Wenjing Ke
MonoGS++: Fast and Accurate Monocular RGB Gaussian SLAM
Apr 03, 2025Abstract:We present MonoGS++, a novel fast and accurate Simultaneous Localization and Mapping (SLAM) method that leverages 3D Gaussian representations and operates solely on RGB inputs. While previous 3D Gaussian Splatting (GS)-based methods largely depended on depth sensors, our approach reduces the hardware dependency and only requires RGB input, leveraging online visual odometry (VO) to generate sparse point clouds in real-time. To reduce redundancy and enhance the quality of 3D scene reconstruction, we implemented a series of methodological enhancements in 3D Gaussian mapping. Firstly, we introduced dynamic 3D Gaussian insertion to avoid adding redundant Gaussians in previously well-reconstructed areas. Secondly, we introduced clarity-enhancing Gaussian densification module and planar regularization to handle texture-less areas and flat surfaces better. We achieved precise camera tracking results both on the synthetic Replica and real-world TUM-RGBD datasets, comparable to those of the state-of-the-art. Additionally, our method realized a significant 5.57x improvement in frames per second (fps) over the previous state-of-the-art, MonoGS.
HPS-Det: Dynamic Sample Assignment with Hyper-Parameter Search for Object Detection
Jul 23, 2022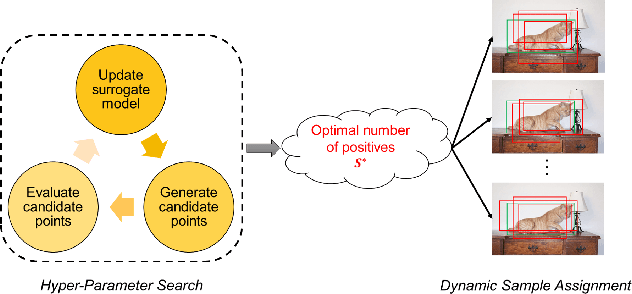
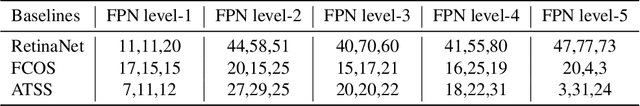
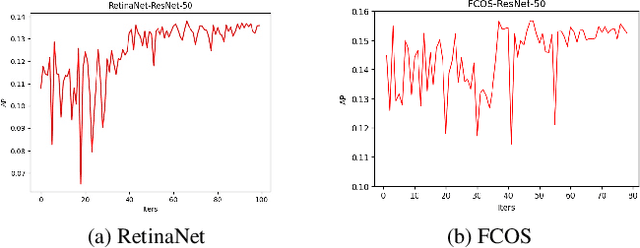
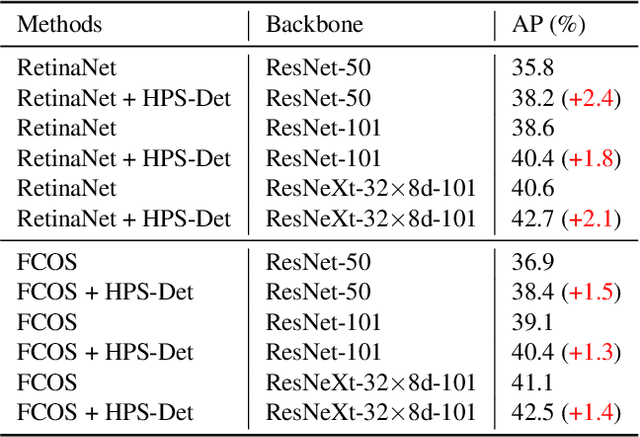
Abstract:Sample assignment plays a prominent part in modern object detection approaches. However, most existing methods rely on manual design to assign positive / negative samples, which do not explicitly establish the relationships between sample assignment and object detection performance. In this work, we propose a novel dynamic sample assignment scheme based on hyper-parameter search. We first define the number of positive samples assigned to each ground truth as the hyper-parameters and employ a surrogate optimization algorithm to derive the optimal choices. Then, we design a dynamic sample assignment procedure to dynamically select the optimal number of positives at each training iteration. Experiments demonstrate that the resulting HPS-Det brings improved performance over different object detection baselines. Moreover, We analyze the hyper-parameter reusability when transferring between different datasets and between different backbones for object detection, which exhibits the superiority and versatility of our method.
Dual Cross-Attention Learning for Fine-Grained Visual Categorization and Object Re-Identification
May 04, 2022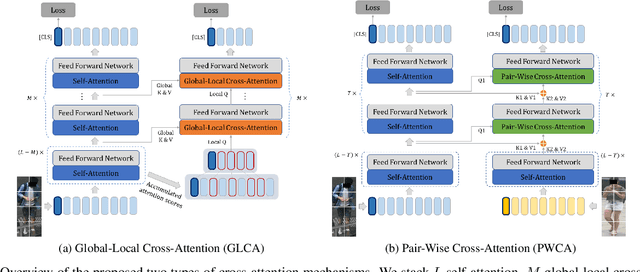
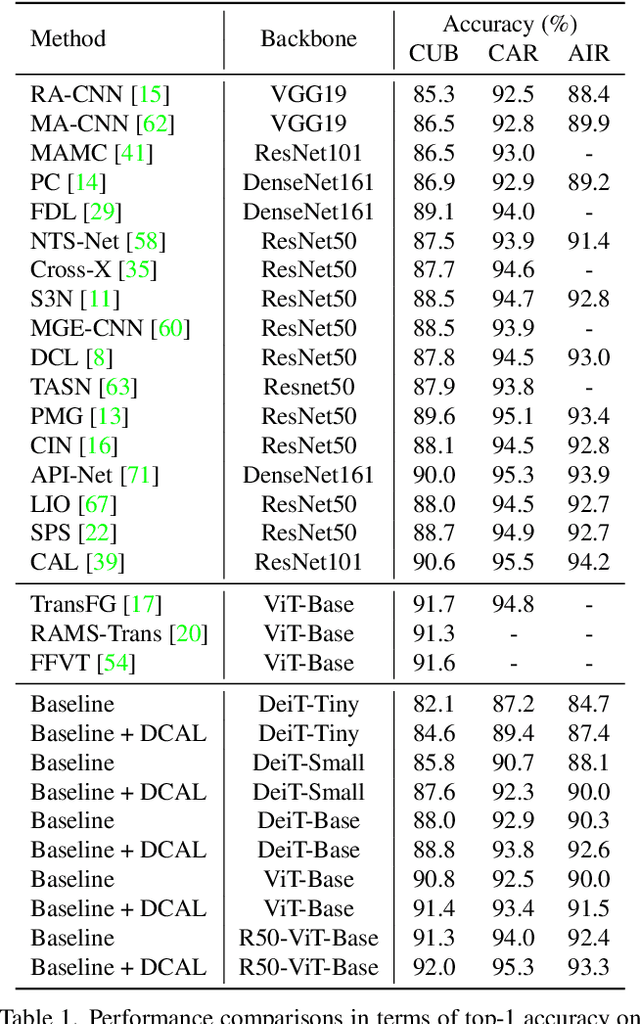
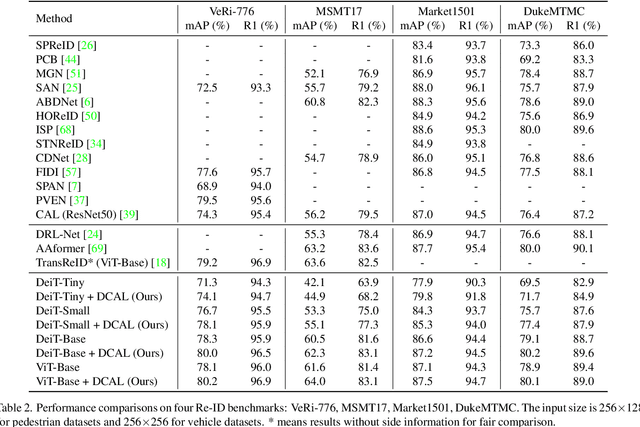
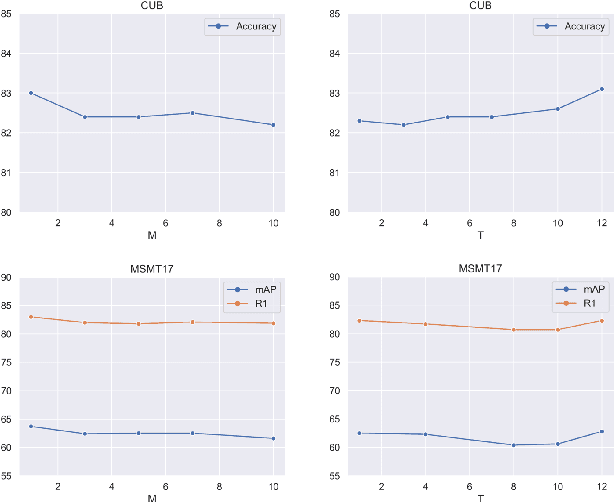
Abstract:Recently, self-attention mechanisms have shown impressive performance in various NLP and CV tasks, which can help capture sequential characteristics and derive global information. In this work, we explore how to extend self-attention modules to better learn subtle feature embeddings for recognizing fine-grained objects, e.g., different bird species or person identities. To this end, we propose a dual cross-attention learning (DCAL) algorithm to coordinate with self-attention learning. First, we propose global-local cross-attention (GLCA) to enhance the interactions between global images and local high-response regions, which can help reinforce the spatial-wise discriminative clues for recognition. Second, we propose pair-wise cross-attention (PWCA) to establish the interactions between image pairs. PWCA can regularize the attention learning of an image by treating another image as distractor and will be removed during inference. We observe that DCAL can reduce misleading attentions and diffuse the attention response to discover more complementary parts for recognition. We conduct extensive evaluations on fine-grained visual categorization and object re-identification. Experiments demonstrate that DCAL performs on par with state-of-the-art methods and consistently improves multiple self-attention baselines, e.g., surpassing DeiT-Tiny and ViT-Base by 2.8% and 2.4% mAP on MSMT17, respectively.
Automatic Streaming Segmentation of Stereo Video Using Bilateral Space
Nov 28, 2017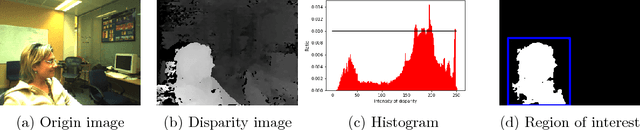


Abstract:In this paper, we take advantage of binocular camera and propose an unsupervised algorithm based on semi-supervised segmentation algorithm and extracting foreground part efficiently. We creatively embed depth information into bilateral grid in the graph cut model and achieve considerable segmenting accuracy in the case of no user input. The experi- ment approves the high precision, time efficiency of our algorithm and its adaptation to complex natural scenario which is significant for practical application.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge