Xiangyang Zhang
School of Automation, Harbin University of Science and Technology, Harbin, 150080, China
Deep Learning Predicts Biomarker Status and Discovers Related Histomorphology Characteristics for Low-Grade Glioma
Oct 11, 2023



Abstract:Biomarker detection is an indispensable part in the diagnosis and treatment of low-grade glioma (LGG). However, current LGG biomarker detection methods rely on expensive and complex molecular genetic testing, for which professionals are required to analyze the results, and intra-rater variability is often reported. To overcome these challenges, we propose an interpretable deep learning pipeline, a Multi-Biomarker Histomorphology Discoverer (Multi-Beholder) model based on the multiple instance learning (MIL) framework, to predict the status of five biomarkers in LGG using only hematoxylin and eosin-stained whole slide images and slide-level biomarker status labels. Specifically, by incorporating the one-class classification into the MIL framework, accurate instance pseudo-labeling is realized for instance-level supervision, which greatly complements the slide-level labels and improves the biomarker prediction performance. Multi-Beholder demonstrates superior prediction performance and generalizability for five LGG biomarkers (AUROC=0.6469-0.9735) in two cohorts (n=607) with diverse races and scanning protocols. Moreover, the excellent interpretability of Multi-Beholder allows for discovering the quantitative and qualitative correlations between biomarker status and histomorphology characteristics. Our pipeline not only provides a novel approach for biomarker prediction, enhancing the applicability of molecular treatments for LGG patients but also facilitates the discovery of new mechanisms in molecular functionality and LGG progression.
EAR-U-Net: EfficientNet and attention-based residual U-Net for automatic liver segmentation in CT
Oct 03, 2021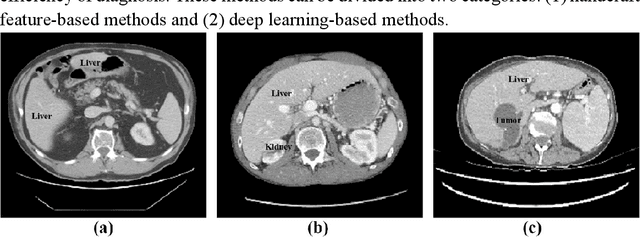
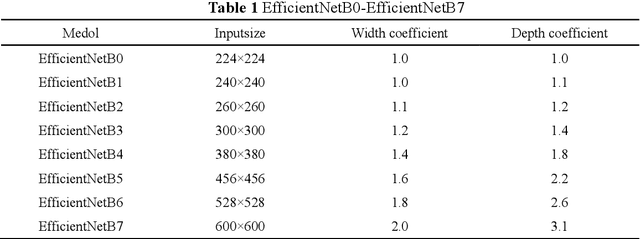
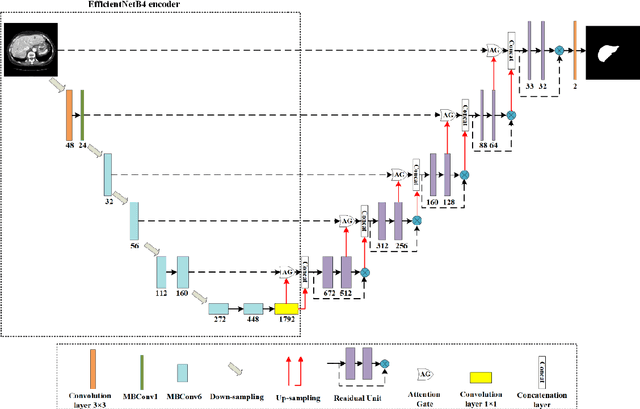
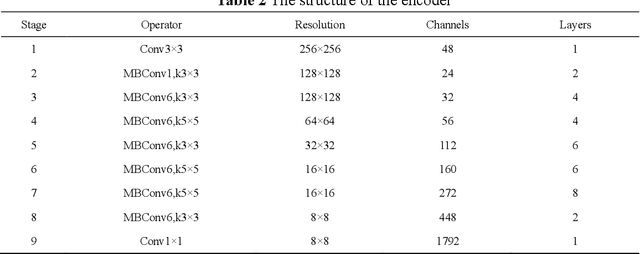
Abstract:Purpose: This paper proposes a new network framework called EAR-U-Net, which leverages EfficientNetB4, attention gate, and residual learning techniques to achieve automatic and accurate liver segmentation. Methods: The proposed method is based on the U-Net framework. First, we use EfficientNetB4 as the encoder to extract more feature information during the encoding stage. Then, an attention gate is introduced in the skip connection to eliminate irrelevant regions and highlight features of a specific segmentation task. Finally, to alleviate the problem of gradient vanishment, we replace the traditional convolution of the decoder with a residual block to improve the segmentation accuracy. Results: We verified the proposed method on the LiTS17 and SLiver07 datasets and compared it with classical networks such as FCN, U-Net, Attention U-Net, and Attention Res-U-Net. In the Sliver07 evaluation, the proposed method achieved the best segmentation performance on all five standard metrics. Meanwhile, in the LiTS17 assessment, the best performance is obtained except for a slight inferior on RVD. Moreover, we also participated in the MICCIA-LiTS17 challenge, and the Dice per case score was 0.952. Conclusion: The proposed method's qualitative and quantitative results demonstrated its applicability in liver segmentation and proved its good prospect in computer-assisted liver segmentation.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge