Tingjun Huang
TextInPlace: Indoor Visual Place Recognition in Repetitive Structures with Scene Text Spotting and Verification
Mar 09, 2025Abstract:Visual Place Recognition (VPR) is a crucial capability for long-term autonomous robots, enabling them to identify previously visited locations using visual information. However, existing methods remain limited in indoor settings due to the highly repetitive structures inherent in such environments. We observe that scene text typically appears in indoor spaces, serving to distinguish visually similar but different places. This inspires us to propose TextInPlace, a simple yet effective VPR framework that integrates Scene Text Spotting (STS) to mitigate visual perceptual ambiguity in repetitive indoor environments. Specifically, TextInPlace adopts a dual-branch architecture within a local parameter sharing network. The VPR branch employs attention-based aggregation to extract global descriptors for coarse-grained retrieval, while the STS branch utilizes a bridging text spotter to detect and recognize scene text. Finally, the discriminative text is filtered to compute text similarity and re-rank the top-K retrieved images. To bridge the gap between current text-based repetitive indoor scene datasets and the typical scenarios encountered in robot navigation, we establish an indoor VPR benchmark dataset, called Maze-with-Text. Extensive experiments on both custom and public datasets demonstrate that TextInPlace achieves superior performance over existing methods that rely solely on appearance information. The dataset, code, and trained models are publicly available at https://github.com/HqiTao/TextInPlace.
NocPlace: Nocturnal Visual Place Recognition Using Generative and Inherited Knowledge Transfer
Feb 27, 2024
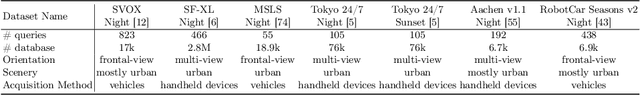

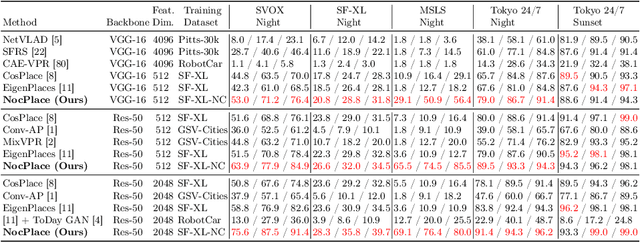
Abstract:Visual Place Recognition (VPR) is crucial in computer vision, aiming to retrieve database images similar to a query image from an extensive collection of known images. However, like many vision-related tasks, learning-based VPR often experiences a decline in performance during nighttime due to the scarcity of nighttime images. Specifically, VPR needs to address the cross-domain problem of night-to-day rather than just the issue of a single nighttime domain. In response to these issues, we present NocPlace, which leverages a generated large-scale, multi-view, nighttime VPR dataset to embed resilience against dazzling lights and extreme darkness in the learned global descriptor. Firstly, we establish a day-night urban scene dataset called NightCities, capturing diverse nighttime scenarios and lighting variations across 60 cities globally. Following this, an unpaired image-to-image translation network is trained on this dataset. Using this trained translation network, we process an existing VPR dataset, thereby obtaining its nighttime version. The NocPlace is then fine-tuned using night-style images, the original labels, and descriptors inherited from the Daytime VPR model. Comprehensive experiments on various nighttime VPR test sets reveal that NocPlace considerably surpasses previous state-of-the-art methods.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge