Walter de Back
Structure-Preserving Multi-Domain Stain Color Augmentation using Style-Transfer with Disentangled Representations
Jul 26, 2021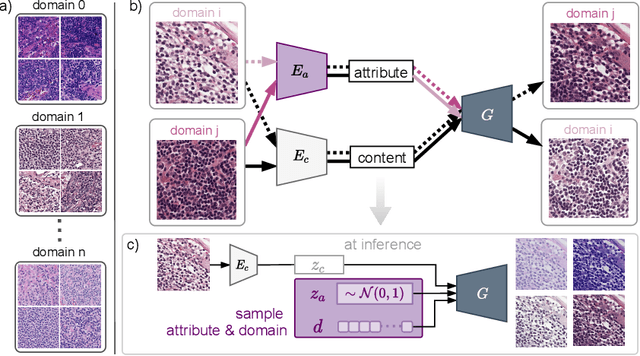
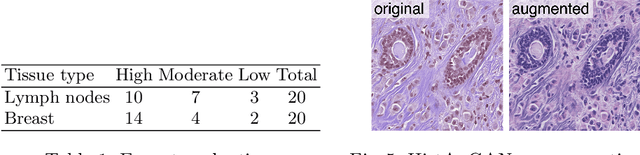
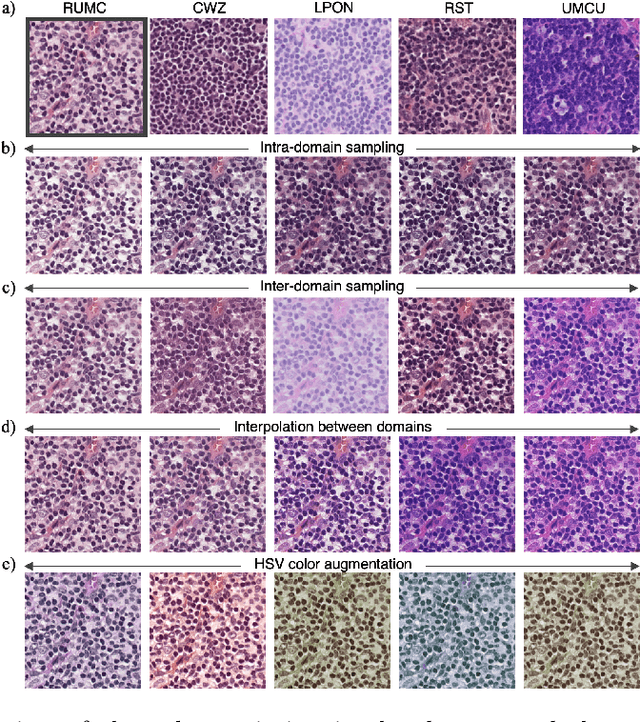
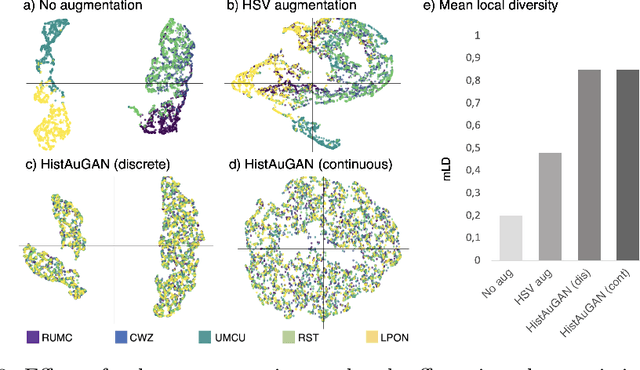
Abstract:In digital pathology, different staining procedures and scanners cause substantial color variations in whole-slide images (WSIs), especially across different laboratories. These color shifts result in a poor generalization of deep learning-based methods from the training domain to external pathology data. To increase test performance, stain normalization techniques are used to reduce the variance between training and test domain. Alternatively, color augmentation can be applied during training leading to a more robust model without the extra step of color normalization at test time. We propose a novel color augmentation technique, HistAuGAN, that can simulate a wide variety of realistic histology stain colors, thus making neural networks stain-invariant when applied during training. Based on a generative adversarial network (GAN) for image-to-image translation, our model disentangles the content of the image, i.e., the morphological tissue structure, from the stain color attributes. It can be trained on multiple domains and, therefore, learns to cover different stain colors as well as other domain-specific variations introduced in the slide preparation and imaging process. We demonstrate that HistAuGAN outperforms conventional color augmentation techniques on a classification task on the publicly available dataset Camelyon17 and show that it is able to mitigate present batch effects.
An interpretable automated detection system for FISH-based HER2 oncogene amplification testing in histo-pathological routine images of breast and gastric cancer diagnostics
May 25, 2020
Abstract:Histo-pathological diagnostics are an inherent part of the everyday work but are particularly laborious and associated with time-consuming manual analysis of image data. In order to cope with the increasing diagnostic case numbers due to the current growth and demographic change of the global population and the progress in personalized medicine, pathologists ask for assistance. Profiting from digital pathology and the use of artificial intelligence, individual solutions can be offered (e.g. detect labeled cancer tissue sections). The testing of the human epidermal growth factor receptor 2 (HER2) oncogene amplification status via fluorescence in situ hybridization (FISH) is recommended for breast and gastric cancer diagnostics and is regularly performed at clinics. Here, we develop an interpretable, deep learning (DL)-based pipeline which automates the evaluation of FISH images with respect to HER2 gene amplification testing. It mimics the pathological assessment and relies on the detection and localization of interphase nuclei based on instance segmentation networks. Furthermore, it localizes and classifies fluorescence signals within each nucleus with the help of image classification and object detection convolutional neural networks (CNNs). Finally, the pipeline classifies the whole image regarding its HER2 amplification status. The visualization of pixels on which the networks' decision occurs, complements an essential part to enable interpretability by pathologists.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge