Gunjan Sehgal
Deep Reader: Information extraction from Document images via relation extraction and Natural Language
Dec 14, 2018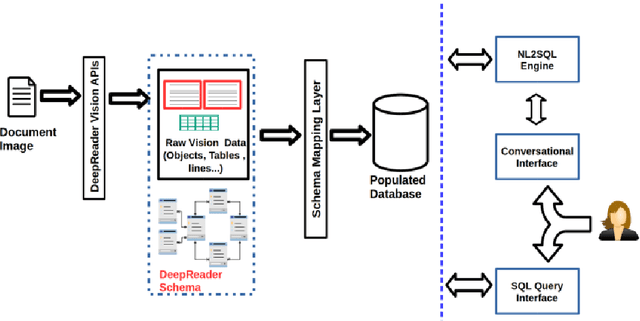
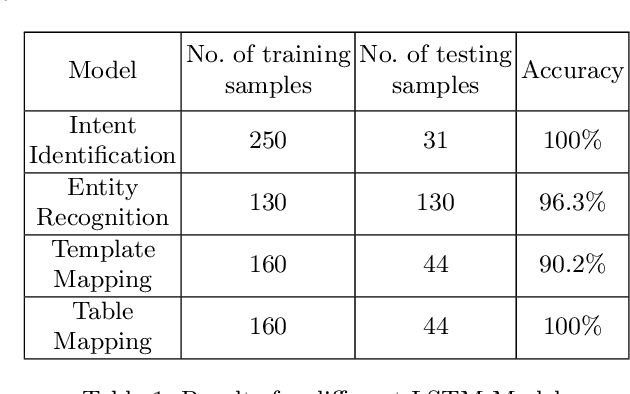
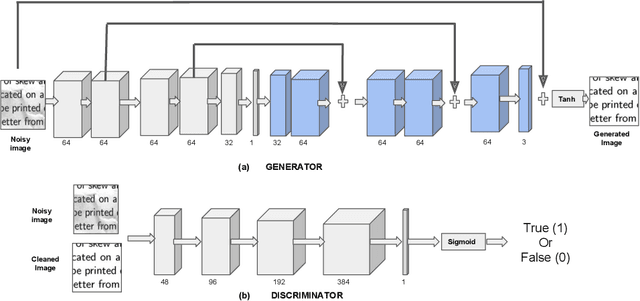

Abstract:Recent advancements in the area of Computer Vision with state-of-art Neural Networks has given a boost to Optical Character Recognition (OCR) accuracies. However, extracting characters/text alone is often insufficient for relevant information extraction as documents also have a visual structure that is not captured by OCR. Extracting information from tables, charts, footnotes, boxes, headings and retrieving the corresponding structured representation for the document remains a challenge and finds application in a large number of real-world use cases. In this paper, we propose a novel enterprise based end-to-end framework called DeepReader which facilitates information extraction from document images via identification of visual entities and populating a meta relational model across different entities in the document image. The model schema allows for an easy to understand abstraction of the entities detected by the deep vision models and the relationships between them. DeepReader has a suite of state-of-the-art vision algorithms which are applied to recognize handwritten and printed text, eliminate noisy effects, identify the type of documents and detect visual entities like tables, lines and boxes. Deep Reader maps the extracted entities into a rich relational schema so as to capture all the relevant relationships between entities (words, textboxes, lines etc) detected in the document. Relevant information and fields can then be extracted from the document by writing SQL queries on top of the relationship tables. A natural language based interface is added on top of the relationship schema so that a non-technical user, specifying the queries in natural language, can fetch the information with minimal effort. In this paper, we also demonstrate many different capabilities of Deep Reader and report results on a real-world use case.
Crop Planning using Stochastic Visual Optimization
Oct 25, 2017

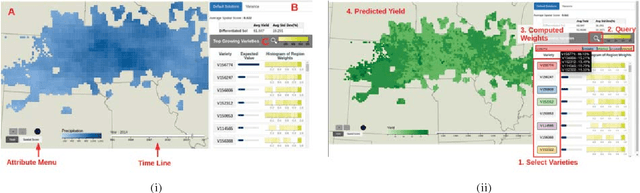

Abstract:As the world population increases and arable land decreases, it becomes vital to improve the productivity of the agricultural land available. Given the weather and soil properties, farmers need to take critical decisions such as which seed variety to plant and in what proportion, in order to maximize productivity. These decisions are irreversible and any unusual behavior of external factors, such as weather, can have catastrophic impact on the productivity of crop. A variety which is highly desirable to a farmer might be unavailable or in short supply, therefore, it is very critical to evaluate which variety or varieties are more likely to be chosen by farmers from a growing region in order to meet demand. In this paper, we present our visual analytics tool, ViSeed, showcased on the data given in Syngenta 2016 crop data challenge 1 . This tool helps to predict optimal soybean seed variety or mix of varieties in appropriate proportions which is more likely to be chosen by farmers from a growing region. It also allows to analyse solutions generated from our approach and helps in the decision making process by providing insightful visualizations
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge