Vinod Subramanian
Anomalous behaviour in loss-gradient based interpretability methods
Jul 15, 2022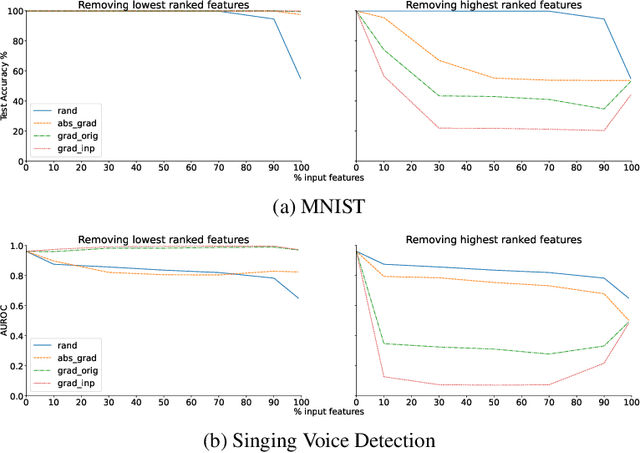
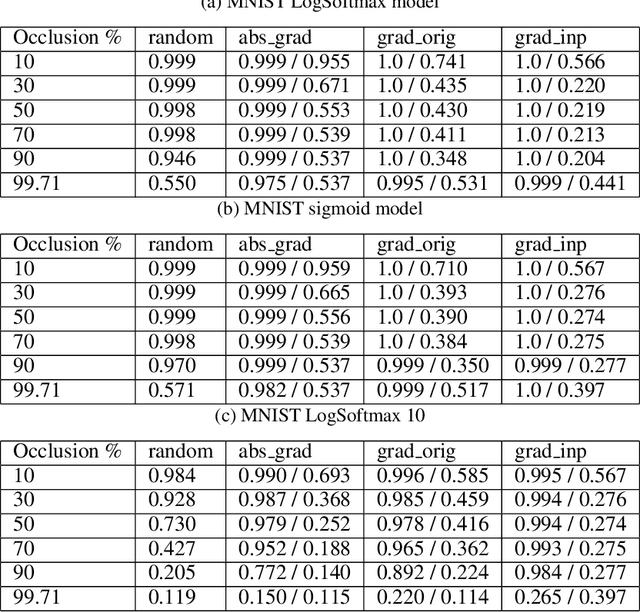
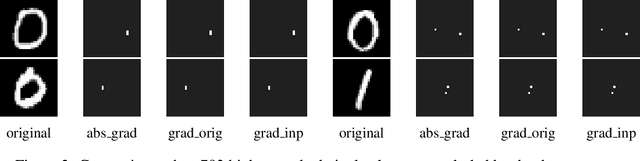
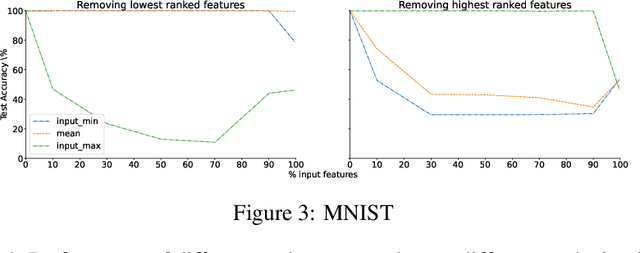
Abstract:Loss-gradients are used to interpret the decision making process of deep learning models. In this work, we evaluate loss-gradient based attribution methods by occluding parts of the input and comparing the performance of the occluded input to the original input. We observe that the occluded input has better performance than the original across the test dataset under certain conditions. Similar behaviour is observed in sound and image recognition tasks. We explore different loss-gradient attribution methods, occlusion levels and replacement values to explain the phenomenon of performance improvement under occlusion.
Deep Embeddings for Robust User-Based Amateur Vocal Percussion Classification
Apr 10, 2022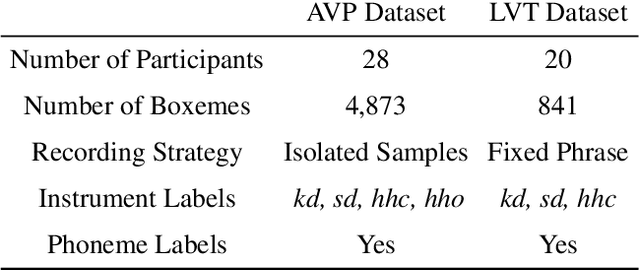

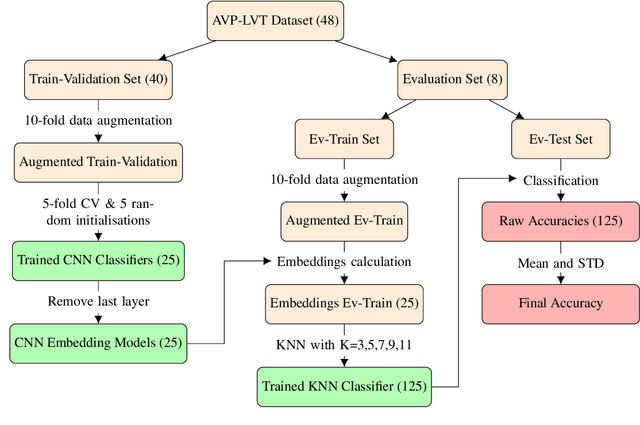
Abstract:Vocal Percussion Transcription (VPT) is concerned with the automatic detection and classification of vocal percussion sound events, allowing music creators and producers to sketch drum lines on the fly. Classifier algorithms in VPT systems learn best from small user-specific datasets, which usually restrict modelling to small input feature sets to avoid data overfitting. This study explores several deep supervised learning strategies to obtain informative feature sets for amateur vocal percussion classification. We evaluated the performance of these sets on regular vocal percussion classification tasks and compared them with several baseline approaches including feature selection methods and a speech recognition engine. These proposed learning models were supervised with several label sets containing information from four different levels of abstraction: instrument-level, syllable-level, phoneme-level, and boxeme-level. Results suggest that convolutional neural networks supervised with syllable-level annotations produced the most informative embeddings for classification, which can be used as input representations to fit classifiers with. Finally, we used back-propagation-based saliency maps to investigate the importance of different spectrogram regions for feature learning.
Memory Controlled Sequential Self Attention for Sound Recognition
Jun 11, 2020


Abstract:In this paper we investigate the importance of the extent of memory in sequential self attention for sound recognition. We propose to use a memory controlled sequential self attention mechanism on top of a convolutional recurrent neural network (CRNN) model for polyphonic sound event detection (SED). Experiments on the URBAN-SED dataset demonstrate the impact of the extent of memory on sound recognition performance with the self attention induced SED model. We extend the proposed idea with a multi-head self attention mechanism where each attention head processes the audio embedding with explicit attention width values. The proposed use of memory controlled sequential self attention offers a way to induce relations among frames of sound event tokens. We show that our memory controlled self attention model achieves an event based F -score of 33.92% on the URBAN-SED dataset, outperforming the F -score of 20.10% reported by the model without self attention.
Adversarial Attacks in Sound Event Classification
Aug 15, 2019

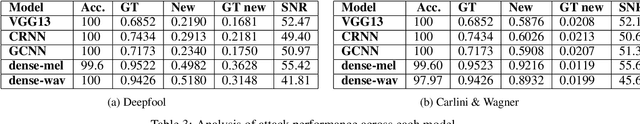

Abstract:Adversarial attacks refer to a set of methods that perturb the input to a classification model in order to fool the classifier. In this paper we apply different gradient based adversarial attack algorithms on five deep learning models trained for sound event classification. Four of the models use mel-spectrogram input and one model uses raw audio input. The models represent standard architectures such as convolutional, recurrent and dense networks. The dataset used for training is the Freesound dataset released for task 2 of the DCASE 2018 challenge and the models used are from participants of the challenge who open sourced their code. Our experiments show that adversarial attacks can be generated with high confidence and low perturbation. In addition, we show that the adversarial attacks are very effective across the different models.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge