Tianyi Gui
AdPO: Enhancing the Adversarial Robustness of Large Vision-Language Models with Preference Optimization
Apr 02, 2025



Abstract:Large Vision-Language Models (LVLMs), such as GPT-4o and LLaVA, have recently witnessed remarkable advancements and are increasingly being deployed in real-world applications. However, inheriting the sensitivity of visual neural networks, LVLMs remain vulnerable to adversarial attacks, which can result in erroneous or malicious outputs. While existing efforts utilize adversarial fine-tuning to enhance robustness, they often suffer from performance degradation on clean inputs. In this paper, we proposes AdPO, a novel adversarial defense strategy for LVLMs based on preference optimization. For the first time, we reframe adversarial training as a preference optimization problem, aiming to enhance the model's preference for generating normal outputs on clean inputs while rejecting the potential misleading outputs for adversarial examples. Notably, AdPO achieves this by solely modifying the image encoder, e.g., CLIP ViT, resulting in superior clean and adversarial performance in a variety of downsream tasks. Considering that training involves large language models (LLMs), the computational cost increases significantly. We validate that training on smaller LVLMs and subsequently transferring to larger models can achieve competitive performance while maintaining efficiency comparable to baseline methods. Our comprehensive experiments confirm the effectiveness of the proposed AdPO, which provides a novel perspective for future adversarial defense research.
Wan: Open and Advanced Large-Scale Video Generative Models
Mar 26, 2025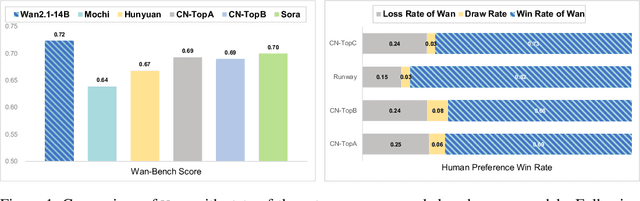



Abstract:This report presents Wan, a comprehensive and open suite of video foundation models designed to push the boundaries of video generation. Built upon the mainstream diffusion transformer paradigm, Wan achieves significant advancements in generative capabilities through a series of innovations, including our novel VAE, scalable pre-training strategies, large-scale data curation, and automated evaluation metrics. These contributions collectively enhance the model's performance and versatility. Specifically, Wan is characterized by four key features: Leading Performance: The 14B model of Wan, trained on a vast dataset comprising billions of images and videos, demonstrates the scaling laws of video generation with respect to both data and model size. It consistently outperforms the existing open-source models as well as state-of-the-art commercial solutions across multiple internal and external benchmarks, demonstrating a clear and significant performance superiority. Comprehensiveness: Wan offers two capable models, i.e., 1.3B and 14B parameters, for efficiency and effectiveness respectively. It also covers multiple downstream applications, including image-to-video, instruction-guided video editing, and personal video generation, encompassing up to eight tasks. Consumer-Grade Efficiency: The 1.3B model demonstrates exceptional resource efficiency, requiring only 8.19 GB VRAM, making it compatible with a wide range of consumer-grade GPUs. Openness: We open-source the entire series of Wan, including source code and all models, with the goal of fostering the growth of the video generation community. This openness seeks to significantly expand the creative possibilities of video production in the industry and provide academia with high-quality video foundation models. All the code and models are available at https://github.com/Wan-Video/Wan2.1.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge