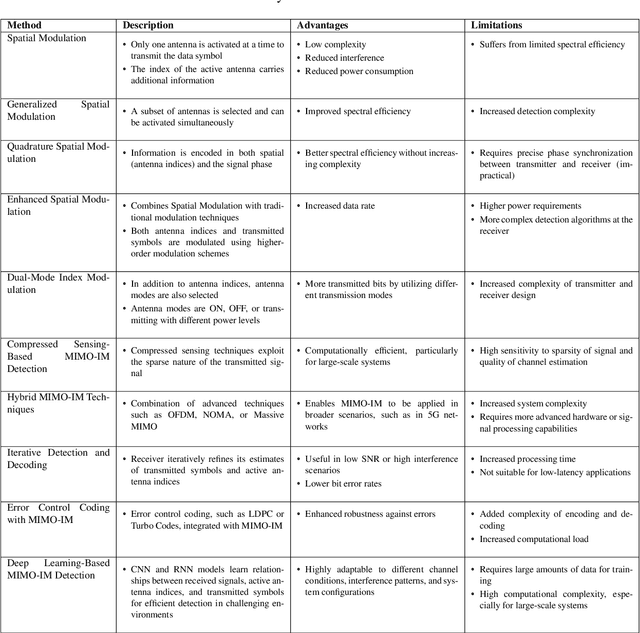
Abstract:This white paper discusses the role of large-scale AI in the telecommunications industry, with a specific focus on the potential of generative AI to revolutionize network functions and user experiences, especially in the context of 6G systems. It highlights the development and deployment of Large Telecom Models (LTMs), which are tailored AI models designed to address the complex challenges faced by modern telecom networks. The paper covers a wide range of topics, from the architecture and deployment strategies of LTMs to their applications in network management, resource allocation, and optimization. It also explores the regulatory, ethical, and standardization considerations for LTMs, offering insights into their future integration into telecom infrastructure. The goal is to provide a comprehensive roadmap for the adoption of LTMs to enhance scalability, performance, and user-centric innovation in telecom networks.
Adaptive Layer Splitting for Wireless LLM Inference in Edge Computing: A Model-Based Reinforcement Learning Approach
Jun 06, 2024



Abstract:Optimizing the deployment of large language models (LLMs) in edge computing environments is critical for enhancing privacy and computational efficiency. Toward efficient wireless LLM inference in edge computing, this study comprehensively analyzes the impact of different splitting points in mainstream open-source LLMs. On this basis, this study introduces a framework taking inspiration from model-based reinforcement learning (MBRL) to determine the optimal splitting point across the edge and user equipment (UE). By incorporating a reward surrogate model, our approach significantly reduces the computational cost of frequent performance evaluations. Extensive simulations demonstrate that this method effectively balances inference performance and computational load under varying network conditions, providing a robust solution for LLM deployment in decentralized settings.
Snake Learning: A Communication- and Computation-Efficient Distributed Learning Framework for 6G
May 06, 2024



Abstract:In the evolution towards 6G, integrating Artificial Intelligence (AI) with advanced network infrastructure emerges as a pivotal strategy for enhancing network intelligence and resource utilization. Existing distributed learning frameworks like Federated Learning and Split Learning often struggle with significant challenges in dynamic network environments including high synchronization demands, costly communication overheads, severe computing resource consumption, and data heterogeneity across network nodes. These obstacles hinder the applications of ubiquitous computing capabilities of 6G networks, especially in light of the trend of escalating model parameters and training data volumes. To address these challenges effectively, this paper introduces "Snake Learning", a cost-effective distributed learning framework. Specifically, Snake Learning respects the heterogeneity of inter-node computing capability and local data distribution in 6G networks, and sequentially trains the designated part of model layers on individual nodes. This layer-by-layer serpentine update mechanism contributes to significantly reducing the requirements for storage, memory and communication during the model training phase, and demonstrates superior adaptability and efficiency for both Computer Vision (CV) training and Large Language Model (LLM) fine-tuning tasks across homogeneous and heterogeneous data distributions.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge