Tsung-Han Yang
Automated Clinical Coding for Outpatient Departments
Dec 24, 2023Abstract:Computerised clinical coding approaches aim to automate the process of assigning a set of codes to medical records. While there is active research pushing the state of the art on clinical coding for hospitalized patients, the outpatient setting -- where doctors tend to non-hospitalised patients -- is overlooked. Although both settings can be formalised as a multi-label classification task, they present unique and distinct challenges, which raises the question of whether the success of inpatient clinical coding approaches translates to the outpatient setting. This paper is the first to investigate how well state-of-the-art deep learning-based clinical coding approaches work in the outpatient setting at hospital scale. To this end, we collect a large outpatient dataset comprising over 7 million notes documenting over half a million patients. We adapt four state-of-the-art clinical coding approaches to this setting and evaluate their potential to assist coders. We find evidence that clinical coding in outpatient settings can benefit from more innovations in popular inpatient coding benchmarks. A deeper analysis of the factors contributing to the success -- amount and form of data and choice of document representation -- reveals the presence of easy-to-solve examples, the coding of which can be completely automated with a low error rate.
Parameter Selection: Why We Should Pay More Attention to It
Jul 08, 2021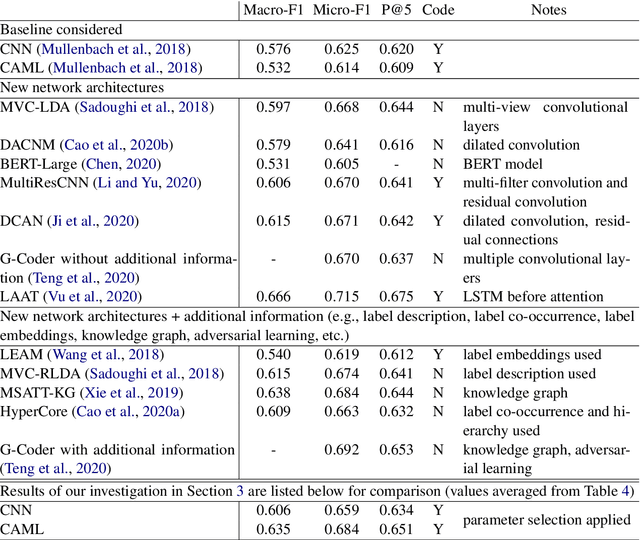
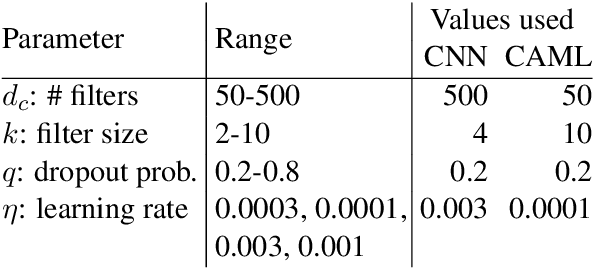
Abstract:The importance of parameter selection in supervised learning is well known. However, due to the many parameter combinations, an incomplete or an insufficient procedure is often applied. This situation may cause misleading or confusing conclusions. In this opinion paper, through an intriguing example we point out that the seriousness goes beyond what is generally recognized. In the topic of multi-label classification for medical code prediction, one influential paper conducted a proper parameter selection on a set, but when moving to a subset of frequently occurring labels, the authors used the same parameters without a separate tuning. The set of frequent labels became a popular benchmark in subsequent studies, which kept pushing the state of the art. However, we discovered that most of the results in these studies cannot surpass the approach in the original paper if a parameter tuning had been conducted at the time. Thus it is unclear how much progress the subsequent developments have actually brought. The lesson clearly indicates that without enough attention on parameter selection, the research progress in our field can be uncertain or even illusive.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge