Wee Kiat New
A Tutorial on Fluid Antenna System for 6G Networks: Encompassing Communication Theory, Optimization Methods and Hardware Designs
Jul 03, 2024
Abstract:The advent of the sixth-generation (6G) networks presents another round of revolution for the mobile communication landscape, promising an immersive experience, robust reliability, minimal latency, extreme connectivity, ubiquitous coverage, and capabilities beyond communication, including intelligence and sensing. To achieve these ambitious goals, it is apparent that 6G networks need to incorporate the state-of-the-art technologies. One of the technologies that has garnered rising interest is fluid antenna system (FAS) which represents any software-controllable fluidic, conductive, or dielectric structure capable of dynamically changing its shape and position to reconfigure essential radio-frequency (RF) characteristics. Compared to traditional antenna systems (TASs) with fixed-position radiating elements, the core idea of FAS revolves around the unique flexibility of reconfiguring the radiating elements within a given space. One recent driver of FAS is the recognition of its position-flexibility as a new degree of freedom (dof) to harness diversity and multiplexing gains. In this paper, we provide a comprehensive tutorial, covering channel modeling, signal processing and estimation methods, information-theoretic insights, new multiple access techniques, and hardware designs. Moreover, we delineate the challenges of FAS and explore the potential of using FAS to improve the performance of other contemporary technologies. By providing insights and guidance, this tutorial paper serves to inspire researchers to explore new horizons and fully unleash the potential of FAS.
Coding-Enhanced Cooperative Jamming for Secret Communication in Fluid Antenna Systems
Jul 02, 2024Abstract:This letter investigates the secret communication problem for a fluid antenna system (FAS)-assisted wiretap channel, where the legitimate transmitter transmits an information-bearing signal to the legitimate receiver, and at the same time, transmits a jamming signal to interfere with the eavesdropper (Eve). Unlike the conventional jamming scheme, which usually transmits Gaussian noise that interferes not only with Eve but also with the legitimate receiver, in this letter, we consider that encoded codewords are transmitted to jam Eve. Then, by employing appropriate coding schemes, the legitimate receiver can successfully decode the jamming signal and then cancel the interference, while Eve cannot, even if it knows the codebooks. We aim to maximize the secrecy rate through port selection and power control. Although the problem is non-convex, we show that the optimal solution can be found. Simulation results show that by using the FAS technique and the proposed jamming scheme, the secrecy rate of the system can be significantly increased.
Channel Estimation and Reconstruction in Fluid Antenna System: Oversampling is Essential
May 24, 2024



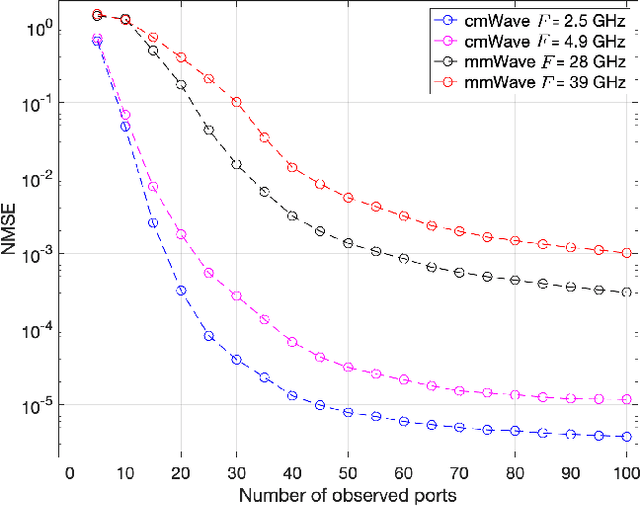
Abstract:Fluid antenna system (FAS) has recently surfaced as a promising technology for the upcoming sixth generation (6G) wireless networks. Unlike traditional antenna system (TAS) with fixed antenna location, FAS introduces a flexible component where the radiating element can switch its position within a predefined space. This capability allows FAS to achieve additional diversity and multiplexing gains. Nevertheless, to fully reap the benefits of FAS, obtaining channel state information (CSI) over the predefined space is crucial. In this paper, we explore the interaction between a transmitter equipped with a traditional antenna and a receiver with a fluid antenna over an electromagnetic-compliant channel model. We address the challenges of channel estimation and reconstruction using Nyquist sampling and maximum likelihood estimation (MLE) methods. Our analysis reveals a fundamental tradeoff between the accuracy of the reconstructed channel and the number of estimated channels, indicating that half-wavelength sampling is insufficient for perfect reconstruction and that oversampling is essential to enhance accuracy. Despite its advantages, oversampling can introduce practical challenges. Consequently, we propose a suboptimal sampling distance that facilitates efficient channel reconstruction. In addition, we employ the MLE method to bound the channel estimation error by $\epsilon$, with a specific confidence interval (CI). Our findings enable us to determine the minimum number of estimated channels and the total number of pilot symbols required for efficient channel reconstruction in a given space. Lastly, we investigate the rate performance of FAS and TAS and demonstrate that FAS with imperfect CSI can outperform TAS with perfect CSI.
On Performance of RIS-Aided Fluid Antenna Systems
Feb 25, 2024



Abstract:This letter studies the performance of reconfigurable intelligent surface (RIS)-aided communications for a fluid antenna system (FAS) enabled receiver. Specifically, a fixed singleantenna base station (BS) transmits information through a RIS to a mobile user (MU) which is equipped with a planar fluid antenna in the absence of a direct link.We first analyze the spatial correlation structures among the positions (or ports) in the planar FAS, and then derive the joint distribution of the equivalent channel gain at the user by exploiting the central limit theorem. Furthermore, we obtain compact analytical expressions for the outage probability (OP) and delay outage rate (DOR). Numerical results illustrate that using FAS with only one activated port into the RIS-aided communication network can greatly enhance the performance, when compared to traditional antenna systems (TAS).
Physical Layer Security over Fluid Antenna Systems
Feb 08, 2024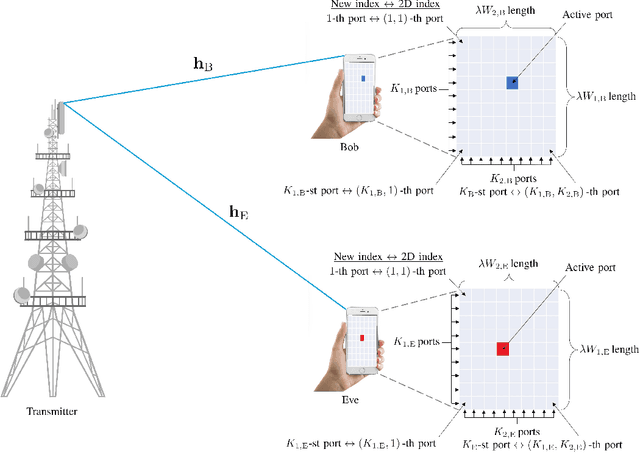



Abstract:This paper investigates the performance of physical layer security (PLS) in fluid antenna-aided communication systems under arbitrary correlated fading channels. In particular, it is considered that a single fixed-antenna transmitter aims to send confidential information to a legitimate receiver equipped with a planar fluid antenna system (FAS), while an eavesdropper, also taking advantage of a planar FAS, attempts to decode the desired message. For this scenario, we first present analytical expressions of the equivalent channel distributions at the legitimate user and eavesdropper by using copula, so that the obtained analytical results are valid for any arbitrarily correlated fading distributions. Then, with the help of Gauss-Laguerre quadrature, we derive compact analytical expressions for the average secrecy capacity (ASC), the secrecy outage probability (SOP), and the secrecy energy efficiency (SEE) for the FAS wiretap channel. Moreover, for exemplary purposes, we also obtain the compact expression of ASC, SOP, and SEE by utilizing the Gaussian copula under correlated Rayleigh fading channels as a special case. Eventually, numerical results indicate that applying the fluid antenna with only one active port to PLS can guarantee more secure and reliable transmission, when compared to traditional antenna systems (TAS) exploiting maximal ratio combining (MRC).
Channel Estimation for FAS-assisted Multiuser mmWave Systems
Nov 18, 2023


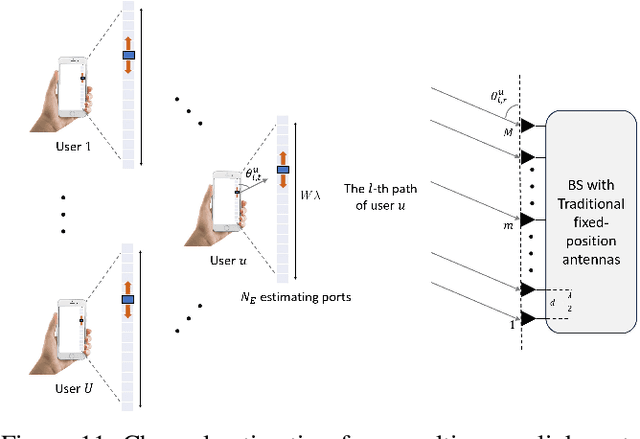
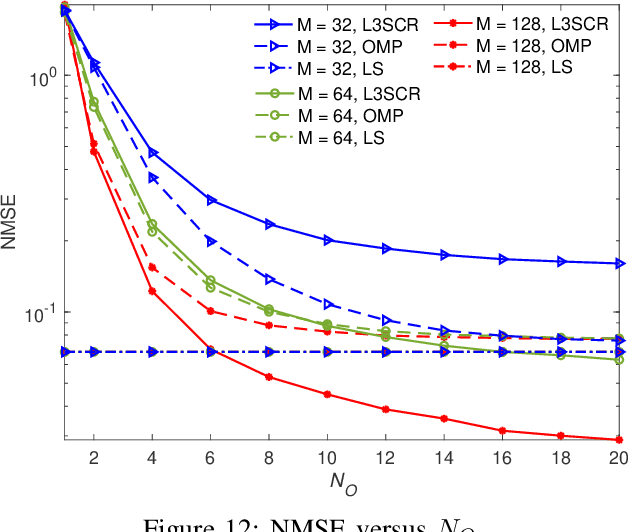
Abstract:This letter investigates the challenge of channel estimation in a multiuser millimeter-wave (mmWave) time-division duplexing (TDD) system. In this system, the base station (BS) employs a multi-antenna uniform linear array (ULA), while each mobile user is equipped with a fluid antenna system (FAS). Accurate channel state information (CSI) plays a crucial role in the precise placement of antennas in FAS. Traditional channel estimation methods designed for fixed-antenna systems are inadequate due to the high dimensionality of FAS. To address this issue, we propose a low-sample-size sparse channel reconstruction (L3SCR) method, capitalizing on the sparse propagation paths characteristic of mmWave channels. In this approach, each fluid antenna only needs to switch and measure the channel at a few specific locations. By observing this reduced-dimensional data, we can effectively extract angular and gain information related to the sparse channel, enabling us to reconstruct the full CSI. Simulation results demonstrate that our proposed method allows us to obtain precise CSI with minimal hardware switching and pilot overhead. As a result, the system sum-rate approaches the upper bound achievable with perfect CSI.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge