Théophile Gaudin
Leap: molecular synthesisability scoring with intermediates
Mar 14, 2024Abstract:Assessing whether a molecule can be synthesised is a primary task in drug discovery. It enables computational chemists to filter for viable compounds or bias molecular generative models. The notion of synthesisability is dynamic as it evolves depending on the availability of key compounds. A common approach in drug discovery involves exploring the chemical space surrounding synthetically-accessible intermediates. This strategy improves the synthesisability of the derived molecules due to the availability of key intermediates. Existing synthesisability scoring methods such as SAScore, SCScore and RAScore, cannot condition on intermediates dynamically. Our approach, Leap, is a GPT-2 model trained on the depth, or longest linear path, of predicted synthesis routes that allows information on the availability of key intermediates to be included at inference time. We show that Leap surpasses all other scoring methods by at least 5% on AUC score when identifying synthesisable molecules, and can successfully adapt predicted scores when presented with a relevant intermediate compound.
SELFIES and the future of molecular string representations
Mar 31, 2022
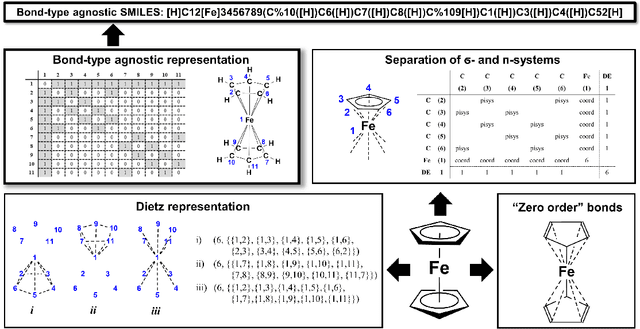
Abstract:Artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) are expanding in popularity for broad applications to challenging tasks in chemistry and materials science. Examples include the prediction of properties, the discovery of new reaction pathways, or the design of new molecules. The machine needs to read and write fluently in a chemical language for each of these tasks. Strings are a common tool to represent molecular graphs, and the most popular molecular string representation, SMILES, has powered cheminformatics since the late 1980s. However, in the context of AI and ML in chemistry, SMILES has several shortcomings -- most pertinently, most combinations of symbols lead to invalid results with no valid chemical interpretation. To overcome this issue, a new language for molecules was introduced in 2020 that guarantees 100\% robustness: SELFIES (SELF-referencIng Embedded Strings). SELFIES has since simplified and enabled numerous new applications in chemistry. In this manuscript, we look to the future and discuss molecular string representations, along with their respective opportunities and challenges. We propose 16 concrete Future Projects for robust molecular representations. These involve the extension toward new chemical domains, exciting questions at the interface of AI and robust languages and interpretability for both humans and machines. We hope that these proposals will inspire several follow-up works exploiting the full potential of molecular string representations for the future of AI in chemistry and materials science.
Molecular Transformer for Chemical Reaction Prediction and Uncertainty Estimation
Nov 06, 2018

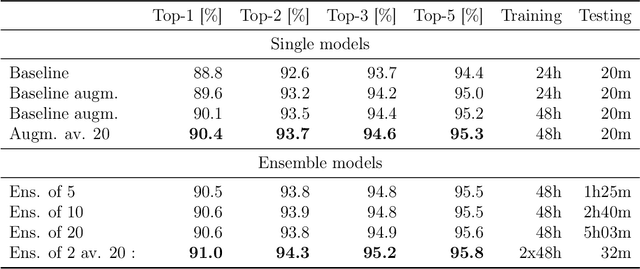
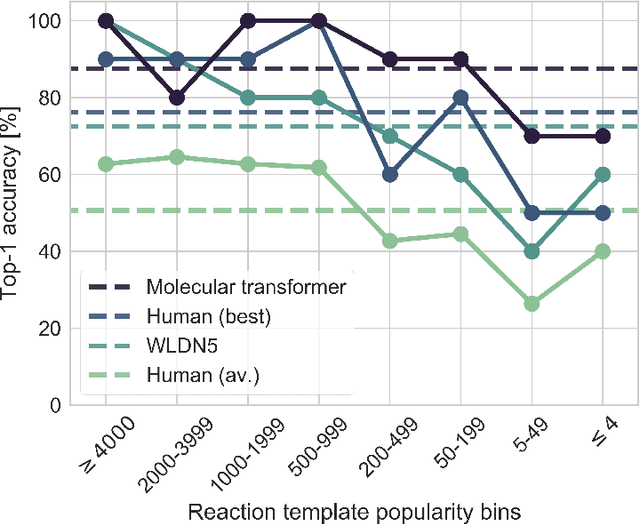
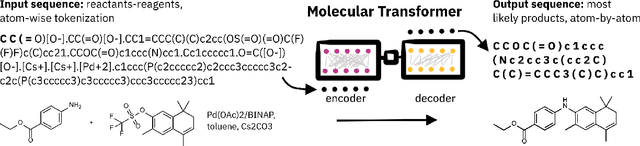
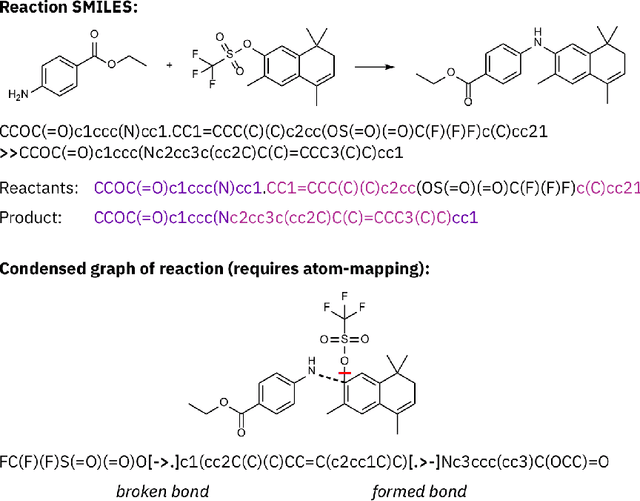
Abstract:Organic synthesis is one of the key stumbling blocks in medicinal chemistry. A necessary yet unsolved step in planning synthesis is solving the forward problem: given reactants and reagents, predict the products. Similar to other works, we treat reaction prediction as a machine translation problem between SMILES strings of reactants-reagents and the products. We show that a multi-head attention Molecular Transformer model outperforms all algorithms in the literature, achieving a top-1 accuracy above 90% on a common benchmark dataset. Our algorithm requires no handcrafted rules, and accurately predicts subtle chemical transformations. Crucially, our model can accurately estimate its own uncertainty, with an uncertainty score that is 89% accurate in terms of classifying whether a prediction is correct. Furthermore, we show that the model is able to handle inputs without reactant-reagent split and including stereochemistry, which makes our method universally applicable.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge