Jie-Jyun Liu
A Step-by-step Introduction to the Implementation of Automatic Differentiation
Feb 25, 2024Abstract:Automatic differentiation is a key component in deep learning. This topic is well studied and excellent surveys such as Baydin et al. (2018) have been available to clearly describe the basic concepts. Further, sophisticated implementations of automatic differentiation are now an important part of popular deep learning frameworks. However, it is difficult, if not impossible, to directly teach students the implementation of existing systems due to the complexity. On the other hand, if the teaching stops at the basic concept, students fail to sense the realization of an implementation. For example, we often mention the computational graph in teaching automatic differentiation, but students wonder how to implement and use it. In this document, we partially fill the gap by giving a step by step introduction of implementing a simple automatic differentiation system. We streamline the mathematical concepts and the implementation. Further, we give the motivation behind each implementation detail, so the whole setting becomes very natural.
Linear Classifier: An Often-Forgotten Baseline for Text Classification
Jun 12, 2023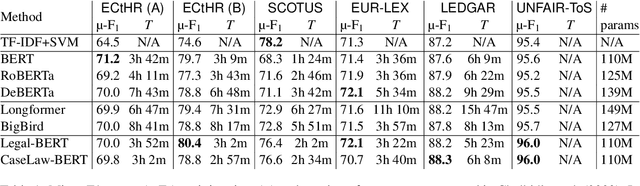
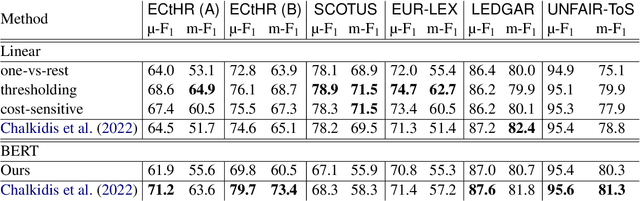
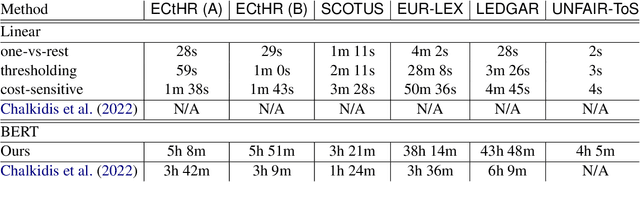
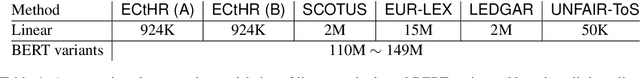
Abstract:Large-scale pre-trained language models such as BERT are popular solutions for text classification. Due to the superior performance of these advanced methods, nowadays, people often directly train them for a few epochs and deploy the obtained model. In this opinion paper, we point out that this way may only sometimes get satisfactory results. We argue the importance of running a simple baseline like linear classifiers on bag-of-words features along with advanced methods. First, for many text data, linear methods show competitive performance, high efficiency, and robustness. Second, advanced models such as BERT may only achieve the best results if properly applied. Simple baselines help to confirm whether the results of advanced models are acceptable. Our experimental results fully support these points.
Mimic-IV-ICD: A new benchmark for eXtreme MultiLabel Classification
Apr 27, 2023



Abstract:Clinical notes are assigned ICD codes - sets of codes for diagnoses and procedures. In the recent years, predictive machine learning models have been built for automatic ICD coding. However, there is a lack of widely accepted benchmarks for automated ICD coding models based on large-scale public EHR data. This paper proposes a public benchmark suite for ICD-10 coding using a large EHR dataset derived from MIMIC-IV, the most recent public EHR dataset. We implement and compare several popular methods for ICD coding prediction tasks to standardize data preprocessing and establish a comprehensive ICD coding benchmark dataset. This approach fosters reproducibility and model comparison, accelerating progress toward employing automated ICD coding in future studies. Furthermore, we create a new ICD-9 benchmark using MIMIC-IV data, providing more data points and a higher number of ICD codes than MIMIC-III. Our open-source code offers easy access to data processing steps, benchmark creation, and experiment replication for those with MIMIC-IV access, providing insights, guidance, and protocols to efficiently develop ICD coding models.
Parameter Selection: Why We Should Pay More Attention to It
Jul 08, 2021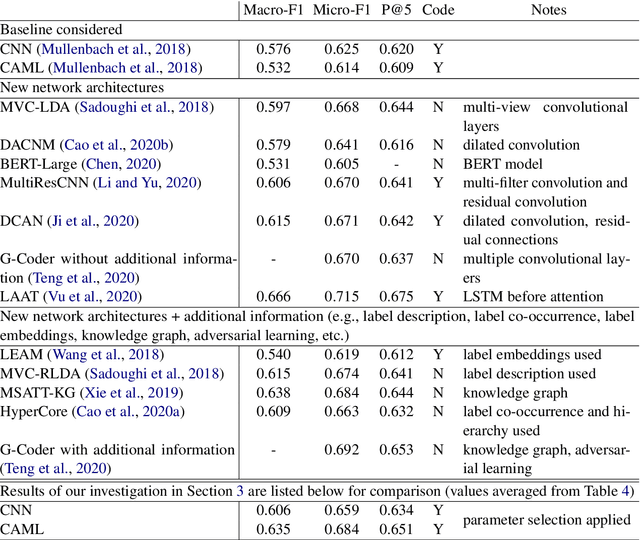
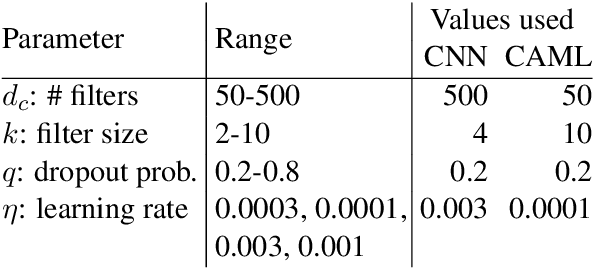
Abstract:The importance of parameter selection in supervised learning is well known. However, due to the many parameter combinations, an incomplete or an insufficient procedure is often applied. This situation may cause misleading or confusing conclusions. In this opinion paper, through an intriguing example we point out that the seriousness goes beyond what is generally recognized. In the topic of multi-label classification for medical code prediction, one influential paper conducted a proper parameter selection on a set, but when moving to a subset of frequently occurring labels, the authors used the same parameters without a separate tuning. The set of frequent labels became a popular benchmark in subsequent studies, which kept pushing the state of the art. However, we discovered that most of the results in these studies cannot surpass the approach in the original paper if a parameter tuning had been conducted at the time. Thus it is unclear how much progress the subsequent developments have actually brought. The lesson clearly indicates that without enough attention on parameter selection, the research progress in our field can be uncertain or even illusive.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge