Thomas Eriksson
Statistical Properties of Target Localization Using Passive Radar Systems
Jan 28, 2026Abstract:Passive Radar Systems have received tremendous attention during the past few decades, due to their low cost and ability to remain covert during operation. Such systems do not transmit any energy themselves, but rely on a so-called Illuminator-of-Opportunity (IO), for example a commercial TV station. A network of Receiving Nodes (RN) receive the direct signal as well as reflections from possible targets. The RNs transmit information to a Central Node (CN), that performs the final target detection, localization and tracking. A large number of methods and algorithms for target detection and localization have been proposed in the literature. In the present contribution, the focus is on the seminal Extended Cancelation Algorithm (ECA), in which each RN estimates target parameters after canceling interference from the direct-path as well as clutter from unwanted stationary objects. This is done by exploiting a separate Reference Channel (RC), which captures the IO signal without interference apart from receiver noise. We derive the statistical properties of the ECA parameter estimates under the assumption of a high Signal-to-Noise Ratio (SNR), and we give a sufficient condition for the SNR in the RC to enable statistically efficient estimates. The theoretical results are corroborated through computer simulations, which show that the theory agrees well with empirical results above a certain SNR threshold. The results can be used to predict the performance of passive radar systems in given scenarios, which is useful for feasibility studies as well as system design.
Separable Delay And Doppler Estimation In Passive Radar
Jan 22, 2026Abstract:In passive radar, a network of distributed sensors exploit signals from so-called Illuminators-of-Opportunity to detect and localize targets. We consider the case where the IO signal is available at each receiver node through a reference channel, whereas target returns corrupted by interference are collected in a separate surveillance channel. The problem formulation is similar to an active radar that uses a noise-like waveform, or an integrated sensing and communication application. The available data is first split into batches of manageable size. In the direct approach, the target's time-delay and Doppler parameters are estimated jointly by incoherently combining the batch-wise data. We propose a new method to estimate the time-delay separately, thus avoiding a costly 2-D search. Our approach is designed for slowly moving targets, and the accuracy of the time-delay estimate is similar to that of the full batch-wise 2-D method. Given the time-delay, the coherency between batches can be restored when estimating the Doppler parameter. Thereby, the separable approach is found to yield superior Doppler estimates over a wide parameter range. In addition to reducing computational complexity, the proposed separable estimation technique also significantly reduces the communication overhead in a distributed radar setting.
Statistical Analysis of Target Parameter Estimation Using Passive Radar
Oct 09, 2025Abstract:A passive radar system uses one or more so-called Illuminators of Opportunity (IO) to detect and localize targets. In such systems, a reference channel is often used at each receiving node to capture the transmitted IO signal, while targets are detected using the main surveillance channel. The purpose of the present contribution is to analyze a method for estimating the target parameters in such a system. Specifically, we quantify the additional error contribution due to not knowing the transmitted IO waveform perfectly. A sufficient condition for this error to be negligible as compared to errors due to clutter and noise in the surveillance channel is then given.
Autoregressive Stochastic Clock Jitter Compensation in Analog-to-Digital Converters
May 08, 2025Abstract:This paper deals with the mathematical modeling and compensation of stochastic discrete time clock jitter in Analog-to-Digital Converters (ADCs). Two novel, computationally efficient de-jittering sample pilots-based algorithms for baseband signals are proposed: one consisting in solving a sequence of weighted least-squares problems and another that fully leverages the correlated jitter structure in a Kalman filter-type routine. Alongside, a comprehensive and rigorous mathematical analysis of the linearization errors committed is presented, and the work is complemented with extensive synthetic simulations and performance benchmarking with the scope of gauging and stress-testing the techniques in different scenarios.
Modeling, Analysis, and Optimization of Cascaded Power Amplifiers
Mar 19, 2025



Abstract:This paper deals with modeling, analysis, and optimization of power amplifiers (PAs) placed in a cascaded structure, particularly the effect of cascaded nonlinearities is studied by showing potential ways to minimize the total nonlinearities. The nonlinear least-squares algorithm is proposed to optimize the PA parameters along with the input power level, and thereby minimize the total nonlinearities in the cascaded structure. The simulation results demonstrate that the performance of the optimized configurations for up to five PAs using the proposed framework can improve the linearity properties of the overall cascade.
6G Radio Testbeds: Requirements, Trends, and Approaches
Sep 13, 2023



Abstract:The proof of the pudding is in the eating - that is why 6G testbeds are essential in the progress towards the next generation of wireless networks. Theoretical research towards 6G wireless networks is proposing advanced technologies to serve new applications and drastically improve the energy performance of the network. Testbeds are indispensable to validate these new technologies under more realistic conditions. This paper clarifies the requirements for 6G radio testbeds, reveals trends, and introduces approaches towards their development.
Modeling and Analysis of 6G Joint Localization and Communication under Hardware Impairments
Jan 03, 2023



Abstract:Localization (position and orientation estimation) is envisioned as a key enabler to satisfy the requirements of communication and context-aware services in the sixth generation (6G) communication systems. User localization can be achieved based on delay and angle estimation using uplink or downlink pilot signals. However, hardware impairments (HWIs) distort the signals at both the transmitter and receiver sides and thus affect the localization performance. While this impact can be ignored at lower frequencies where HWIs are less severe, and the localization requirements are not stringent, modeling and analysis efforts are needed for high-frequency 6G bands (e.g., sub-THz) to assess degradation in localization accuracy due to HWIs. In this work, we model various types of impairments for a sub-THz multiple-input-multiple-output communication system and conduct a misspecified Cram\'er-Rao bound analysis to evaluate HWI-induced performance losses in terms of angle/delay estimation and the resulting 3D position/orientation estimation error. Complementary to the localization analysis, we also investigate the effect of individual and overall HWIs on communication in terms of symbol error rate (SER). Our extensive simulation results demonstrate that each type of HWI leads to a different level of degradation in angle and delay estimation performance. The prominent factors on delay estimation (e.g., phase noise and carrier frequency offset) will have a dominant negative effect on SER, while the impairments affecting only the angle estimation (e.g., mutual coupling and antenna displacement) induce slight degradation in SER performance.
MCRB-based Performance Analysis of 6G Localization under Hardware Impairments
Apr 27, 2022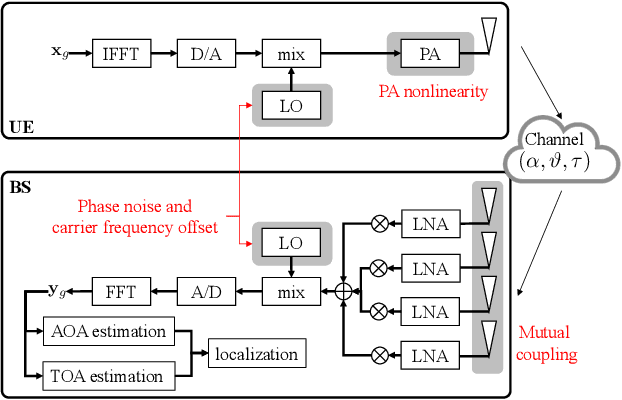
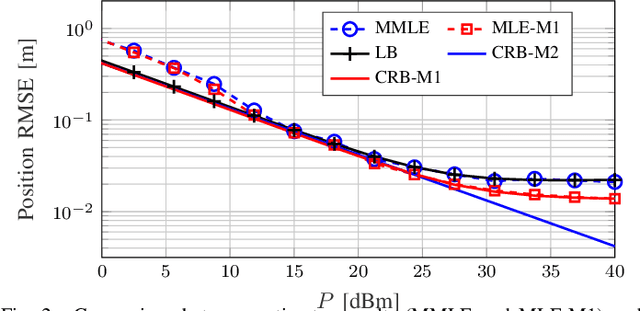
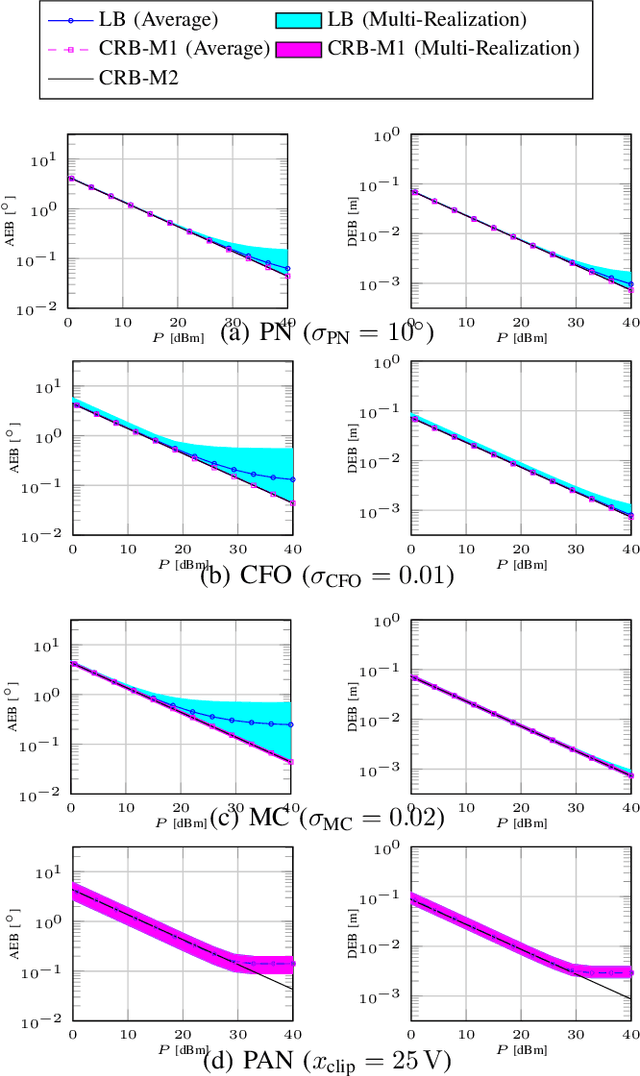
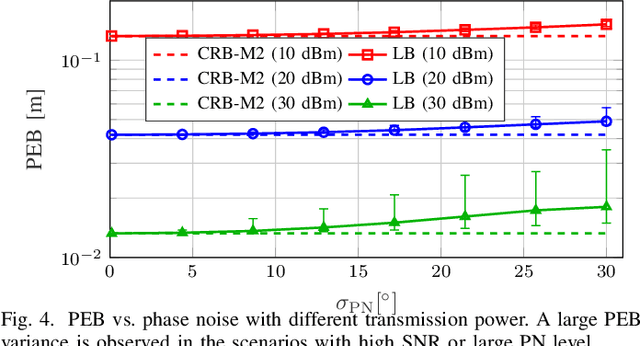
Abstract:Location information is expected to be the key to meeting the needs of communication and context-aware services in 6G systems. User localization is achieved based on delay and/or angle estimation using uplink or downlink pilot signals. However, hardware impairments (HWIs) distort the signals at both the transmitter and receiver sides and thus affect the localization performance. While this impact can be ignored at lower frequencies where HWIs are less severe, modeling and analysis efforts are needed for 6G to evaluate the localization degradation due to HWIs. In this work, we model various types of impairments and conduct a misspecified Cram\'er-Rao bound analysis to evaluate the HWI-induced performance loss. Simulation results with different types of HWIs show that each HWI leads to a different level of degradation in angle and delay estimation performance.
Distortion-Aware Linear Precoding for Massive MIMO Downlink Systems with Nonlinear Power Amplifiers
Dec 24, 2020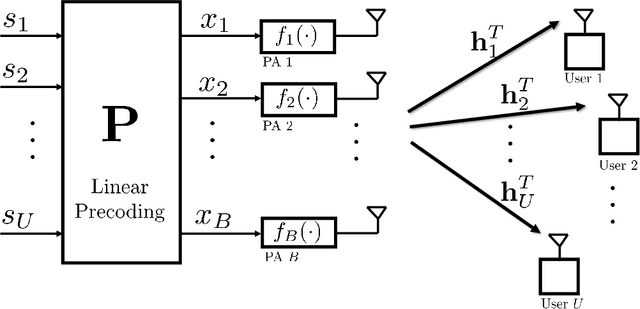
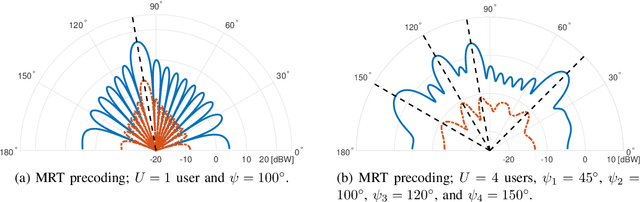
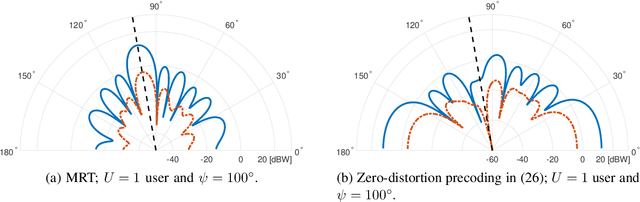
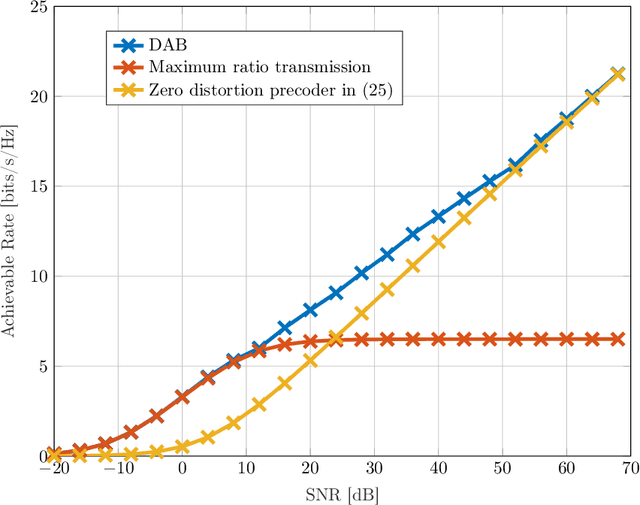
Abstract:We introduce a framework for linear precoder design over a massive multiple-input multiple-output downlink system and in presence of nonlinear power amplifiers (PAs). By studying the spatial characteristics of the distortion, we demonstrate that conventional linear precoding techniques steer nonlinear distortions in the direction of the users. We show that, by taking into account PA nonlinearity characteristics, one can design linear precoders that reduce, and in single-user scenarios, even remove completely the distortion transmitted in the direction of the users. This, however, is achieved at the price of a considerably reduced array gain. To address this issue, we present precoder optimization algorithms which simultaneously take into account the effects of array gain, distortion, multiuser interference, and receiver noise. Specifically, we derive an expression for the achievable sum rate and propose an iterative algorithm that attempts to find the precoding matrix maximizing this expression. Moreover, using a model for PA power consumption, we propose an algorithm that attempts to find the precoding matrix minimizing the consumed power for a given minimum achievable sum rate. Our numerical results demonstrate that the proposed distortion-aware precoding techniques yield considerable improvements in terms of spectral and energy efficiency compared to conventional linear precoding techniques.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge