Tien-Fu Chen
Time-IMM: A Dataset and Benchmark for Irregular Multimodal Multivariate Time Series
Jun 12, 2025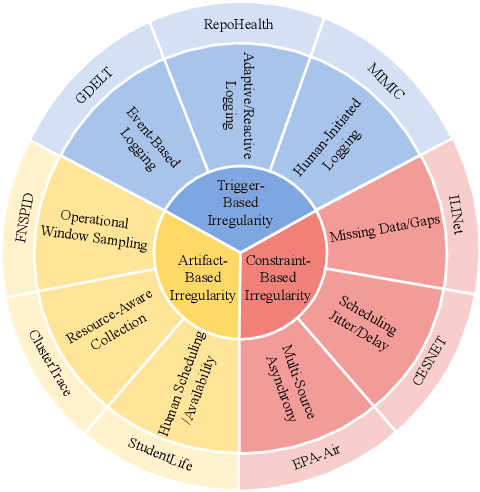
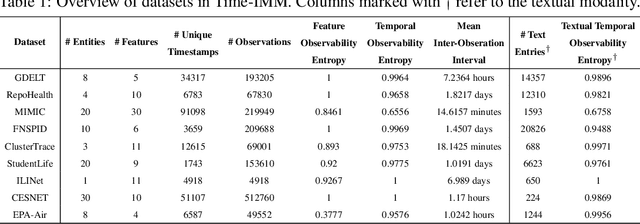
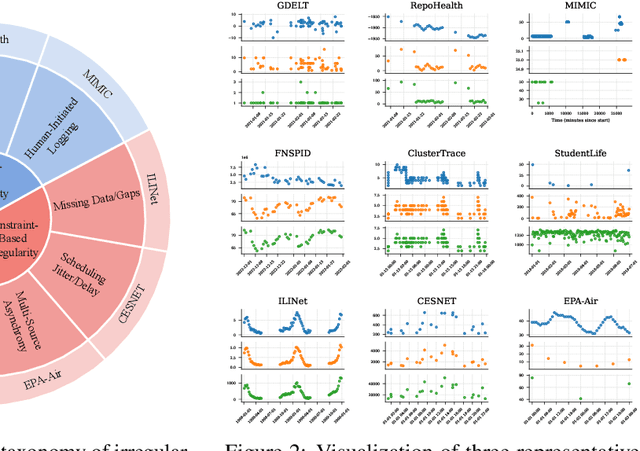
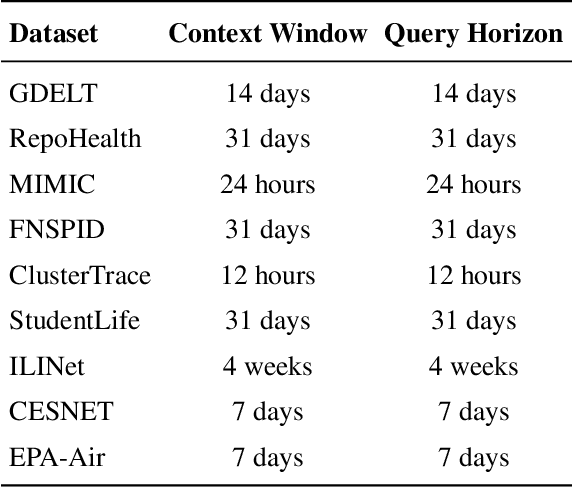
Abstract:Time series data in real-world applications such as healthcare, climate modeling, and finance are often irregular, multimodal, and messy, with varying sampling rates, asynchronous modalities, and pervasive missingness. However, existing benchmarks typically assume clean, regularly sampled, unimodal data, creating a significant gap between research and real-world deployment. We introduce Time-IMM, a dataset specifically designed to capture cause-driven irregularity in multimodal multivariate time series. Time-IMM represents nine distinct types of time series irregularity, categorized into trigger-based, constraint-based, and artifact-based mechanisms. Complementing the dataset, we introduce IMM-TSF, a benchmark library for forecasting on irregular multimodal time series, enabling asynchronous integration and realistic evaluation. IMM-TSF includes specialized fusion modules, including a timestamp-to-text fusion module and a multimodality fusion module, which support both recency-aware averaging and attention-based integration strategies. Empirical results demonstrate that explicitly modeling multimodality on irregular time series data leads to substantial gains in forecasting performance. Time-IMM and IMM-TSF provide a foundation for advancing time series analysis under real-world conditions. The dataset is publicly available at https://www.kaggle.com/datasets/blacksnail789521/time-imm/data, and the benchmark library can be accessed at https://anonymous.4open.science/r/IMMTSF_NeurIPS2025.
PromptTSS: A Prompting-Based Approach for Interactive Multi-Granularity Time Series Segmentation
Jun 12, 2025Abstract:Multivariate time series data, collected across various fields such as manufacturing and wearable technology, exhibit states at multiple levels of granularity, from coarse-grained system behaviors to fine-grained, detailed events. Effectively segmenting and integrating states across these different granularities is crucial for tasks like predictive maintenance and performance optimization. However, existing time series segmentation methods face two key challenges: (1) the inability to handle multiple levels of granularity within a unified model, and (2) limited adaptability to new, evolving patterns in dynamic environments. To address these challenges, we propose PromptTSS, a novel framework for time series segmentation with multi-granularity states. PromptTSS uses a unified model with a prompting mechanism that leverages label and boundary information to guide segmentation, capturing both coarse- and fine-grained patterns while adapting dynamically to unseen patterns. Experiments show PromptTSS improves accuracy by 24.49% in multi-granularity segmentation, 17.88% in single-granularity segmentation, and up to 599.24% in transfer learning, demonstrating its adaptability to hierarchical states and evolving time series dynamics.
Self-Supervised Learning of Disentangled Representations for Multivariate Time-Series
Oct 16, 2024



Abstract:Multivariate time-series data in fields like healthcare and industry are informative but challenging due to high dimensionality and lack of labels. Recent self-supervised learning methods excel in learning rich representations without labels but struggle with disentangled embeddings and inductive bias issues like transformation-invariance. To address these challenges, we introduce TimeDRL, a framework for multivariate time-series representation learning with dual-level disentangled embeddings. TimeDRL features: (i) disentangled timestamp-level and instance-level embeddings using a [CLS] token strategy; (ii) timestamp-predictive and instance-contrastive tasks for representation learning; and (iii) avoidance of augmentation methods to eliminate inductive biases. Experiments on forecasting and classification datasets show TimeDRL outperforms existing methods, with further validation in semi-supervised settings with limited labeled data.
TimeDRL: Disentangled Representation Learning for Multivariate Time-Series
Dec 07, 2023



Abstract:Multivariate time-series data in numerous real-world applications (e.g., healthcare and industry) are informative but challenging due to the lack of labels and high dimensionality. Recent studies in self-supervised learning have shown their potential in learning rich representations without relying on labels, yet they fall short in learning disentangled embeddings and addressing issues of inductive bias (e.g., transformation-invariance). To tackle these challenges, we propose TimeDRL, a generic multivariate time-series representation learning framework with disentangled dual-level embeddings. TimeDRL is characterized by three novel features: (i) disentangled derivation of timestamp-level and instance-level embeddings from patched time-series data using a [CLS] token strategy; (ii) utilization of timestamp-predictive and instance-contrastive tasks for disentangled representation learning, with the former optimizing timestamp-level embeddings with predictive loss, and the latter optimizing instance-level embeddings with contrastive loss; and (iii) avoidance of augmentation methods to eliminate inductive biases, such as transformation-invariance from cropping and masking. Comprehensive experiments on 6 time-series forecasting datasets and 5 time-series classification datasets have shown that TimeDRL consistently surpasses existing representation learning approaches, achieving an average improvement of forecasting by 57.98% in MSE and classification by 1.25% in accuracy. Furthermore, extensive ablation studies confirmed the relative contribution of each component in TimeDRL's architecture, and semi-supervised learning evaluations demonstrated its effectiveness in real-world scenarios, even with limited labeled data.
LLM4TS: Two-Stage Fine-Tuning for Time-Series Forecasting with Pre-Trained LLMs
Aug 16, 2023



Abstract:In this work, we leverage pre-trained Large Language Models (LLMs) to enhance time-series forecasting. Mirroring the growing interest in unifying models for Natural Language Processing and Computer Vision, we envision creating an analogous model for long-term time-series forecasting. Due to limited large-scale time-series data for building robust foundation models, our approach LLM4TS focuses on leveraging the strengths of pre-trained LLMs. By combining time-series patching with temporal encoding, we have enhanced the capability of LLMs to handle time-series data effectively. Inspired by the supervised fine-tuning in chatbot domains, we prioritize a two-stage fine-tuning process: first conducting supervised fine-tuning to orient the LLM towards time-series data, followed by task-specific downstream fine-tuning. Furthermore, to unlock the flexibility of pre-trained LLMs without extensive parameter adjustments, we adopt several Parameter-Efficient Fine-Tuning (PEFT) techniques. Drawing on these innovations, LLM4TS has yielded state-of-the-art results in long-term forecasting. Our model has also shown exceptional capabilities as both a robust representation learner and an effective few-shot learner, thanks to the knowledge transferred from the pre-trained LLM.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge