Wangchun Sun
Debate on Graph: a Flexible and Reliable Reasoning Framework for Large Language Models
Sep 05, 2024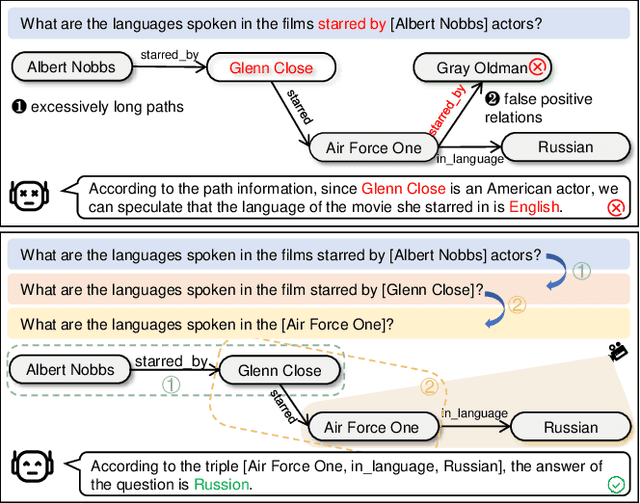
Abstract:Large Language Models (LLMs) may suffer from hallucinations in real-world applications due to the lack of relevant knowledge. In contrast, knowledge graphs encompass extensive, multi-relational structures that store a vast array of symbolic facts. Consequently, integrating LLMs with knowledge graphs has been extensively explored, with Knowledge Graph Question Answering (KGQA) serving as a critical touchstone for the integration. This task requires LLMs to answer natural language questions by retrieving relevant triples from knowledge graphs. However, existing methods face two significant challenges: \textit{excessively long reasoning paths distracting from the answer generation}, and \textit{false-positive relations hindering the path refinement}. In this paper, we propose an iterative interactive KGQA framework that leverages the interactive learning capabilities of LLMs to perform reasoning and Debating over Graphs (DoG). Specifically, DoG employs a subgraph-focusing mechanism, allowing LLMs to perform answer trying after each reasoning step, thereby mitigating the impact of lengthy reasoning paths. On the other hand, DoG utilizes a multi-role debate team to gradually simplify complex questions, reducing the influence of false-positive relations. This debate mechanism ensures the reliability of the reasoning process. Experimental results on five public datasets demonstrate the effectiveness and superiority of our architecture. Notably, DoG outperforms the state-of-the-art method ToG by 23.7\% and 9.1\% in accuracy on WebQuestions and GrailQA, respectively. Furthermore, the integration experiments with various LLMs on the mentioned datasets highlight the flexibility of DoG. Code is available at \url{https://github.com/reml-group/DoG}.
Look, Listen, and Answer: Overcoming Biases for Audio-Visual Question Answering
Apr 18, 2024



Abstract:Audio-Visual Question Answering (AVQA) is a complex multi-modal reasoning task, demanding intelligent systems to accurately respond to natural language queries based on audio-video input pairs. Nevertheless, prevalent AVQA approaches are prone to overlearning dataset biases, resulting in poor robustness. Furthermore, current datasets may not provide a precise diagnostic for these methods. To tackle these challenges, firstly, we propose a novel dataset, \textit{MUSIC-AVQA-R}, crafted in two steps: rephrasing questions within the test split of a public dataset (\textit{MUSIC-AVQA}) and subsequently introducing distribution shifts to split questions. The former leads to a large, diverse test space, while the latter results in a comprehensive robustness evaluation on rare, frequent, and overall questions. Secondly, we propose a robust architecture that utilizes a multifaceted cycle collaborative debiasing strategy to overcome bias learning. Experimental results show that this architecture achieves state-of-the-art performance on both datasets, especially obtaining a significant improvement of 9.68\% on the proposed dataset. Extensive ablation experiments are conducted on these two datasets to validate the effectiveness of the debiasing strategy. Additionally, we highlight the limited robustness of existing multi-modal QA methods through the evaluation on our dataset.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge