Tara Rezaei Kheirkhah
Opening the AI black box: program synthesis via mechanistic interpretability
Feb 07, 2024Abstract:We present MIPS, a novel method for program synthesis based on automated mechanistic interpretability of neural networks trained to perform the desired task, auto-distilling the learned algorithm into Python code. We test MIPS on a benchmark of 62 algorithmic tasks that can be learned by an RNN and find it highly complementary to GPT-4: MIPS solves 32 of them, including 13 that are not solved by GPT-4 (which also solves 30). MIPS uses an integer autoencoder to convert the RNN into a finite state machine, then applies Boolean or integer symbolic regression to capture the learned algorithm. As opposed to large language models, this program synthesis technique makes no use of (and is therefore not limited by) human training data such as algorithms and code from GitHub. We discuss opportunities and challenges for scaling up this approach to make machine-learned models more interpretable and trustworthy.
Universal Neurons in GPT2 Language Models
Jan 22, 2024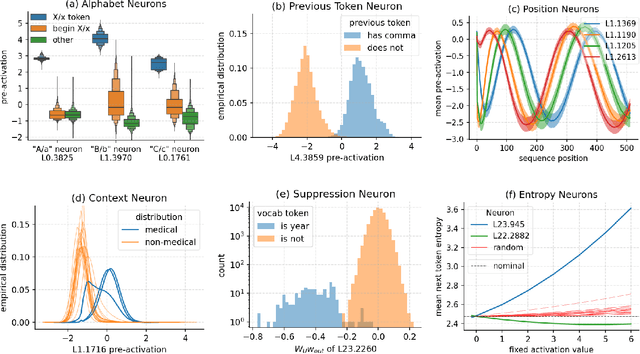
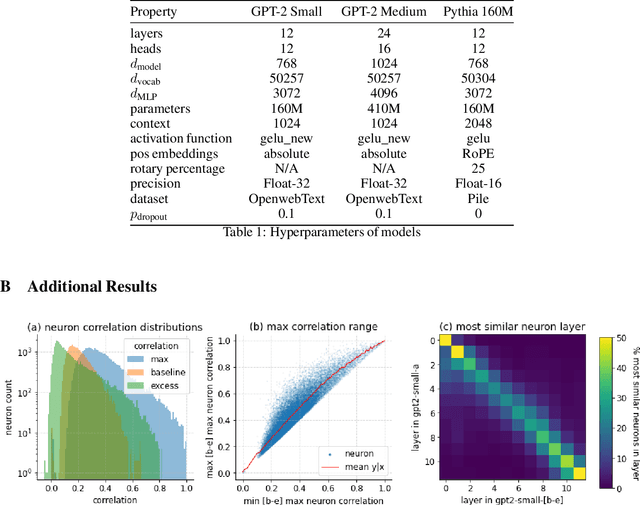
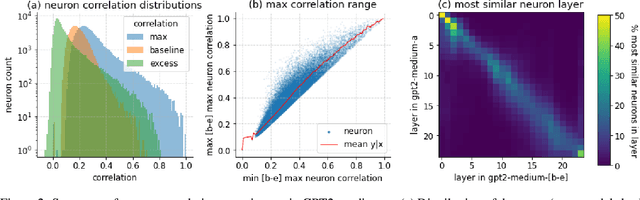
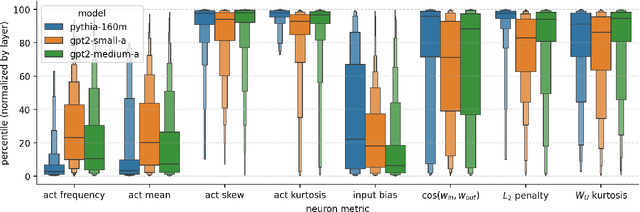
Abstract:A basic question within the emerging field of mechanistic interpretability is the degree to which neural networks learn the same underlying mechanisms. In other words, are neural mechanisms universal across different models? In this work, we study the universality of individual neurons across GPT2 models trained from different initial random seeds, motivated by the hypothesis that universal neurons are likely to be interpretable. In particular, we compute pairwise correlations of neuron activations over 100 million tokens for every neuron pair across five different seeds and find that 1-5\% of neurons are universal, that is, pairs of neurons which consistently activate on the same inputs. We then study these universal neurons in detail, finding that they usually have clear interpretations and taxonomize them into a small number of neuron families. We conclude by studying patterns in neuron weights to establish several universal functional roles of neurons in simple circuits: deactivating attention heads, changing the entropy of the next token distribution, and predicting the next token to (not) be within a particular set.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge