Tingting He
Do Large Language Models Judge Error Severity Like Humans?
Jun 05, 2025
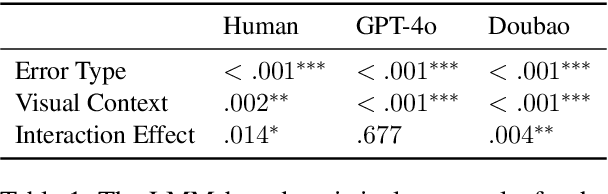

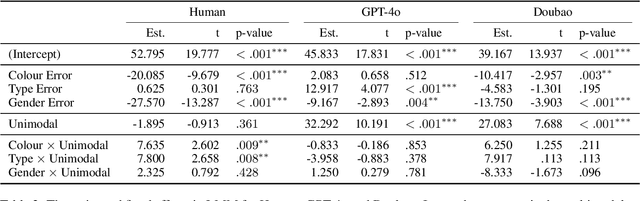
Abstract:Large Language Models (LLMs) are increasingly used as automated evaluators in natural language generation, yet it remains unclear whether they can accurately replicate human judgments of error severity. In this study, we systematically compare human and LLM assessments of image descriptions containing controlled semantic errors. We extend the experimental framework of van Miltenburg et al. (2020) to both unimodal (text-only) and multimodal (text + image) settings, evaluating four error types: age, gender, clothing type, and clothing colour. Our findings reveal that humans assign varying levels of severity to different error types, with visual context significantly amplifying perceived severity for colour and type errors. Notably, most LLMs assign low scores to gender errors but disproportionately high scores to colour errors, unlike humans, who judge both as highly severe but for different reasons. This suggests that these models may have internalised social norms influencing gender judgments but lack the perceptual grounding to emulate human sensitivity to colour, which is shaped by distinct neural mechanisms. Only one of the evaluated LLMs, Doubao, replicates the human-like ranking of error severity, but it fails to distinguish between error types as clearly as humans. Surprisingly, DeepSeek-V3, a unimodal LLM, achieves the highest alignment with human judgments across both unimodal and multimodal conditions, outperforming even state-of-the-art multimodal models.
Emotional Supporters often Use Multiple Strategies in a Single Turn
May 21, 2025Abstract:Emotional Support Conversations (ESC) are crucial for providing empathy, validation, and actionable guidance to individuals in distress. However, existing definitions of the ESC task oversimplify the structure of supportive responses, typically modelling them as single strategy-utterance pairs. Through a detailed corpus analysis of the ESConv dataset, we identify a common yet previously overlooked phenomenon: emotional supporters often employ multiple strategies consecutively within a single turn. We formally redefine the ESC task to account for this, proposing a revised formulation that requires generating the full sequence of strategy-utterance pairs given a dialogue history. To facilitate this refined task, we introduce several modelling approaches, including supervised deep learning models and large language models. Our experiments show that, under this redefined task, state-of-the-art LLMs outperform both supervised models and human supporters. Notably, contrary to some earlier findings, we observe that LLMs frequently ask questions and provide suggestions, demonstrating more holistic support capabilities.
FISH-Tuning: Enhancing PEFT Methods with Fisher Information
Apr 05, 2025Abstract:The rapid growth in the parameter size of Large Language Models (LLMs) has led to the development of Parameter-Efficient Fine-Tuning (PEFT) methods to alleviate the computational costs of fine-tuning. Among these, Fisher Induced Sparse uncHanging (FISH) Mask is a selection-based PEFT technique that identifies a subset of pre-trained parameters for fine-tuning based on approximate Fisher information. However, the integration of FISH Mask with other PEFT methods, such as LoRA and Adapters, remains underexplored. In this paper, we propose FISH-Tuning, a novel approach that incorporates FISH Mask into addition-based and reparameterization-based PEFT methods, including LoRA, Adapters, and their variants. By leveraging Fisher information to select critical parameters within these methods, FISH-Tuning achieves superior performance without additional memory overhead or inference latency. Experimental results across various datasets and pre-trained models demonstrate that FISH-Tuning consistently outperforms the vanilla PEFT methods with the same proportion of trainable parameters.
Rich Semantic Knowledge Enhanced Large Language Models for Few-shot Chinese Spell Checking
Mar 13, 2024



Abstract:Chinese Spell Checking (CSC) is a widely used technology, which plays a vital role in speech to text (STT) and optical character recognition (OCR). Most of the existing CSC approaches relying on BERT architecture achieve excellent performance. However, limited by the scale of the foundation model, BERT-based method does not work well in few-shot scenarios, showing certain limitations in practical applications. In this paper, we explore using an in-context learning method named RS-LLM (Rich Semantic based LLMs) to introduce large language models (LLMs) as the foundation model. Besides, we study the impact of introducing various Chinese rich semantic information in our framework. We found that by introducing a small number of specific Chinese rich semantic structures, LLMs achieve better performance than the BERT-based model on few-shot CSC task. Furthermore, we conduct experiments on multiple datasets, and the experimental results verified the superiority of our proposed framework.
Data-oriented Dynamic Fine-tuning Parameter Selection Strategy for FISH Mask based Efficient Fine-tuning
Mar 13, 2024



Abstract:In view of the huge number of parameters of Large language models (LLMs) , tuning all parameters is very costly, and accordingly fine-tuning specific parameters is more sensible. Most of parameter efficient fine-tuning (PEFT) concentrate on parameter selection strategies, such as additive method, selective method and reparametrization-based method. However, there are few methods that consider the impact of data samples on parameter selecting, such as Fish Mask based method. Fish Mask randomly choose a part of data samples and treat them equally during parameter selection, which is unable to dynamically select optimal parameters for inconstant data distributions. In this work, we adopt a data-oriented perspective, then proposing an IRD ($\mathrm{\underline I}$terative sample-parameter $\mathrm{\underline R}$ange $\mathrm{\underline D}$ecreasing) algorithm to search the best setting of sample-parameter pair for FISH Mask. In each iteration, by searching the set of samples and parameters with larger Fish information, IRD can find better sample-parameter pair in most scale. We demonstrate the effectiveness and rationality of proposed strategy by conducting experiments on GLUE benchmark. Experimental results show our strategy optimizes the parameter selection and achieves preferable performance.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge