Wennan Liu
Joint Prediction of Meningioma Grade and Brain Invasion via Task-Aware Contrastive Learning
Sep 04, 2022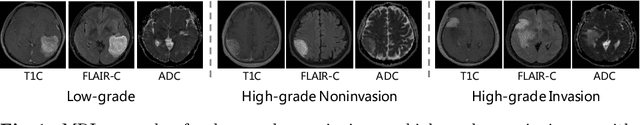
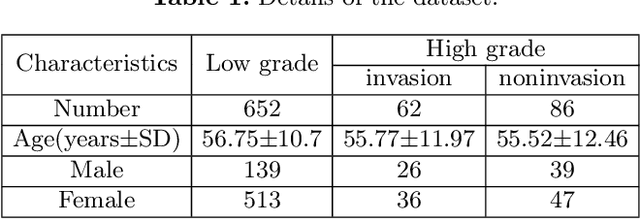
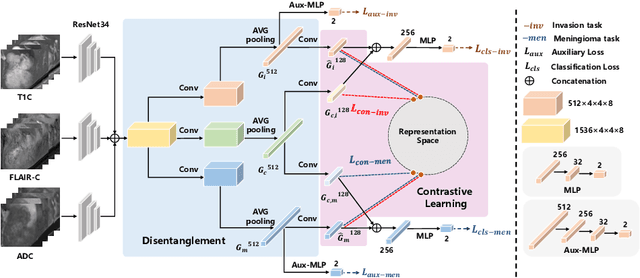
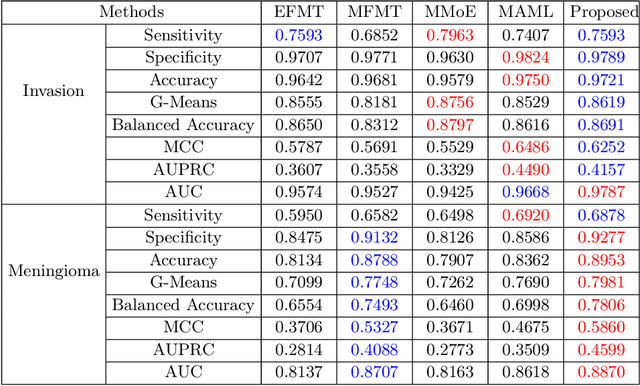
Abstract:Preoperative and noninvasive prediction of the meningioma grade is important in clinical practice, as it directly influences the clinical decision making. What's more, brain invasion in meningioma (i.e., the presence of tumor tissue within the adjacent brain tissue) is an independent criterion for the grading of meningioma and influences the treatment strategy. Although efforts have been reported to address these two tasks, most of them rely on hand-crafted features and there is no attempt to exploit the two prediction tasks simultaneously. In this paper, we propose a novel task-aware contrastive learning algorithm to jointly predict meningioma grade and brain invasion from multi-modal MRIs. Based on the basic multi-task learning framework, our key idea is to adopt contrastive learning strategy to disentangle the image features into task-specific features and task-common features, and explicitly leverage their inherent connections to improve feature representation for the two prediction tasks. In this retrospective study, an MRI dataset was collected, for which 800 patients (containing 148 high-grade, 62 invasion) were diagnosed with meningioma by pathological analysis. Experimental results show that the proposed algorithm outperforms alternative multi-task learning methods, achieving AUCs of 0:8870 and 0:9787 for the prediction of meningioma grade and brain invasion, respectively. The code is available at https://github.com/IsDling/predictTCL.
Triple-cooperative Video Shadow Detection
Mar 11, 2021
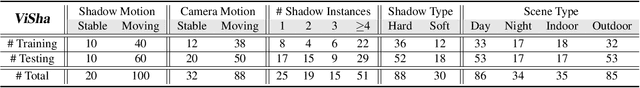
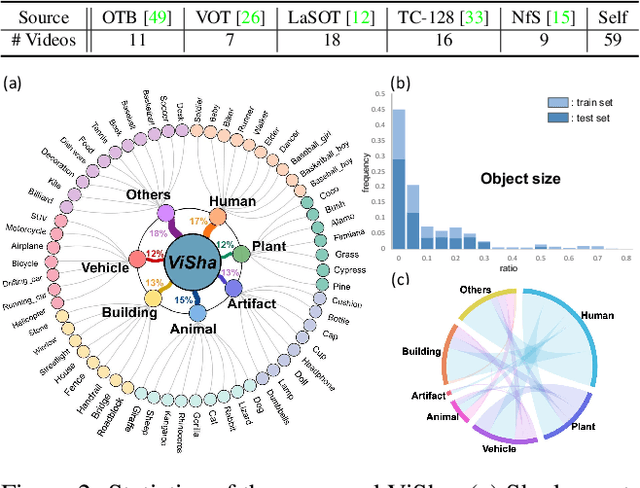
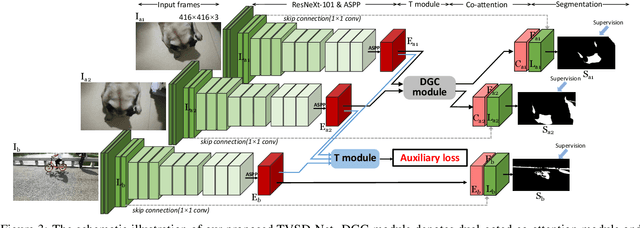
Abstract:Shadow detection in a single image has received significant research interest in recent years. However, much fewer works have been explored in shadow detection over dynamic scenes. The bottleneck is the lack of a well-established dataset with high-quality annotations for video shadow detection. In this work, we collect a new video shadow detection dataset, which contains 120 videos with 11, 685 frames, covering 60 object categories, varying lengths, and different motion/lighting conditions. All the frames are annotated with a high-quality pixel-level shadow mask. To the best of our knowledge, this is the first learning-oriented dataset for video shadow detection. Furthermore, we develop a new baseline model, named triple-cooperative video shadow detection network (TVSD-Net). It utilizes triple parallel networks in a cooperative manner to learn discriminative representations at intra-video and inter-video levels. Within the network, a dual gated co-attention module is proposed to constrain features from neighboring frames in the same video, while an auxiliary similarity loss is introduced to mine semantic information between different videos. Finally, we conduct a comprehensive study on ViSha, evaluating 12 state-of-the-art models (including single image shadow detectors, video object segmentation, and saliency detection methods). Experiments demonstrate that our model outperforms SOTA competitors.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge