Xiandong Zou
Variational Speculative Decoding: Rethinking Draft Training from Token Likelihood to Sequence Acceptance
Feb 05, 2026Abstract:Speculative decoding accelerates inference for (M)LLMs, yet a training-decoding discrepancy persists: while existing methods optimize single greedy trajectories, decoding involves verifying and ranking multiple sampled draft paths. We propose Variational Speculative Decoding (VSD), formulating draft training as variational inference over latent proposals (draft paths). VSD maximizes the marginal probability of target-model acceptance, yielding an ELBO that promotes high-quality latent proposals while minimizing divergence from the target distribution. To enhance quality and reduce variance, we incorporate a path-level utility and optimize via an Expectation-Maximization procedure. The E-step draws MCMC samples from an oracle-filtered posterior, while the M-step maximizes weighted likelihood using Adaptive Rejection Weighting (ARW) and Confidence-Aware Regularization (CAR). Theoretical analysis confirms that VSD increases expected acceptance length and speedup. Extensive experiments across LLMs and MLLMs show that VSD achieves up to a 9.6% speedup over EAGLE-3 and 7.9% over ViSpec, significantly improving decoding efficiency.
DreamCS: Geometry-Aware Text-to-3D Generation with Unpaired 3D Reward Supervision
Jun 11, 2025Abstract:While text-to-3D generation has attracted growing interest, existing methods often struggle to produce 3D assets that align well with human preferences. Current preference alignment techniques for 3D content typically rely on hardly-collected preference-paired multi-view 2D images to train 2D reward models, when then guide 3D generation -- leading to geometric artifacts due to their inherent 2D bias. To address these limitations, we construct 3D-MeshPref, the first large-scale unpaired 3D preference dataset, featuring diverse 3D meshes annotated by a large language model and refined by human evaluators. We then develop RewardCS, the first reward model trained directly on unpaired 3D-MeshPref data using a novel Cauchy-Schwarz divergence objective, enabling effective learning of human-aligned 3D geometric preferences without requiring paired comparisons. Building on this, we propose DreamCS, a unified framework that integrates RewardCS into text-to-3D pipelines -- enhancing both implicit and explicit 3D generation with human preference feedback. Extensive experiments show DreamCS outperforms prior methods, producing 3D assets that are both geometrically faithful and human-preferred. Code and models will be released publicly.
HPS: Hard Preference Sampling for Human Preference Alignment
Feb 20, 2025Abstract:Aligning Large Language Model (LLM) responses with human preferences is vital for building safe and controllable AI systems. While preference optimization methods based on Plackett-Luce (PL) and Bradley-Terry (BT) models have shown promise, they face challenges such as poor handling of harmful content, inefficient use of dispreferred responses, and, specifically for PL, high computational costs. To address these issues, we propose Hard Preference Sampling (HPS), a novel framework for robust and efficient human preference alignment. HPS introduces a training loss that prioritizes the most preferred response while rejecting all dispreferred and harmful ones. It emphasizes "hard" dispreferred responses--those closely resembling preferred ones--to enhance the model's rejection capabilities. By leveraging a single-sample Monte Carlo sampling strategy, HPS reduces computational overhead while maintaining alignment quality. Theoretically, HPS improves sample efficiency over existing PL methods and maximizes the reward margin between preferred and dispreferred responses, ensuring clearer distinctions. Experiments on HH-RLHF and PKU-Safety datasets validate HPS's effectiveness, achieving comparable BLEU and reward scores while greatly improving reward margins and thus reducing harmful content generation.
Cached Multi-Lora Composition for Multi-Concept Image Generation
Feb 07, 2025Abstract:Low-Rank Adaptation (LoRA) has emerged as a widely adopted technique in text-to-image models, enabling precise rendering of multiple distinct elements, such as characters and styles, in multi-concept image generation. However, current approaches face significant challenges when composing these LoRAs for multi-concept image generation, resulting in diminished generated image quality. In this paper, we initially investigate the role of LoRAs in the denoising process through the lens of the Fourier frequency domain. Based on the hypothesis that applying multiple LoRAs could lead to "semantic conflicts", we find that certain LoRAs amplify high-frequency features such as edges and textures, whereas others mainly focus on low-frequency elements, including the overall structure and smooth color gradients. Building on these insights, we devise a frequency domain based sequencing strategy to determine the optimal order in which LoRAs should be integrated during inference. This strategy offers a methodical and generalizable solution compared to the naive integration commonly found in existing LoRA fusion techniques. To fully leverage our proposed LoRA order sequence determination method in multi-LoRA composition tasks, we introduce a novel, training-free framework, Cached Multi-LoRA (CMLoRA), designed to efficiently integrate multiple LoRAs while maintaining cohesive image generation. With its flexible backbone for multi-LoRA fusion and a non-uniform caching strategy tailored to individual LoRAs, CMLoRA has the potential to reduce semantic conflicts in LoRA composition and improve computational efficiency. Our experimental evaluations demonstrate that CMLoRA outperforms state-of-the-art training-free LoRA fusion methods by a significant margin -- it achieves an average improvement of $2.19\%$ in CLIPScore, and $11.25\%$ in MLLM win rate compared to LoraHub, LoRA Composite, and LoRA Switch.
Will More Expressive Graph Neural Networks do Better on Generative Tasks?
Aug 23, 2023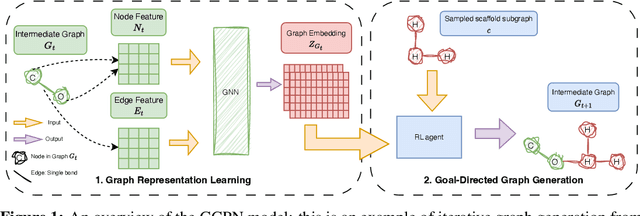
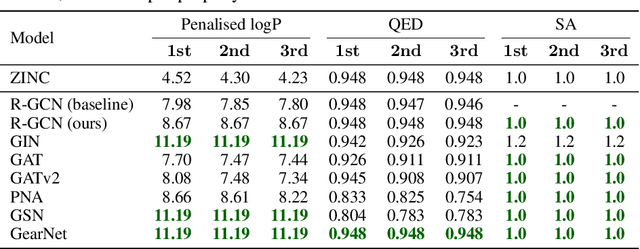
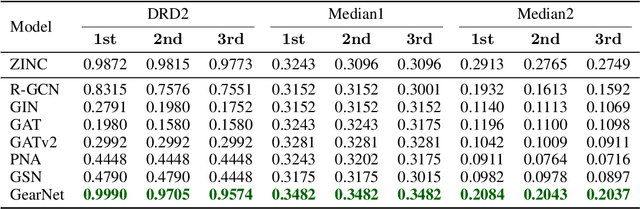
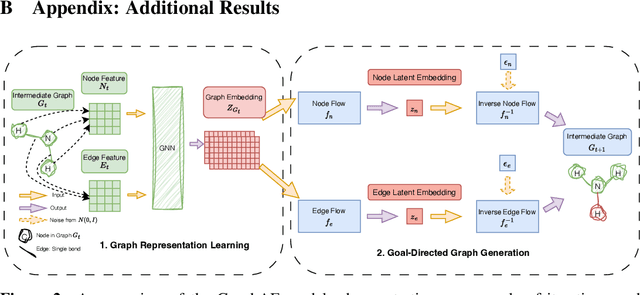
Abstract:Graph generation poses a significant challenge as it involves predicting a complete graph with multiple nodes and edges based on simply a given label. This task also carries fundamental importance to numerous real-world applications, including de-novo drug and molecular design. In recent years, several successful methods have emerged in the field of graph generation. However, these approaches suffer from two significant shortcomings: (1) the underlying Graph Neural Network (GNN) architectures used in these methods are often underexplored; and (2) these methods are often evaluated on only a limited number of metrics. To fill this gap, we investigate the expressiveness of GNNs under the context of the molecular graph generation task, by replacing the underlying GNNs of graph generative models with more expressive GNNs. Specifically, we analyse the performance of six GNNs in two different generative frameworks (GCPN and GraphAF), on six different molecular generative objectives on the ZINC-250k dataset. Through our extensive experiments, we demonstrate that advanced GNNs can indeed improve the performance of GCPN and GraphAF on molecular generation tasks, but GNN expressiveness is not a necessary condition for a good GNN-based generative model. Moreover, we show that GCPN and GraphAF with advanced GNNs can achieve state-of-the-art results across 17 other non-GNN-based graph generative approaches, such as variational autoencoders and Bayesian optimisation models, on the proposed molecular generative objectives (DRD2, Median1, Median2), which are important metrics for de-novo molecular design.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge