Tejas Mehta
Instant Answering in E-Commerce Buyer-Seller Messaging using Message-to-Question Reformulation
Jan 30, 2024
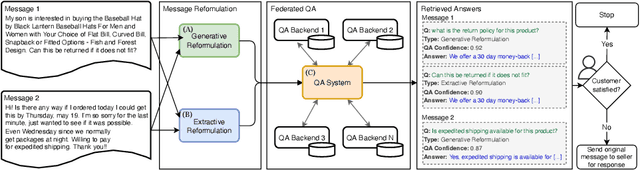
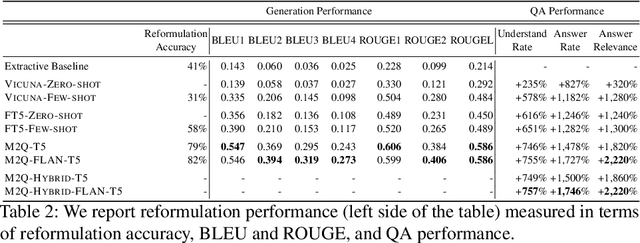
Abstract:E-commerce customers frequently seek detailed product information for purchase decisions, commonly contacting sellers directly with extended queries. This manual response requirement imposes additional costs and disrupts buyer's shopping experience with response time fluctuations ranging from hours to days. We seek to automate buyer inquiries to sellers in a leading e-commerce store using a domain-specific federated Question Answering (QA) system. The main challenge is adapting current QA systems, designed for single questions, to address detailed customer queries. We address this with a low-latency, sequence-to-sequence approach, MESSAGE-TO-QUESTION ( M2Q ). It reformulates buyer messages into succinct questions by identifying and extracting the most salient information from a message. Evaluation against baselines shows that M2Q yields relative increases of 757% in question understanding, and 1,746% in answering rate from the federated QA system. Live deployment shows that automatic answering saves sellers from manually responding to millions of messages per year, and also accelerates customer purchase decisions by eliminating the need for buyers to wait for a reply
Toward Automatic Threat Recognition for Airport X-ray Baggage Screening with Deep Convolutional Object Detection
Dec 13, 2019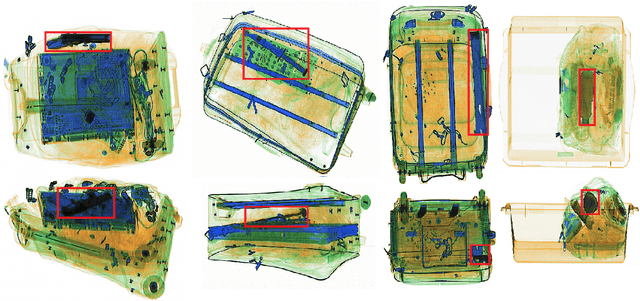
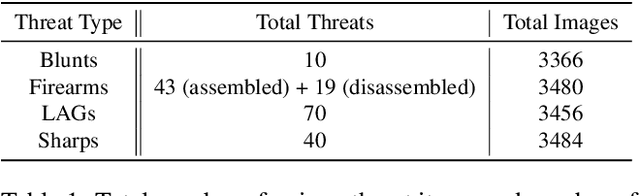
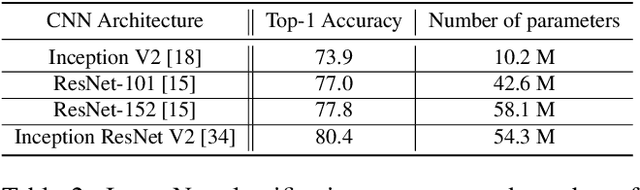
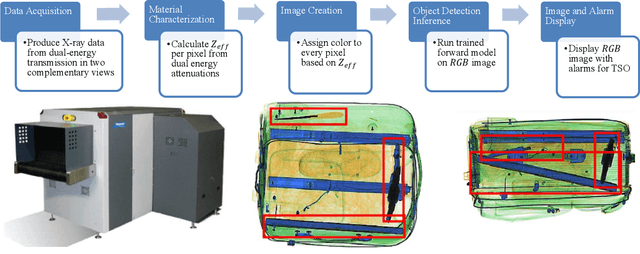
Abstract:For the safety of the traveling public, the Transportation Security Administration (TSA) operates security checkpoints at airports in the United States, seeking to keep dangerous items off airplanes. At these checkpoints, the TSA employs a fleet of X-ray scanners, such as the Rapiscan 620DV, so Transportation Security Officers (TSOs) can inspect the contents of carry-on possessions. However, identifying and locating all potential threats can be a challenging task. As a result, the TSA has taken a recent interest in deep learning-based automated detection algorithms that can assist TSOs. In a collaboration funded by the TSA, we collected a sizable new dataset of X-ray scans with a diverse set of threats in a wide array of contexts, trained several deep convolutional object detection models, and integrated such models into the Rapiscan 620DV, resulting in functional prototypes capable of operating in real time. We show performance of our models on held-out evaluation sets, analyze several design parameters, and demonstrate the potential of such systems for automated detection of threats that can be found in airports.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge