Tarik Alafif
An Adaptive Batch Normalization in Deep Learning
Nov 03, 2022Abstract:Batch Normalization (BN) is a way to accelerate and stabilize training in deep convolutional neural networks. However, the BN works continuously within the network structure, although some training data may not always require it. In this research work, we propose a threshold-based adaptive BN approach that separates the data that requires the BN and data that does not require it. The experimental evaluation demonstrates that proposed approach achieves better performance mostly in small batch sizes than the traditional BN using MNIST, Fashion-MNIST, CIFAR-10, and CIFAR-100. It also reduces the occurrence of internal variable transformation to increase network stability
ViT-DeiT: An Ensemble Model for Breast Cancer Histopathological Images Classification
Nov 01, 2022Abstract:Breast cancer is the most common cancer in the world and the second most common type of cancer that causes death in women. The timely and accurate diagnosis of breast cancer using histopathological images is crucial for patient care and treatment. Pathologists can make more accurate diagnoses with the help of a novel approach based on image processing. This approach is an ensemble model of two types of pre-trained vision transformer models, namely, Vision Transformer and Data-Efficient Image Transformer. The proposed ensemble model classifies breast cancer histopathology images into eight classes, four of which are categorized as benign, whereas the others are categorized as malignant. A public dataset was used to evaluate the proposed model. The experimental results showed 98.17% accuracy, 98.18% precision, 98.08% recall, and a 98.12% F1 score.
Hybrid Classifiers for Spatio-temporal Real-time Abnormal Behaviors Detection, Tracking, and Recognition in Massive Hajj Crowds
Jul 25, 2022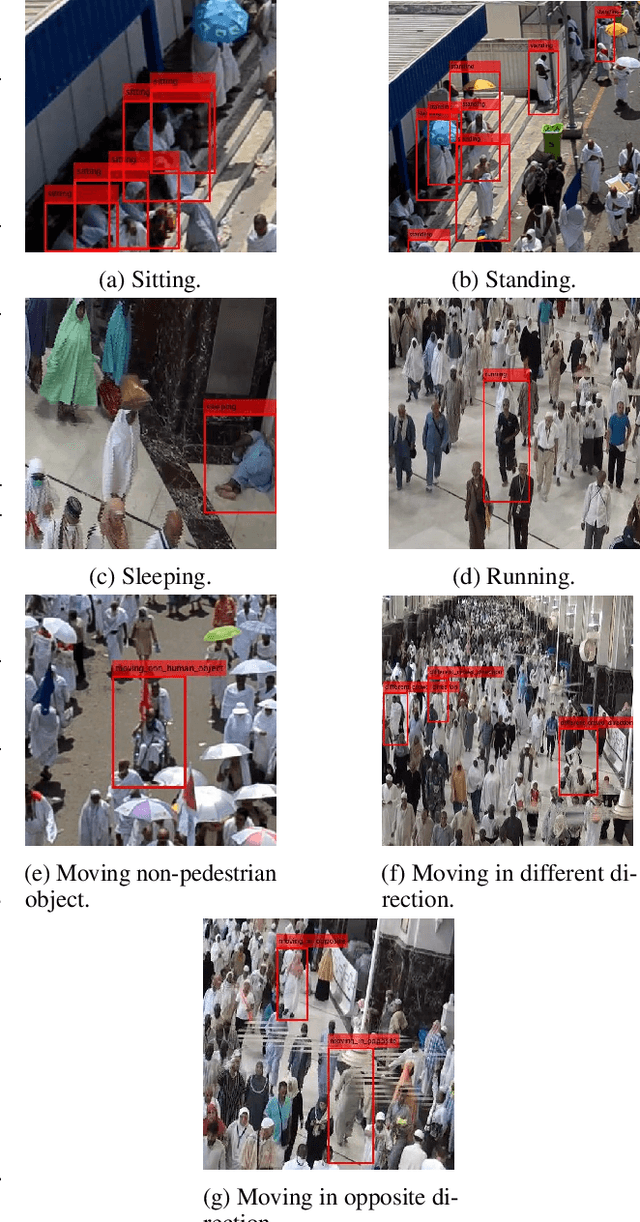
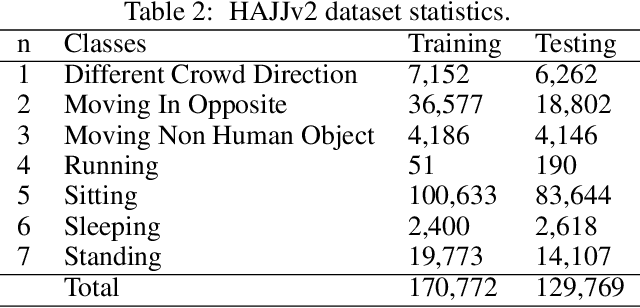
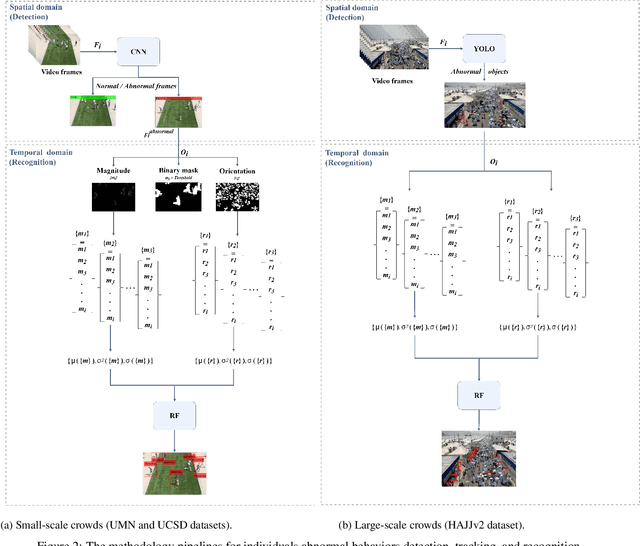
Abstract:Individual abnormal behaviors vary depending on crowd sizes, contexts, and scenes. Challenges such as partial occlusions, blurring, large-number abnormal behavior, and camera viewing occur in large-scale crowds when detecting, tracking, and recognizing individuals with abnormal behaviors. In this paper, our contribution is twofold. First, we introduce an annotated and labeled large-scale crowd abnormal behaviors Hajj dataset (HAJJv2). Second, we propose two methods of hybrid Convolutional Neural Networks (CNNs) and Random Forests (RFs) to detect and recognize Spatio-temporal abnormal behaviors in small and large-scales crowd videos. In small-scale crowd videos, a ResNet-50 pre-trained CNN model is fine-tuned to verify whether every frame is normal or abnormal in the spatial domain. If anomalous behaviors are observed, a motion-based individuals detection method based on the magnitudes and orientations of Horn-Schunck optical flow is used to locate and track individuals with abnormal behaviors. A Kalman filter is employed in large-scale crowd videos to predict and track the detected individuals in the subsequent frames. Then, means, variances, and standard deviations statistical features are computed and fed to the RF to classify individuals with abnormal behaviors in the temporal domain. In large-scale crowds, we fine-tune the ResNet-50 model using YOLOv2 object detection technique to detect individuals with abnormal behaviors in the spatial domain.
Prostate Cancer Malignancy Detection and localization from mpMRI using auto-Deep Learning: One Step Closer to Clinical Utilization
Jun 13, 2022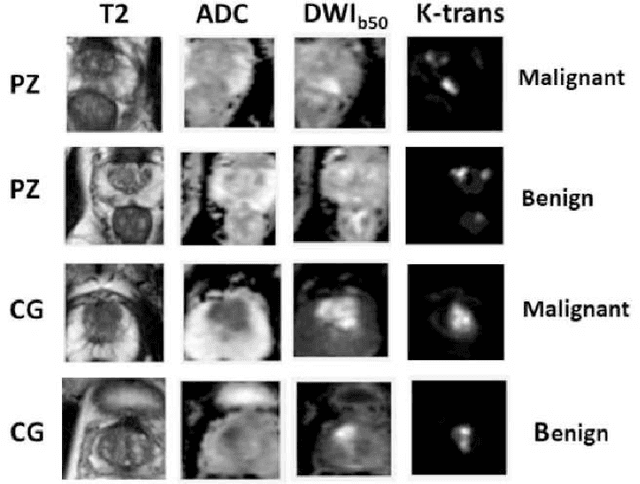

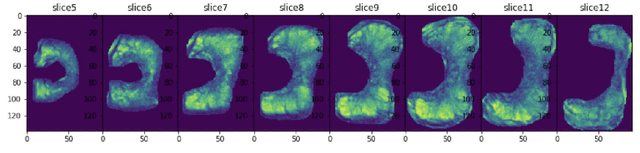
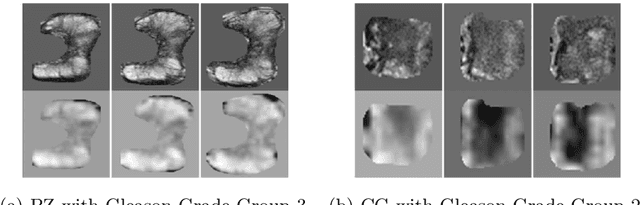
Abstract:Automatic diagnosis of malignant prostate cancer patients from mpMRI has been studied heavily in the past years. Model interpretation and domain drift have been the main road blocks for clinical utilization. As an extension from our previous work where we trained a customized convolutional neural network on a public cohort with 201 patients and the cropped 2D patches around the region of interest were used as the input, the cropped 2.5D slices of the prostate glands were used as the input, and the optimal model were searched in the model space using autoKeras. Something different was peripheral zone (PZ) and central gland (CG) were trained and tested separately, the PZ detector and CG detector were demonstrated effectively in highlighting the most suspicious slices out of a sequence, hopefully to greatly ease the workload for the physicians.
Large-scale Datasets: Faces with Partial Occlusions and Pose Variations in the Wild
Jun 27, 2017



Abstract:Face detection methods have relied on face datasets for training. However, existing face datasets tend to be in small scales for face learning in both constrained and unconstrained environments. In this paper, we first introduce our large-scale image datasets, Large-scale Labeled Face (LSLF) and noisy Large-scale Labeled Non-face (LSLNF). Our LSLF dataset consists of a large number of unconstrained multi-view and partially occluded faces. The faces have many variations in color and grayscale, image quality, image resolution, image illumination, image background, image illusion, human face, cartoon face, facial expression, light and severe partial facial occlusion, make up, gender, age, and race. Many of these faces are partially occluded with accessories such as tattoos, hats, glasses, sunglasses, hands, hair, beards, scarves, microphones, or other objects or persons. The LSLF dataset is currently the largest labeled face image dataset in the literature in terms of the number of labeled images and the number of individuals compared to other existing labeled face image datasets. Second, we introduce our CrowedFaces and CrowedNonFaces image datasets. The crowedFaces and CrowedNonFaces datasets include faces and non-faces images from crowed scenes. These datasets essentially aim for researchers to provide a large number of training examples with many variations for large scale face learning and face recognition tasks.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge