Wuxia Jin
On the Opportunities of Green Computing: A Survey
Nov 09, 2023



Abstract:Artificial Intelligence (AI) has achieved significant advancements in technology and research with the development over several decades, and is widely used in many areas including computing vision, natural language processing, time-series analysis, speech synthesis, etc. During the age of deep learning, especially with the arise of Large Language Models, a large majority of researchers' attention is paid on pursuing new state-of-the-art (SOTA) results, resulting in ever increasing of model size and computational complexity. The needs for high computing power brings higher carbon emission and undermines research fairness by preventing small or medium-sized research institutions and companies with limited funding in participating in research. To tackle the challenges of computing resources and environmental impact of AI, Green Computing has become a hot research topic. In this survey, we give a systematic overview of the technologies used in Green Computing. We propose the framework of Green Computing and devide it into four key components: (1) Measures of Greenness, (2) Energy-Efficient AI, (3) Energy-Efficient Computing Systems and (4) AI Use Cases for Sustainability. For each components, we discuss the research progress made and the commonly used techniques to optimize the AI efficiency. We conclude that this new research direction has the potential to address the conflicts between resource constraints and AI development. We encourage more researchers to put attention on this direction and make AI more environmental friendly.
BDMMT: Backdoor Sample Detection for Language Models through Model Mutation Testing
Jan 25, 2023



Abstract:Deep neural networks (DNNs) and natural language processing (NLP) systems have developed rapidly and have been widely used in various real-world fields. However, they have been shown to be vulnerable to backdoor attacks. Specifically, the adversary injects a backdoor into the model during the training phase, so that input samples with backdoor triggers are classified as the target class. Some attacks have achieved high attack success rates on the pre-trained language models (LMs), but there have yet to be effective defense methods. In this work, we propose a defense method based on deep model mutation testing. Our main justification is that backdoor samples are much more robust than clean samples if we impose random mutations on the LMs and that backdoors are generalizable. We first confirm the effectiveness of model mutation testing in detecting backdoor samples and select the most appropriate mutation operators. We then systematically defend against three extensively studied backdoor attack levels (i.e., char-level, word-level, and sentence-level) by detecting backdoor samples. We also make the first attempt to defend against the latest style-level backdoor attacks. We evaluate our approach on three benchmark datasets (i.e., IMDB, Yelp, and AG news) and three style transfer datasets (i.e., SST-2, Hate-speech, and AG news). The extensive experimental results demonstrate that our approach can detect backdoor samples more efficiently and accurately than the three state-of-the-art defense approaches.
Explanation-Guided Fairness Testing through Genetic Algorithm
May 16, 2022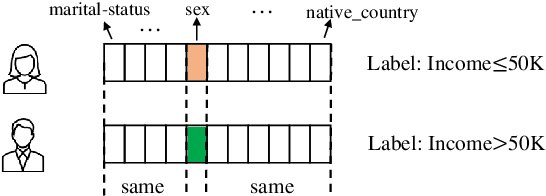
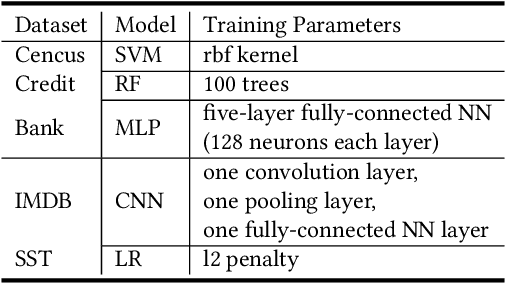
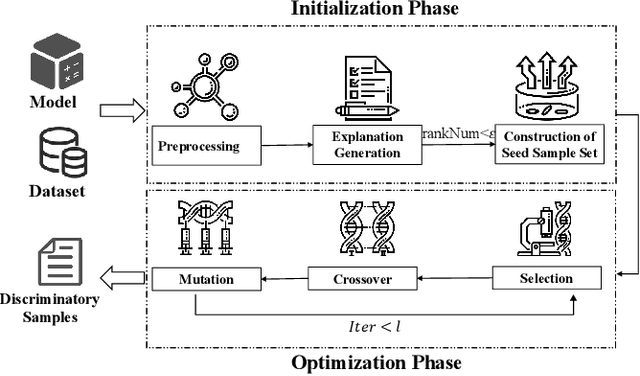
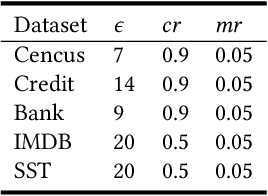
Abstract:The fairness characteristic is a critical attribute of trusted AI systems. A plethora of research has proposed diverse methods for individual fairness testing. However, they are suffering from three major limitations, i.e., low efficiency, low effectiveness, and model-specificity. This work proposes ExpGA, an explanationguided fairness testing approach through a genetic algorithm (GA). ExpGA employs the explanation results generated by interpretable methods to collect high-quality initial seeds, which are prone to derive discriminatory samples by slightly modifying feature values. ExpGA then adopts GA to search discriminatory sample candidates by optimizing a fitness value. Benefiting from this combination of explanation results and GA, ExpGA is both efficient and effective to detect discriminatory individuals. Moreover, ExpGA only requires prediction probabilities of the tested model, resulting in a better generalization capability to various models. Experiments on multiple real-world benchmarks, including tabular and text datasets, show that ExpGA presents higher efficiency and effectiveness than four state-of-the-art approaches.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge