Wei Di
HD-CNN: Hierarchical Deep Convolutional Neural Network for Large Scale Visual Recognition
May 16, 2015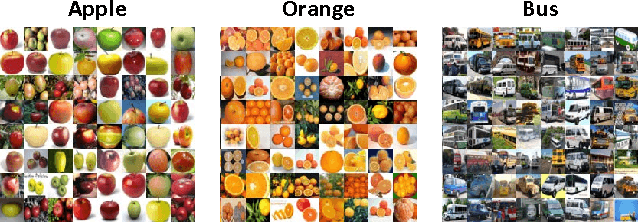
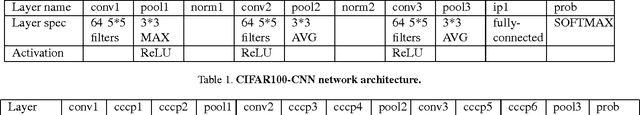
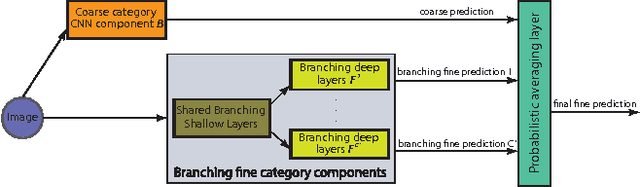
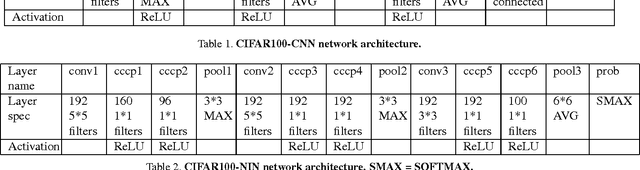
Abstract:In image classification, visual separability between different object categories is highly uneven, and some categories are more difficult to distinguish than others. Such difficult categories demand more dedicated classifiers. However, existing deep convolutional neural networks (CNN) are trained as flat N-way classifiers, and few efforts have been made to leverage the hierarchical structure of categories. In this paper, we introduce hierarchical deep CNNs (HD-CNNs) by embedding deep CNNs into a category hierarchy. An HD-CNN separates easy classes using a coarse category classifier while distinguishing difficult classes using fine category classifiers. During HD-CNN training, component-wise pretraining is followed by global finetuning with a multinomial logistic loss regularized by a coarse category consistency term. In addition, conditional executions of fine category classifiers and layer parameter compression make HD-CNNs scalable for large-scale visual recognition. We achieve state-of-the-art results on both CIFAR100 and large-scale ImageNet 1000-class benchmark datasets. In our experiments, we build up three different HD-CNNs and they lower the top-1 error of the standard CNNs by 2.65%, 3.1% and 1.1%, respectively.
Efficient Media Retrieval from Non-Cooperative Queries
Nov 19, 2014
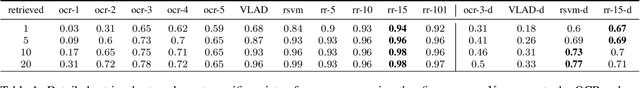

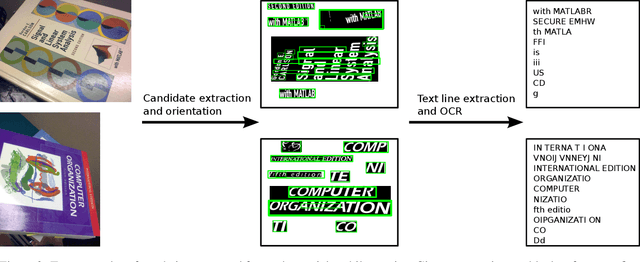
Abstract:Text is ubiquitous in the artificial world and easily attainable when it comes to book title and author names. Using the images from the book cover set from the Stanford Mobile Visual Search dataset and additional book covers and metadata from openlibrary.org, we construct a large scale book cover retrieval dataset, complete with 100K distractor covers and title and author strings for each. Because our query images are poorly conditioned for clean text extraction, we propose a method for extracting a matching noisy and erroneous OCR readings and matching it against clean author and book title strings in a standard document look-up problem setup. Finally, we demonstrate how to use this text-matching as a feature in conjunction with popular retrieval features such as VLAD using a simple learning setup to achieve significant improvements in retrieval accuracy over that of either VLAD or the text alone.
Geometric VLAD for Large Scale Image Search
Mar 15, 2014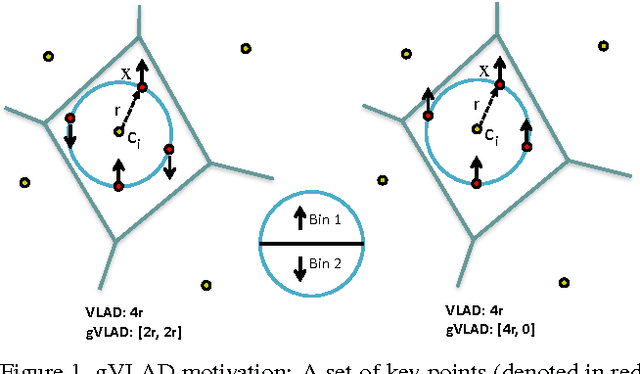
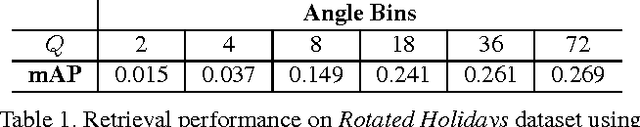

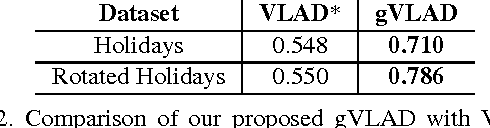
Abstract:We present a novel compact image descriptor for large scale image search. Our proposed descriptor - Geometric VLAD (gVLAD) is an extension of VLAD (Vector of Locally Aggregated Descriptors) that incorporates weak geometry information into the VLAD framework. The proposed geometry cues are derived as a membership function over keypoint angles which contain evident and informative information but yet often discarded. A principled technique for learning the membership function by clustering angles is also presented. Further, to address the overhead of iterative codebook training over real-time datasets, a novel codebook adaptation strategy is outlined. Finally, we demonstrate the efficacy of proposed gVLAD based retrieval framework where we achieve more than 15% improvement in mAP over existing benchmarks.
Large Scale Visual Recommendations From Street Fashion Images
Jan 08, 2014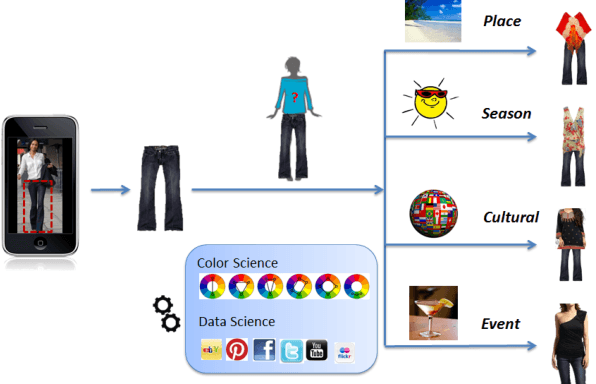
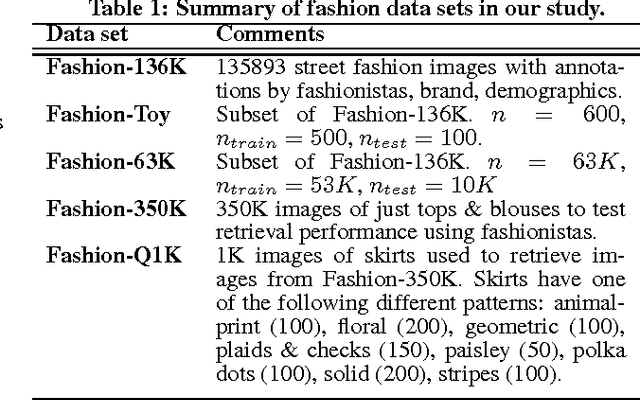

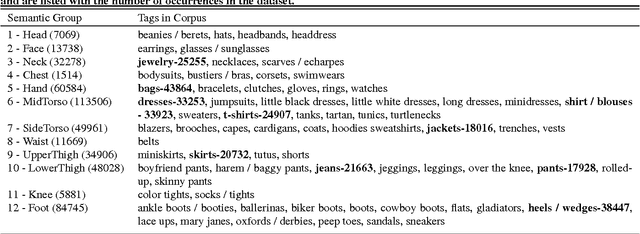
Abstract:We describe a completely automated large scale visual recommendation system for fashion. Our focus is to efficiently harness the availability of large quantities of online fashion images and their rich meta-data. Specifically, we propose four data driven models in the form of Complementary Nearest Neighbor Consensus, Gaussian Mixture Models, Texture Agnostic Retrieval and Markov Chain LDA for solving this problem. We analyze relative merits and pitfalls of these algorithms through extensive experimentation on a large-scale data set and baseline them against existing ideas from color science. We also illustrate key fashion insights learned through these experiments and show how they can be employed to design better recommendation systems. Finally, we also outline a large-scale annotated data set of fashion images (Fashion-136K) that can be exploited for future vision research.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge