William Bankes
Detecting High-Stakes Interactions with Activation Probes
Jun 12, 2025Abstract:Monitoring is an important aspect of safely deploying Large Language Models (LLMs). This paper examines activation probes for detecting "high-stakes" interactions -- where the text indicates that the interaction might lead to significant harm -- as a critical, yet underexplored, target for such monitoring. We evaluate several probe architectures trained on synthetic data, and find them to exhibit robust generalization to diverse, out-of-distribution, real-world data. Probes' performance is comparable to that of prompted or finetuned medium-sized LLM monitors, while offering computational savings of six orders-of-magnitude. Our experiments also highlight the potential of building resource-aware hierarchical monitoring systems, where probes serve as an efficient initial filter and flag cases for more expensive downstream analysis. We release our novel synthetic dataset and codebase to encourage further study.
Robust Multi-Objective Controlled Decoding of Large Language Models
Mar 11, 2025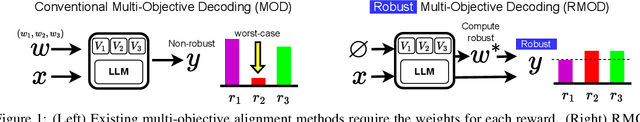
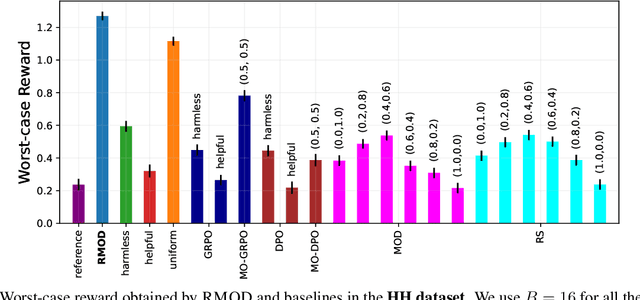
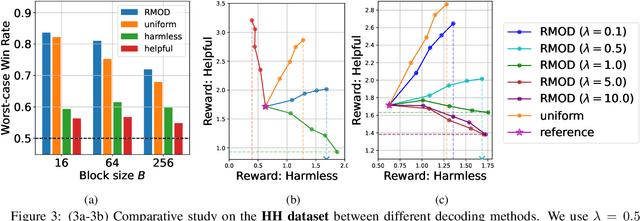
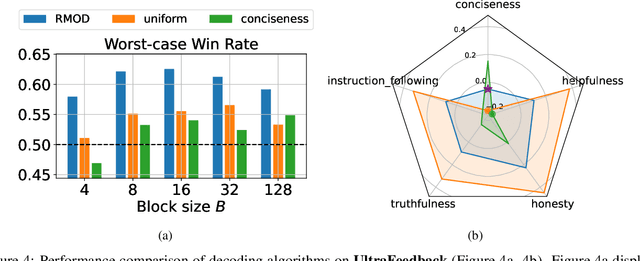
Abstract:Test-time alignment of Large Language Models (LLMs) to human preferences offers a flexible way to generate responses aligned to diverse objectives without extensive retraining of LLMs. Existing methods achieve alignment to multiple objectives simultaneously (e.g., instruction-following, helpfulness, conciseness) by optimizing their corresponding reward functions. However, they often rely on predefined weights or optimize for averages, sacrificing one objective for another and leading to unbalanced outcomes. To address this, we introduce Robust Multi-Objective Decoding (RMOD), a novel inference-time algorithm that optimizes for improving worst-case rewards. RMOD formalizes the robust decoding problem as a maximin two-player game between reward weights and the sampling policy, solving for the Nash equilibrium. We show that the game reduces to a convex optimization problem to find the worst-case weights, while the best response policy can be computed analytically. We also introduce a practical RMOD variant designed for efficient decoding with contemporary LLMs, incurring minimal computational overhead compared to non-robust Multi-Objective Decoding (MOD) methods. Our experimental results showcase the effectiveness of RMOD in generating responses equitably aligned with diverse objectives, outperforming baselines up to 20%.
Right Now, Wrong Then: Non-Stationary Direct Preference Optimization under Preference Drift
Jul 26, 2024



Abstract:Reinforcement learning from human feedback (RLHF) aligns Large Language Models (LLMs) with human preferences. However, these preferences can often change over time due to external factors (e.g. environment change and societal influence). Consequently, what was wrong then might be right now. Current preference optimization algorithms do not account for temporal preference drift in their modeling, which can lead to severe misalignment. To address this limitation, we use a Dynamic Bradley-Terry model that models preferences via time-dependent reward functions, and propose Non-Stationary Direct Preference Optimisation (NS-DPO). By introducing a discount parameter in the loss function, NS-DPO applies exponential weighting, which proportionally focuses learning on more time-relevant datapoints. We theoretically analyse the convergence of NS-DPO in the offline setting, providing upper bounds on the estimation error caused by non-stationary preferences. Finally, we demonstrate the effectiveness of NS-DPO1 for fine-tuning LLMs in scenarios with drifting preferences. By simulating preference drift using renowned reward models and modifying popular LLM datasets accordingly, we show that NS-DPO fine-tuned LLMs remain robust under non-stationarity, significantly outperforming baseline algorithms that ignore temporal preference changes, without sacrificing performance in stationary cases.
REDUCR: Robust Data Downsampling Using Class Priority Reweighting
Dec 01, 2023Abstract:Modern machine learning models are becoming increasingly expensive to train for real-world image and text classification tasks, where massive web-scale data is collected in a streaming fashion. To reduce the training cost, online batch selection techniques have been developed to choose the most informative datapoints. However, these techniques can suffer from poor worst-class generalization performance due to class imbalance and distributional shifts. This work introduces REDUCR, a robust and efficient data downsampling method that uses class priority reweighting. REDUCR reduces the training data while preserving worst-class generalization performance. REDUCR assigns priority weights to datapoints in a class-aware manner using an online learning algorithm. We demonstrate the data efficiency and robust performance of REDUCR on vision and text classification tasks. On web-scraped datasets with imbalanced class distributions, REDUCR significantly improves worst-class test accuracy (and average accuracy), surpassing state-of-the-art methods by around 15%.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge