Xiaolong Han
Molecular Representations in Implicit Functional Space via Hyper-Networks
Jan 29, 2026Abstract:Molecular representations fundamentally shape how machine learning systems reason about molecular structure and physical properties. Most existing approaches adopt a discrete pipeline: molecules are encoded as sequences, graphs, or point clouds, mapped to fixed-dimensional embeddings, and then used for task-specific prediction. This paradigm treats molecules as discrete objects, despite their intrinsically continuous and field-like physical nature. We argue that molecular learning can instead be formulated as learning in function space. Specifically, we model each molecule as a continuous function over three-dimensional (3D) space and treat this molecular field as the primary object of representation. From this perspective, conventional molecular representations arise as particular sampling schemes of an underlying continuous object. We instantiate this formulation with MolField, a hyper-network-based framework that learns distributions over molecular fields. To ensure physical consistency, these functions are defined over canonicalized coordinates, yielding invariance to global SE(3) transformations. To enable learning directly over functions, we introduce a structured weight tokenization and train a sequence-based hyper-network to model a shared prior over molecular fields. We evaluate MolField on molecular dynamics and property prediction. Our results show that treating molecules as continuous functions fundamentally changes how molecular representations generalize across tasks and yields downstream behavior that is stable to how molecules are discretized or queried.
Heterogeneous Graph Contrastive Multi-view Learning
Oct 01, 2022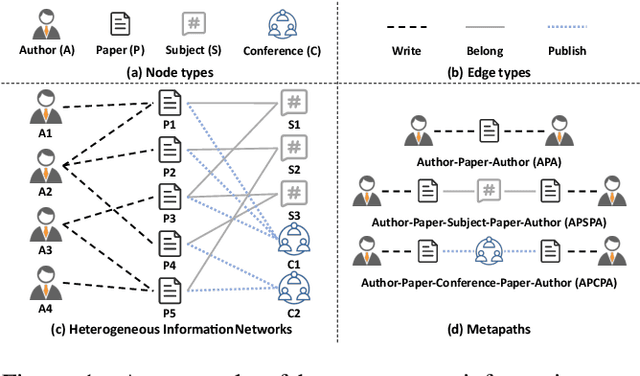

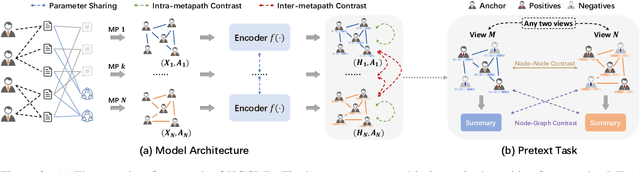

Abstract:Inspired by the success of contrastive learning (CL) in computer vision and natural language processing, graph contrastive learning (GCL) has been developed to learn discriminative node representations on graph datasets. However, the development of GCL on Heterogeneous Information Networks (HINs) is still in the infant stage. For example, it is unclear how to augment the HINs without substantially altering the underlying semantics, and how to design the contrastive objective to fully capture the rich semantics. Moreover, early investigations demonstrate that CL suffers from sampling bias, whereas conventional debiasing techniques are empirically shown to be inadequate for GCL. How to mitigate the sampling bias for heterogeneous GCL is another important problem. To address the aforementioned challenges, we propose a novel Heterogeneous Graph Contrastive Multi-view Learning (HGCML) model. In particular, we use metapaths as the augmentation to generate multiple subgraphs as multi-views, and propose a contrastive objective to maximize the mutual information between any pairs of metapath-induced views. To alleviate the sampling bias, we further propose a positive sampling strategy to explicitly select positives for each node via jointly considering semantic and structural information preserved on each metapath view. Extensive experiments demonstrate HGCML consistently outperforms state-of-the-art baselines on five real-world benchmark datasets.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge