Vishwanath D
TableNet: Deep Learning model for end-to-end Table detection and Tabular data extraction from Scanned Document Images
Jan 06, 2020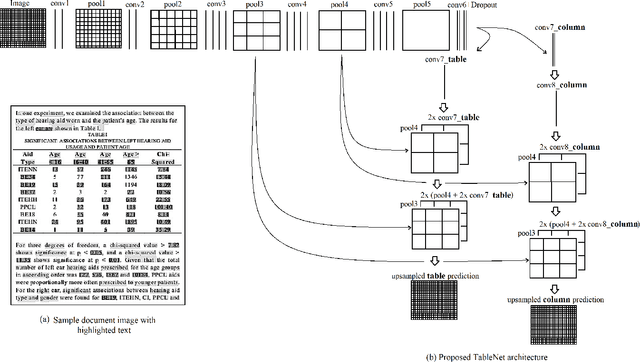

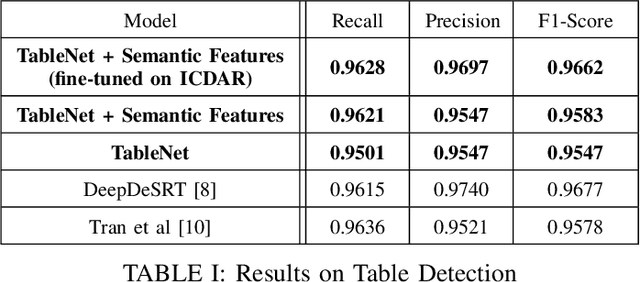
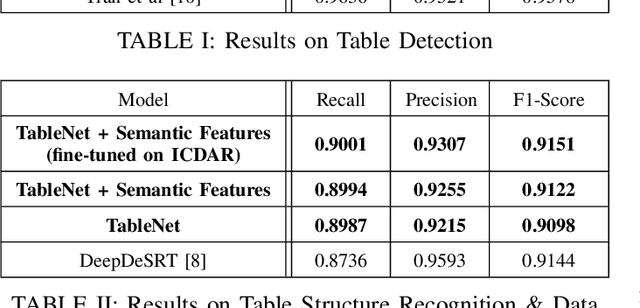
Abstract:With the widespread use of mobile phones and scanners to photograph and upload documents, the need for extracting the information trapped in unstructured document images such as retail receipts, insurance claim forms and financial invoices is becoming more acute. A major hurdle to this objective is that these images often contain information in the form of tables and extracting data from tabular sub-images presents a unique set of challenges. This includes accurate detection of the tabular region within an image, and subsequently detecting and extracting information from the rows and columns of the detected table. While some progress has been made in table detection, extracting the table contents is still a challenge since this involves more fine grained table structure(rows & columns) recognition. Prior approaches have attempted to solve the table detection and structure recognition problems independently using two separate models. In this paper, we propose TableNet: a novel end-to-end deep learning model for both table detection and structure recognition. The model exploits the interdependence between the twin tasks of table detection and table structure recognition to segment out the table and column regions. This is followed by semantic rule-based row extraction from the identified tabular sub-regions. The proposed model and extraction approach was evaluated on the publicly available ICDAR 2013 and Marmot Table datasets obtaining state of the art results. Additionally, we demonstrate that feeding additional semantic features further improves model performance and that the model exhibits transfer learning across datasets. Another contribution of this paper is to provide additional table structure annotations for the Marmot data, which currently only has annotations for table detection.
MEETING BOT: Reinforcement Learning for Dialogue Based Meeting Scheduling
Dec 28, 2018



Abstract:In this paper we present Meeting Bot, a reinforcement learning based conversational system that interacts with multiple users to schedule meetings. The system is able to interpret user utterences and map them to preferred time slots, which are then fed to a reinforcement learning (RL) system with the goal of converging on an agreeable time slot. The RL system is able to adapt to user preferences and environmental changes in meeting arrival rate while still scheduling effectively. Learning is performed via policy gradient with exploration, by utilizing an MLP as an approximator of the policy function. Results demonstrate that the system outperforms standard scheduling algorithms in terms of overall scheduling efficiency. Additionally, the system is able to adapt its strategy to situations when users consistently reject or accept meetings in certain slots (such as Friday afternoon versus Thursday morning), or when the meeting is called by members who are at a more senior designation.
Deep Reader: Information extraction from Document images via relation extraction and Natural Language
Dec 14, 2018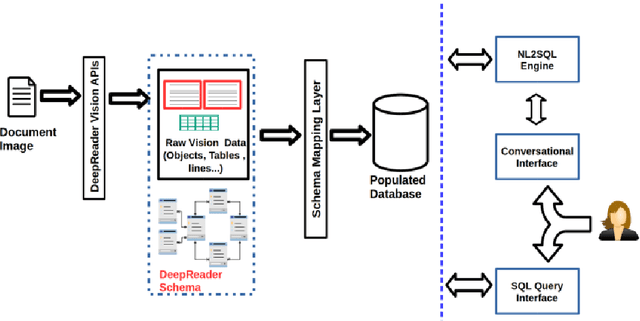
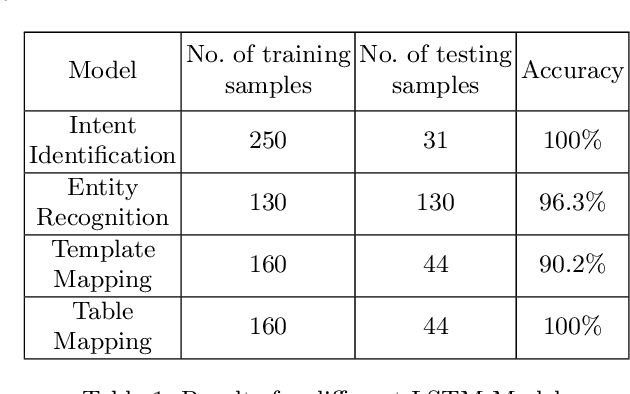
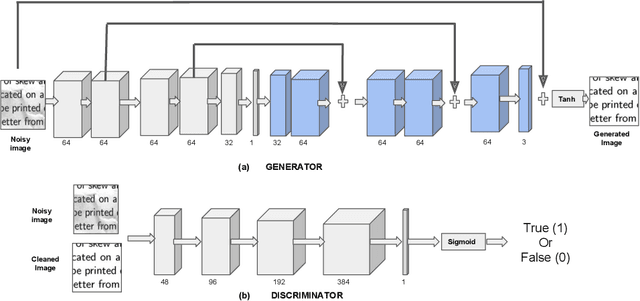

Abstract:Recent advancements in the area of Computer Vision with state-of-art Neural Networks has given a boost to Optical Character Recognition (OCR) accuracies. However, extracting characters/text alone is often insufficient for relevant information extraction as documents also have a visual structure that is not captured by OCR. Extracting information from tables, charts, footnotes, boxes, headings and retrieving the corresponding structured representation for the document remains a challenge and finds application in a large number of real-world use cases. In this paper, we propose a novel enterprise based end-to-end framework called DeepReader which facilitates information extraction from document images via identification of visual entities and populating a meta relational model across different entities in the document image. The model schema allows for an easy to understand abstraction of the entities detected by the deep vision models and the relationships between them. DeepReader has a suite of state-of-the-art vision algorithms which are applied to recognize handwritten and printed text, eliminate noisy effects, identify the type of documents and detect visual entities like tables, lines and boxes. Deep Reader maps the extracted entities into a rich relational schema so as to capture all the relevant relationships between entities (words, textboxes, lines etc) detected in the document. Relevant information and fields can then be extracted from the document by writing SQL queries on top of the relationship tables. A natural language based interface is added on top of the relationship schema so that a non-technical user, specifying the queries in natural language, can fetch the information with minimal effort. In this paper, we also demonstrate many different capabilities of Deep Reader and report results on a real-world use case.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge