Viktor Rakhmatulin
AirTouch: Towards Safe Human-Robot Interaction Using Air Pressure Feedback and IR Mocap System
Jul 31, 2023



Abstract:The growing use of robots in urban environments has raised concerns about potential safety hazards, especially in public spaces where humans and robots may interact. In this paper, we present a system for safe human-robot interaction that combines an infrared (IR) camera with a wearable marker and airflow potential field. IR cameras enable real-time detection and tracking of humans in challenging environments, while controlled airflow creates a physical barrier that guides humans away from dangerous proximity to robots without the need for wearable devices. A preliminary experiment was conducted to measure the accuracy of the perception of safety barriers rendered by controlled air pressure. In a second experiment, we evaluated our approach in an imitation scenario of an interaction between an inattentive person and an autonomous robotic system. Experimental results show that the proposed system significantly improves a participant's ability to maintain a safe distance from the operating robot compared to trials without the system.
CoboGuider: Haptic Potential Fields for Safe Human-Robot Interaction
Oct 25, 2021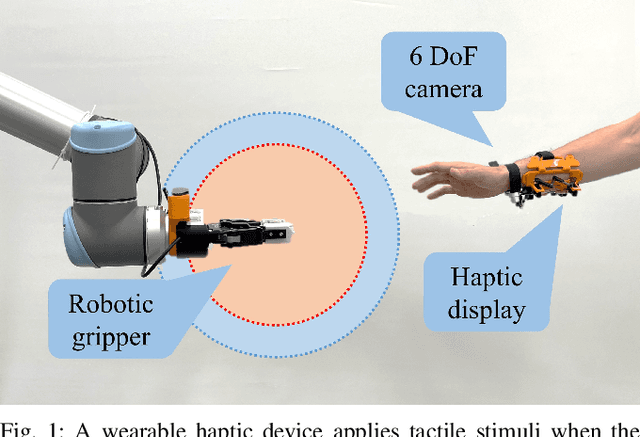
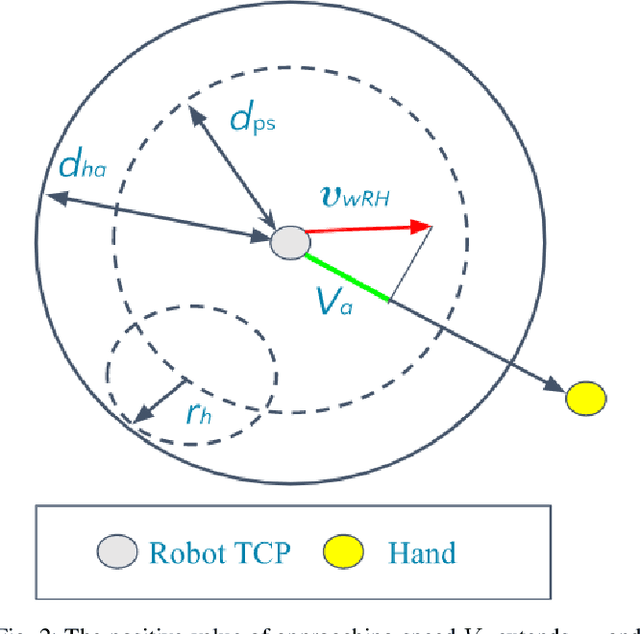
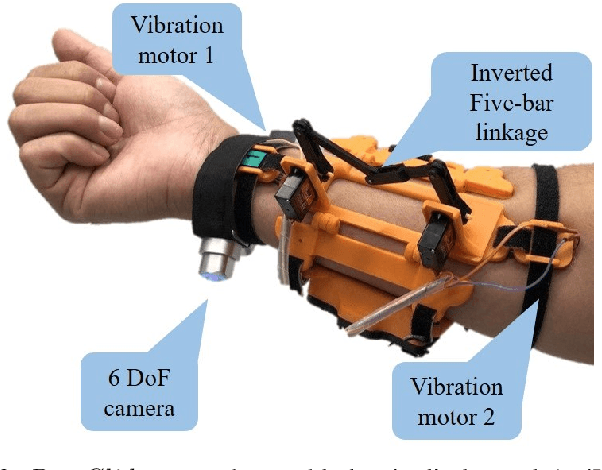
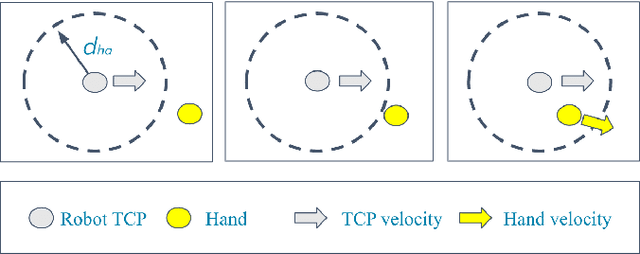
Abstract:Modern industry still relies on manual manufacturing operations and safe human-robot interaction is of great interest nowadays. Speed and Separation Monitoring (SSM) allows close and efficient collaborative scenarios by maintaining a protective separation distance during robot operation. The paper focuses on a novel approach to strengthen the SSM safety requirements by introducing haptic feedback to a robotic cell worker. Tactile stimuli provide early warning of dangerous movements and proximity to the robot, based on the human reaction time and instantaneous velocities of robot and operator. A preliminary experiment was performed to identify the reaction time of participants when they are exposed to tactile stimuli in a collaborative environment with controlled conditions. In a second experiment, we evaluated our approach into a study case where human worker and cobot performed collaborative planetary gear assembly. Results show that the applied approach increased the average minimum distance between the robot's end-effector and hand by 44% compared to the operator relying only on the visual feedback. Moreover, the participants without the haptic support have failed several times to maintain the protective separation distance.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge