Tsz Nam Chan
Understanding and Guiding Layer Placement in Parameter-Efficient Fine-Tuning of Large Language Models
Feb 03, 2026Abstract:As large language models (LLMs) continue to grow, the cost of full-parameter fine-tuning has made parameter-efficient fine-tuning (PEFT) the default strategy for downstream adaptation. Constraints from inference latency in scalable serving and fine-tuning cost in edge or rapid-deployment settings make the choice of which layers to fine-tune unavoidable. Yet current practice typically applies PEFT uniformly across all layers, with limited understanding or leverage of layer selection. This paper develops a unified projected residual view of PEFT on top of a frozen base model. Under a local quadratic approximation, layerwise adaptation is governed by three quantities: (i) the projected residual norm (resnorm), which measures how much correctable bias a layer can capture; (ii) the activation energy, which determines feature conditioning; and (iii) layer coupling, which quantifies how strongly residuals interact across layers. We show that, for squared loss and linear adapters, the resnorm equals a normalized gradient norm, activation energy controls ill-conditioning and noise amplification, and weak coupling yields approximately additive layerwise contributions. Building on these insights, we introduce the Layer Card, a reusable diagnostic that summarizes residual signal strength, compute cost, and performance for each layer of a given model. With an identical model and LoRA configuration, Layer Card-guided placement refines the choice of adapted layers to flexibly prioritize different objectives, such as maximizing performance or reducing fine-tuning cost. Moreover, on Qwen3-8B, we show that selectively adapting a subset of layers can achieve performance close to full-layer LoRA while substantially reducing fine-tuning cost and the number of adapter-augmented layers during inference, offering a more cost-performance-aware alternative to full-layer insertion.
Effective Clustering on Large Attributed Bipartite Graphs
May 20, 2024Abstract:Attributed bipartite graphs (ABGs) are an expressive data model for describing the interactions between two sets of heterogeneous nodes that are associated with rich attributes, such as customer-product purchase networks and author-paper authorship graphs. Partitioning the target node set in such graphs into k disjoint clusters (referred to as k-ABGC) finds widespread use in various domains, including social network analysis, recommendation systems, information retrieval, and bioinformatics. However, the majority of existing solutions towards k-ABGC either overlook attribute information or fail to capture bipartite graph structures accurately, engendering severely compromised result quality. The severity of these issues is accentuated in real ABGs, which often encompass millions of nodes and a sheer volume of attribute data, rendering effective k-ABGC over such graphs highly challenging. In this paper, we propose TPO, an effective and efficient approach to k-ABGC that achieves superb clustering performance on multiple real datasets. TPO obtains high clustering quality through two major contributions: (i) a novel formulation and transformation of the k-ABGC problem based on multi-scale attribute affinity specialized for capturing attribute affinities between nodes with the consideration of their multi-hop connections in ABGs, and (ii) a highly efficient solver that includes a suite of carefully-crafted optimizations for sidestepping explicit affinity matrix construction and facilitating faster convergence. Extensive experiments, comparing TPO against 19 baselines over 5 real ABGs, showcase the superior clustering quality of TPO measured against ground-truth labels. Moreover, compared to the state of the arts, TPO is often more than 40x faster over both small and large ABGs.
Attention-Guided Progressive Neural Texture Fusion for High Dynamic Range Image Restoration
Jul 13, 2021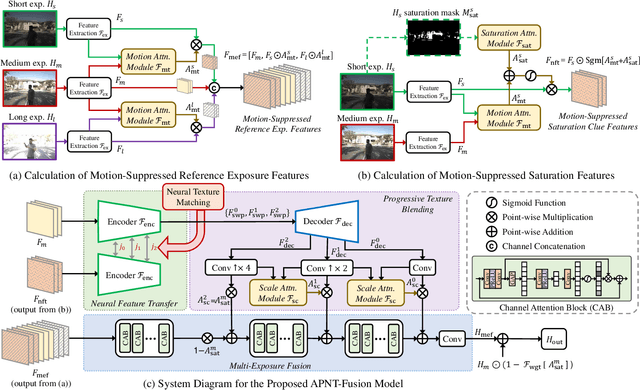
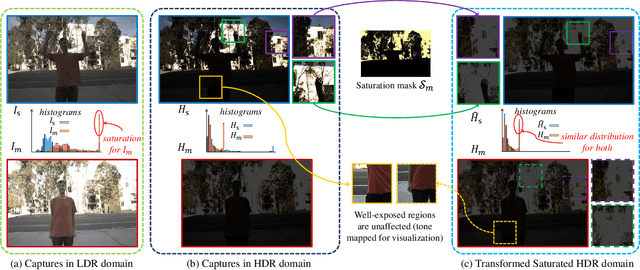
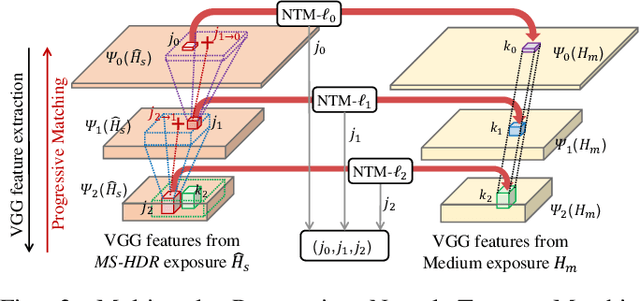
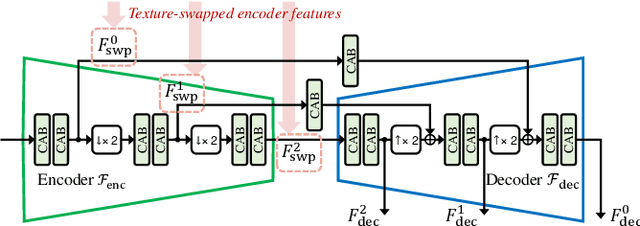
Abstract:High Dynamic Range (HDR) imaging via multi-exposure fusion is an important task for most modern imaging platforms. In spite of recent developments in both hardware and algorithm innovations, challenges remain over content association ambiguities caused by saturation, motion, and various artifacts introduced during multi-exposure fusion such as ghosting, noise, and blur. In this work, we propose an Attention-guided Progressive Neural Texture Fusion (APNT-Fusion) HDR restoration model which aims to address these issues within one framework. An efficient two-stream structure is proposed which separately focuses on texture feature transfer over saturated regions and multi-exposure tonal and texture feature fusion. A neural feature transfer mechanism is proposed which establishes spatial correspondence between different exposures based on multi-scale VGG features in the masked saturated HDR domain for discriminative contextual clues over the ambiguous image areas. A progressive texture blending module is designed to blend the encoded two-stream features in a multi-scale and progressive manner. In addition, we introduce several novel attention mechanisms, i.e., the motion attention module detects and suppresses the content discrepancies among the reference images; the saturation attention module facilitates differentiating the misalignment caused by saturation from those caused by motion; and the scale attention module ensures texture blending consistency between different coder/decoder scales. We carry out comprehensive qualitative and quantitative evaluations and ablation studies, which validate that these novel modules work coherently under the same framework and outperform state-of-the-art methods.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge