Tyler Loakman
Seeing isn't Hearing: Benchmarking Vision Language Models at Interpreting Spectrograms
Nov 17, 2025Abstract:With the rise of Large Language Models (LLMs) and their vision-enabled counterparts (VLMs), numerous works have investigated their capabilities in tasks that fuse the modalities of vision and language. In this work, we benchmark the extent to which VLMs are able to act as highly-trained phoneticians, interpreting spectrograms and waveforms of speech. To do this, we synthesise a novel dataset containing 4k+ English words spoken in isolation alongside stylistically consistent spectrogram and waveform figures. We test the ability of VLMs to understand these representations of speech through a multiple-choice task whereby models must predict the correct phonemic or graphemic transcription of a spoken word when presented amongst 3 distractor transcriptions that have been selected based on their phonemic edit distance to the ground truth. We observe that both zero-shot and finetuned models rarely perform above chance, demonstrating the requirement for specific parametric knowledge of how to interpret such figures, rather than paired samples alone.
Drivel-ology: Challenging LLMs with Interpreting Nonsense with Depth
Sep 04, 2025



Abstract:We introduce Drivelology, a unique linguistic phenomenon characterised as "nonsense with depth", utterances that are syntactically coherent yet pragmatically paradoxical, emotionally loaded, or rhetorically subversive. While such expressions may resemble surface-level nonsense, they encode implicit meaning requiring contextual inference, moral reasoning, or emotional interpretation. We find that current large language models (LLMs), despite excelling at many natural language processing (NLP) tasks, consistently fail to grasp the layered semantics of Drivelological text. To investigate this, we construct a small but diverse benchmark dataset of over 1,200 meticulously curated examples, with select instances in English, Mandarin, Spanish, French, Japanese, and Korean. Annotation was especially challenging: each of the examples required careful expert review to verify that it truly reflected Drivelological characteristics. The process involved multiple rounds of discussion and adjudication to address disagreements, highlighting the subtle and subjective nature of the Drivelology. We evaluate a range of LLMs on classification, generation, and reasoning tasks. Our results reveal clear limitations of LLMs: models often confuse Drivelology with shallow nonsense, produce incoherent justifications, or miss the implied rhetorical function altogether. These findings highlight a deeper representational gap in LLMs' pragmatic understanding and challenge the assumption that statistical fluency implies cognitive comprehension. We release our dataset and code to facilitate further research in modelling linguistic depth beyond surface-level coherence.
Comparing Apples to Oranges: A Dataset & Analysis of LLM Humour Understanding from Traditional Puns to Topical Jokes
Jul 17, 2025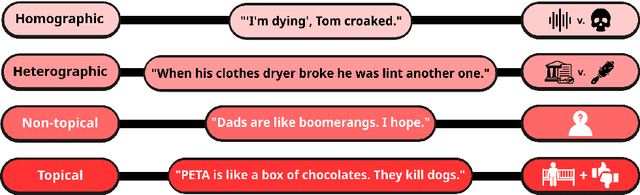
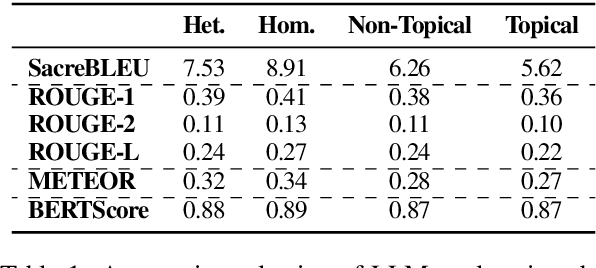
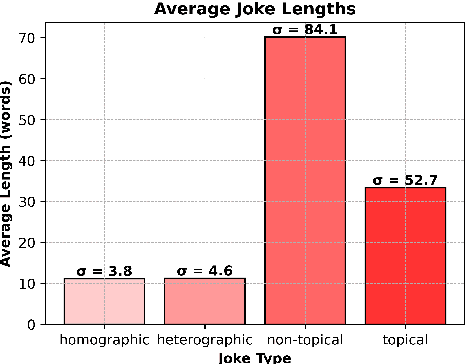
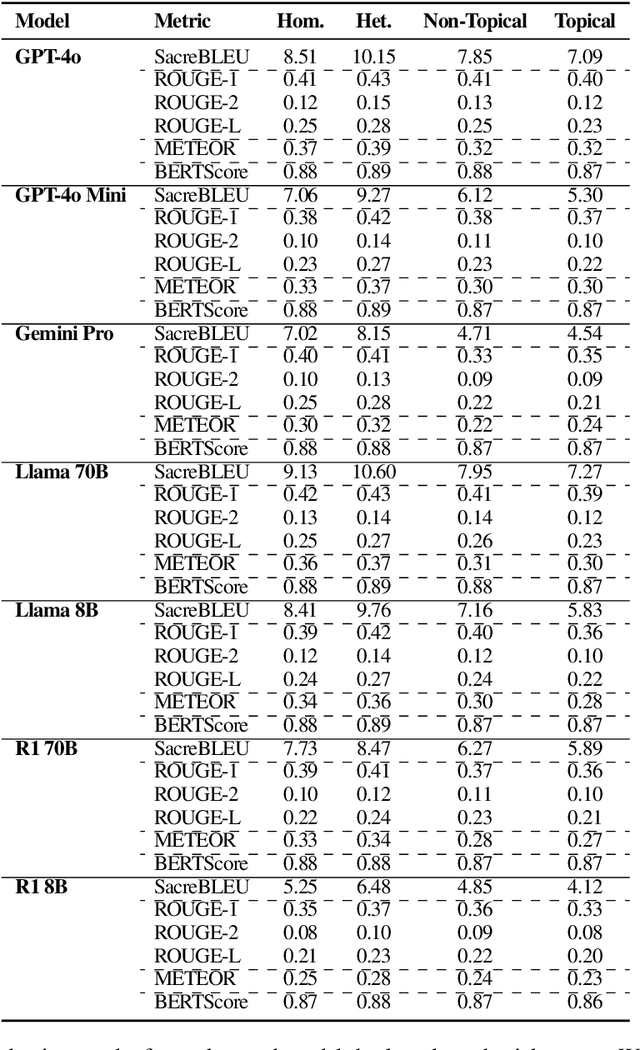
Abstract:Humour, as a complex language form, is derived from myriad aspects of life, whilst existing work on computational humour has focussed almost exclusively on short pun-based jokes. In this work, we investigate whether the ability of Large Language Models (LLMs) to explain humour depends on the particular humour form. We compare models on simple puns and more complex topical humour that requires knowledge of real-world entities and events. In doing so, we curate a dataset of 600 jokes split across 4 joke types and manually write high-quality explanations. These jokes include heterographic and homographic puns, contemporary internet humour, and topical jokes, where understanding relies on reasoning beyond "common sense", rooted instead in world knowledge regarding news events and pop culture. Using this dataset, we compare the zero-shot abilities of a range of LLMs to accurately and comprehensively explain jokes of different types, identifying key research gaps in the task of humour explanation. We find that none of the tested models (inc. reasoning models) are capable of reliably generating adequate explanations of all joke types, further highlighting the narrow focus of most works in computational humour on overly simple joke forms.
Exploring Task Performance with Interpretable Models via Sparse Auto-Encoders
Jul 08, 2025



Abstract:Large Language Models (LLMs) are traditionally viewed as black-box algorithms, therefore reducing trustworthiness and obscuring potential approaches to increasing performance on downstream tasks. In this work, we apply an effective LLM decomposition method using a dictionary-learning approach with sparse autoencoders. This helps extract monosemantic features from polysemantic LLM neurons. Remarkably, our work identifies model-internal misunderstanding, allowing the automatic reformulation of the prompts with additional annotations to improve the interpretation by LLMs. Moreover, this approach demonstrates a significant performance improvement in downstream tasks, such as mathematical reasoning and metaphor detection.
MMTE: Corpus and Metrics for Evaluating Machine Translation Quality of Metaphorical Language
Jun 19, 2024



Abstract:Machine Translation (MT) has developed rapidly since the release of Large Language Models and current MT evaluation is performed through comparison with reference human translations or by predicting quality scores from human-labeled data. However, these mainstream evaluation methods mainly focus on fluency and factual reliability, whilst paying little attention to figurative quality. In this paper, we investigate the figurative quality of MT and propose a set of human evaluation metrics focused on the translation of figurative language. We additionally present a multilingual parallel metaphor corpus generated by post-editing. Our evaluation protocol is designed to estimate four aspects of MT: Metaphorical Equivalence, Emotion, Authenticity, and Quality. In doing so, we observe that translations of figurative expressions display different traits from literal ones.
ReproHum #0087-01: Human Evaluation Reproduction Report for Generating Fact Checking Explanations
Apr 26, 2024Abstract:This paper presents a partial reproduction of Generating Fact Checking Explanations by Anatanasova et al (2020) as part of the ReproHum element of the ReproNLP shared task to reproduce the findings of NLP research regarding human evaluation. This shared task aims to investigate the extent to which NLP as a field is becoming more or less reproducible over time. Following the instructions provided by the task organisers and the original authors, we collect relative rankings of 3 fact-checking explanations (comprising a gold standard and the outputs of 2 models) for 40 inputs on the criteria of Coverage. The results of our reproduction and reanalysis of the original work's raw results lend support to the original findings, with similar patterns seen between the original work and our reproduction. Whilst we observe slight variation from the original results, our findings support the main conclusions drawn by the original authors pertaining to the efficacy of their proposed models.
Train & Constrain: Phonologically Informed Tongue-Twister Generation from Topics and Paraphrases
Mar 20, 2024Abstract:Previous work in phonologically and phonetically grounded language generation has mainly focused on domains such as puns and poetry. In this article, we present new work on the generation of tongue-twisters - a form of language that is required to be conditioned on a phoneme level to maximize sound overlap, whilst maintaining semantic consistency with an input topic and still being grammatically correct. We present TwisterLister, a pipeline for generating phonologically informed tongue-twisters from Large Language Models (LLMs) that we use to generate TwistList 2.0, the largest annotated dataset of tongue-twisters to date, consisting of 17K+ examples from a combination of human and LLM authors. Our generation pipeline involves the use of a phonologically constrained vocabulary alongside LLM prompting to generate novel, non-derivative tongue-twister examples. We additionally present the results of automatic and human evaluation of smaller models trained on our generated dataset to demonstrate the extent to which phonologically motivated language types can be generated without explicit injection of phonological knowledge. Additionally, we introduce a Phoneme-Aware Constrained Decoding module (PACD) that can be integrated into any causal language model and demonstrate that this method generates good quality tongue-twisters both with and without fine-tuning the underlying language model. We also design and implement a range of automatic metrics for the task of tongue-twister generation that is phonologically motivated and captures the unique essence of tongue-twisters based on Phonemic Edit Distance (PED).
A Cross-Attention Augmented Model for Event-Triggered Context-Aware Story Generation
Nov 19, 2023Abstract:Despite recent advancements, existing story generation systems continue to encounter difficulties in effectively incorporating contextual and event features, which greatly influence the quality of generated narratives. To tackle these challenges, we introduce a novel neural generation model, EtriCA, that enhances the relevance and coherence of generated stories by employing a cross-attention mechanism to map context features onto event sequences through residual mapping. This feature capturing mechanism enables our model to exploit logical relationships between events more effectively during the story generation process. To further enhance our proposed model, we employ a post-training framework for knowledge enhancement (KeEtriCA) on a large-scale book corpus. This allows EtriCA to adapt to a wider range of data samples. This results in approximately 5\% improvement in automatic metrics and over 10\% improvement in human evaluation. We conduct extensive experiments, including comparisons with state-of-the-art (SOTA) baseline models, to evaluate the performance of our framework on story generation. The experimental results, encompassing both automated metrics and human assessments, demonstrate the superiority of our model over existing state-of-the-art baselines. These results underscore the effectiveness of our model in leveraging context and event features to improve the quality of generated narratives.
The Iron(ic) Melting Pot: Reviewing Human Evaluation in Humour, Irony and Sarcasm Generation
Nov 09, 2023



Abstract:Human evaluation is often considered to be the gold standard method of evaluating a Natural Language Generation system. However, whilst its importance is accepted by the community at large, the quality of its execution is often brought into question. In this position paper, we argue that the generation of more esoteric forms of language - humour, irony and sarcasm - constitutes a subdomain where the characteristics of selected evaluator panels are of utmost importance, and every effort should be made to report demographic characteristics wherever possible, in the interest of transparency and replicability. We support these claims with an overview of each language form and an analysis of examples in terms of how their interpretation is affected by different participant variables. We additionally perform a critical survey of recent works in NLG to assess how well evaluation procedures are reported in this subdomain, and note a severe lack of open reporting of evaluator demographic information, and a significant reliance on crowdsourcing platforms for recruitment.
Enhancing Dialogue Generation via Dynamic Graph Knowledge Aggregation
Jun 28, 2023



Abstract:Incorporating external graph knowledge into neural chatbot models has been proven effective for enhancing dialogue generation. However, in conventional graph neural networks (GNNs), message passing on a graph is independent from text, resulting in the graph representation hidden space differing from that of the text. This training regime of existing models therefore leads to a semantic gap between graph knowledge and text. In this study, we propose a novel framework for knowledge graph enhanced dialogue generation. We dynamically construct a multi-hop knowledge graph with pseudo nodes to involve the language model in feature aggregation within the graph at all steps. To avoid the semantic biases caused by learning on vanilla subgraphs, the proposed framework applies hierarchical graph attention to aggregate graph features on pseudo nodes and then attains a global feature. Therefore, the framework can better utilise the heterogeneous features from both the post and external graph knowledge. Extensive experiments demonstrate that our framework outperforms state-of-the-art (SOTA) baselines on dialogue generation. Further analysis also shows that our representation learning framework can fill the semantic gap by coagulating representations of both text and graph knowledge. Moreover, the language model also learns how to better select knowledge triples for a more informative response via exploiting subgraph patterns within our feature aggregation process. Our code and resources are available at https://github.com/tangg555/SaBART.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge