Wenyuan Liu
ARCQuant: Boosting NVFP4 Quantization with Augmented Residual Channels for LLMs
Jan 12, 2026Abstract:The emergence of fine-grained numerical formats like NVFP4 presents new opportunities for efficient Large Language Model (LLM) inference. However, it is difficult to adapt existing Post-Training Quantization (PTQ) strategies to these formats: rotation-based methods compromise fine-grained block isolation; smoothing techniques struggle with significant 4-bit quantization errors; and mixed-precision approaches often conflict with hardware constraints on unified-precision computation. To address these challenges, we propose ARCQuant, a framework that boosts NVFP4 performance via Augmented Residual Channels. Distinct from methods that compromise block isolation or hardware uniformity, ARCQuant maintains a strictly unified NVFP4 format by augmenting the activation matrix with quantized residual channels. This design integrates the error compensation process directly into the matrix reduction dimension, enabling the use of standard, highly optimized GEMM kernels with minimal overhead. Theoretical analysis confirms that the worst-case error bound of our dual-stage NVFP4 quantization is comparable to that of standard 8-bit formats such as MXFP8. Extensive experiments on LLaMA and Qwen models demonstrate that ARCQuant achieves state-of-the-art accuracy, comparable to full-precision baselines in perplexity and downstream tasks. Furthermore, deployment on RTX 5090 and RTX PRO 6000 GPUs confirms practical benefits, achieving up to 3x speedup over FP16. Our code is available at https://github.com/actypedef/ARCQuant .
Post-Training Quantization of OpenPangu Models for Efficient Deployment on Atlas A2
Dec 29, 2025Abstract:Huawei's openPangu-Embedded-1B and openPangu-Embedded-7B, variants of the openPangu large language model, integrate three distinct Chain-of-Thought (CoT) reasoning paradigms, namely slow_think, auto_think, and no_think. While these CoT modes enhance reasoning capabilities, their generation of extended reasoning traces introduces substantial memory and latency overheads, posing challenges for practical deployment on Ascend NPUs. This paper addresses these computational constraints by leveraging low-bit quantization, which transforms FP16 computations into more efficient integer arithmetic. We introduce a unified low-bit inference framework, supporting INT8 (W8A8) and W4A8 quantization, specifically optimized for openPangu-Embedded models on the Atlas A2. Our comprehensive evaluation, conducted across all three CoT modes on code generation benchmarks (HumanEval and MBPP), demonstrates the efficacy of this approach. INT8 quantization consistently preserves over 90\% of the FP16 baseline accuracy and achieves a 1.5x prefill speedup on the Atlas A2. Furthermore, W4A8 quantization significantly reduces memory consumption, albeit with a moderate trade-off in accuracy. These findings collectively indicate that low-bit quantization effectively facilitates efficient CoT reasoning on Ascend NPUs, maintaining high model fidelity.
Routing Distilled Knowledge via Mixture of LoRA Experts for Large Language Model based Bundle Generation
Aug 24, 2025Abstract:Large Language Models (LLMs) have shown potential in automatic bundle generation but suffer from prohibitive computational costs. Although knowledge distillation offers a pathway to more efficient student models, our preliminary study reveals that naively integrating diverse types of distilled knowledge from teacher LLMs into student LLMs leads to knowledge conflict, negatively impacting the performance of bundle generation. To address this, we propose RouteDK, a framework for routing distilled knowledge through a mixture of LoRA expert architecture. Specifically, we first distill knowledge from the teacher LLM for bundle generation in two complementary types: high-level knowledge (generalizable rules) and fine-grained knowledge (session-specific reasoning). We then train knowledge-specific LoRA experts for each type of knowledge together with a base LoRA expert. For effective integration, we propose a dynamic fusion module, featuring an input-aware router, where the router balances expert contributions by dynamically determining optimal weights based on input, thereby effectively mitigating knowledge conflicts. To further improve inference reliability, we design an inference-time enhancement module to reduce variance and mitigate suboptimal reasoning. Experiments on three public datasets show that our RouteDK achieves accuracy comparable to or even better than the teacher LLM, while maintaining strong computational efficiency. In addition, it outperforms state-of-the-art approaches for bundle generation.
Does Knowledge Distillation Matter for Large Language Model based Bundle Generation?
Apr 24, 2025Abstract:LLMs are increasingly explored for bundle generation, thanks to their reasoning capabilities and knowledge. However, deploying large-scale LLMs introduces significant efficiency challenges, primarily high computational costs during fine-tuning and inference due to their massive parameterization. Knowledge distillation (KD) offers a promising solution, transferring expertise from large teacher models to compact student models. This study systematically investigates knowledge distillation approaches for bundle generation, aiming to minimize computational demands while preserving performance. We explore three critical research questions: (1) how does the format of KD impact bundle generation performance? (2) to what extent does the quantity of distilled knowledge influence performance? and (3) how do different ways of utilizing the distilled knowledge affect performance? We propose a comprehensive KD framework that (i) progressively extracts knowledge (patterns, rules, deep thoughts); (ii) captures varying quantities of distilled knowledge through different strategies; and (iii) exploits complementary LLM adaptation techniques (in-context learning, supervised fine-tuning, combination) to leverage distilled knowledge in small student models for domain-specific adaptation and enhanced efficiency. Extensive experiments provide valuable insights into how knowledge format, quantity, and utilization methodologies collectively shape LLM-based bundle generation performance, exhibiting KD's significant potential for more efficient yet effective LLM-based bundle generation.
CrossQuant: A Post-Training Quantization Method with Smaller Quantization Kernel for Precise Large Language Model Compression
Oct 10, 2024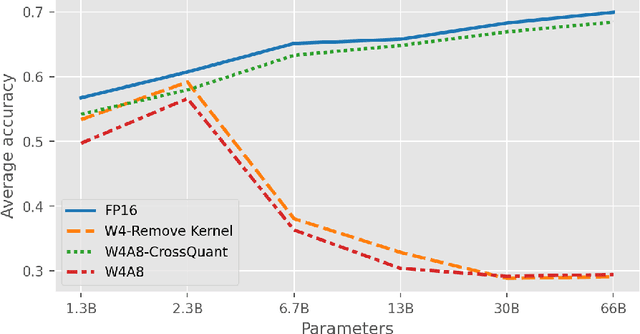

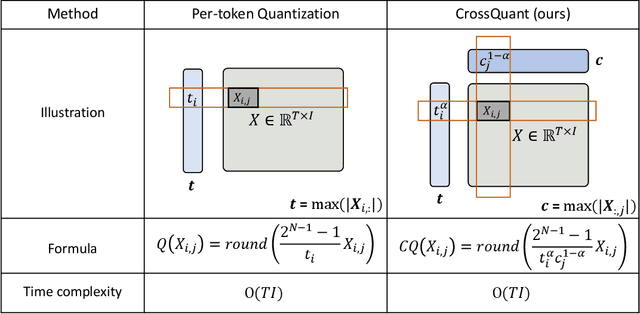

Abstract:Post-Training Quantization (PTQ) is an effective technique for compressing Large Language Models (LLMs). While many studies focus on quantizing both weights and activations, it is still a challenge to maintain the accuracy of LLM after activating quantization. To investigate the primary cause, we extend the concept of kernel from linear algebra to quantization functions to define a new term, "quantization kernel", which refers to the set of elements in activations that are quantized to zero. Through quantitative analysis of the quantization kernel, we find that these elements are crucial for maintaining the accuracy of quantized LLMs. With the decrease of quantization kernel, the precision of quantized LLMs increases. If the quantization kernel proportion is kept below 19% for OPT models and below 1% for LLaMA models, the precision loss from quantizing activations to INT8 becomes negligible. Motivated by the goal of developing a quantization method with small quantization kernel, we propose CrossQuant: a simple yet effective method for quantizing activations. CrossQuant cross-quantizes elements using row and column-wise absolute maximum vectors, achieving a quantization kernel of approximately 16% for OPT models and less than 0.1% for LLaMA models. Experimental results on LLMs (LLaMA, OPT) ranging from 6.7B to 70B parameters demonstrate that CrossQuant improves or maintains perplexity and accuracy in language modeling, zero-shot, and few-shot tasks.
3D-RPE: Enhancing Long-Context Modeling Through 3D Rotary Position Encoding
Jun 14, 2024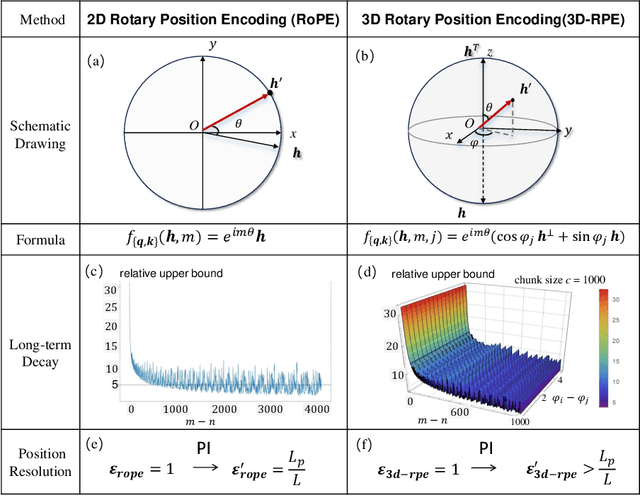
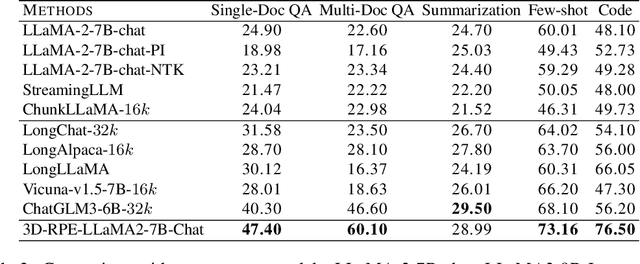
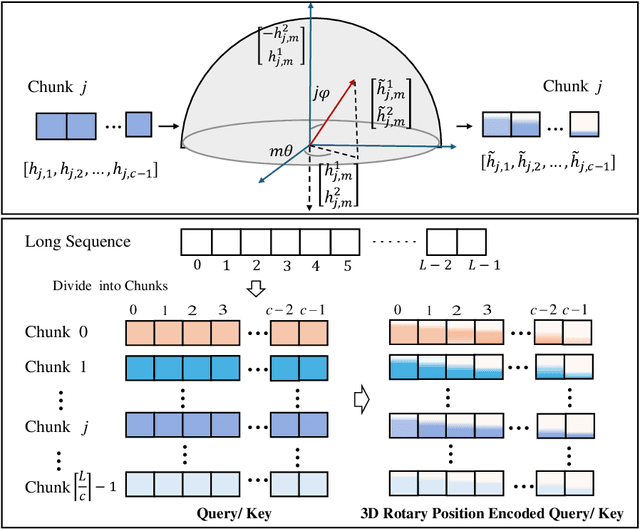
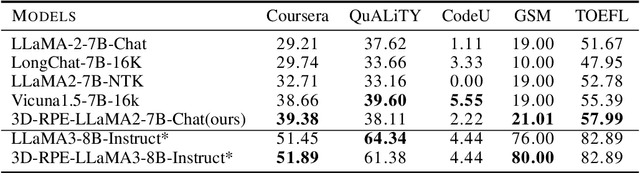
Abstract:Inspired by the Bloch Sphere representation, we propose a novel rotary position encoding on a three-dimensional sphere, named 3D Rotary Position Encoding (3D-RPE). 3D-RPE is an advanced version of the widely used 2D Rotary Position Encoding (RoPE), with two major advantages for modeling long contexts: controllable long-term decay and improved position resolution. For controllable long-term decay, 3D-RPE allows for the regulation of long-term decay within the chunk size, ensuring the modeling of relative positional information between tokens at a distant relative position. For enhanced position resolution, 3D-RPE can mitigate the degradation of position resolution caused by position interpolation on RoPE. We have conducted experiments on long-context Natural Language Understanding (NLU) and long-sequence Language Modeling (LM) tasks. From the experimental results, 3D-RPE achieved performance improvements over RoPE, especially in long-context NLU tasks.
Dynamic In-Context Learning from Nearest Neighbors for Bundle Generation
Dec 26, 2023Abstract:Product bundling has evolved into a crucial marketing strategy in e-commerce. However, current studies are limited to generating (1) fixed-size or single bundles, and most importantly, (2) bundles that do not reflect consistent user intents, thus being less intelligible or useful to users. This paper explores two interrelated tasks, i.e., personalized bundle generation and the underlying intent inference based on users' interactions in a session, leveraging the logical reasoning capability of large language models. We introduce a dynamic in-context learning paradigm, which enables ChatGPT to seek tailored and dynamic lessons from closely related sessions as demonstrations while performing tasks in the target session. Specifically, it first harnesses retrieval augmented generation to identify nearest neighbor sessions for each target session. Then, proper prompts are designed to guide ChatGPT to perform the two tasks on neighbor sessions. To enhance reliability and mitigate the hallucination issue, we develop (1) a self-correction strategy to foster mutual improvement in both tasks without supervision signals; and (2) an auto-feedback mechanism to recurrently offer dynamic supervision based on the distinct mistakes made by ChatGPT on various neighbor sessions. Thus, the target session can receive customized and dynamic lessons for improved performance by observing the demonstrations of its neighbor sessions. Finally, experimental results on three real-world datasets verify the effectiveness of our methods on both tasks. Additionally, the inferred intents can prove beneficial for other intriguing downstream tasks, such as crafting appealing bundle names.
Using Machine Learning to Predict the Evolution of Physics Research
Oct 29, 2018

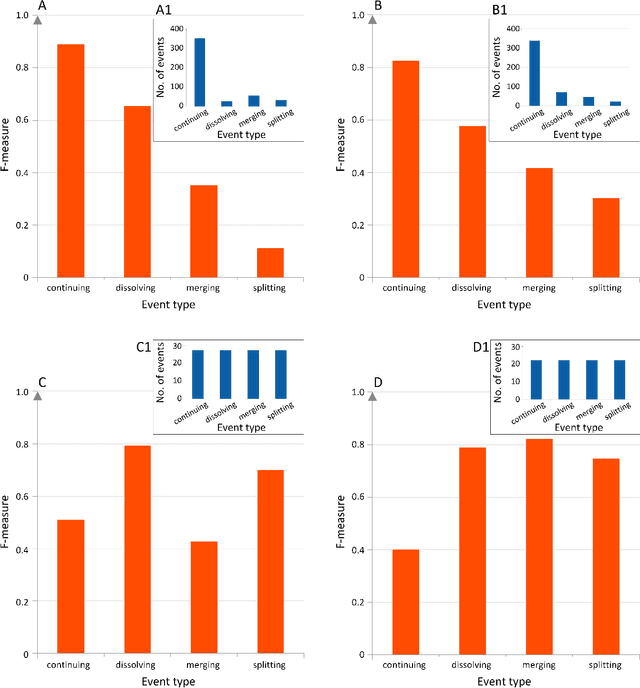
Abstract:The advancement of science as outlined by Popper and Kuhn is largely qualitative, but with bibliometric data it is possible and desirable to develop a quantitative picture of scientific progress. Furthermore it is also important to allocate finite resources to research topics that have growth potential, to accelerate the process from scientific breakthroughs to technological innovations. In this paper, we address this problem of quantitative knowledge evolution by analysing the APS publication data set from 1981 to 2010. We build the bibliographic coupling and co-citation networks, use the Louvain method to detect topical clusters (TCs) in each year, measure the similarity of TCs in consecutive years, and visualize the results as alluvial diagrams. Having the predictive features describing a given TC and its known evolution in the next year, we can train a machine learning model to predict future changes of TCs, i.e., their continuing, dissolving, merging and splitting. We found the number of papers from certain journals, the degree, closeness, and betweenness to be the most predictive features. Additionally, betweenness increases significantly for merging events, and decreases significantly for splitting events. Our results represent a first step from a descriptive understanding of the Science of Science (SciSci), towards one that is ultimately prescriptive.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge