Tanvir Alam
Deep Learning Surrogate for Fast CIR Prediction in Reactive Molecular Diffusion Advection Channels
Dec 19, 2025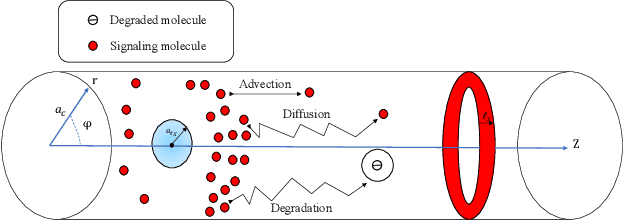
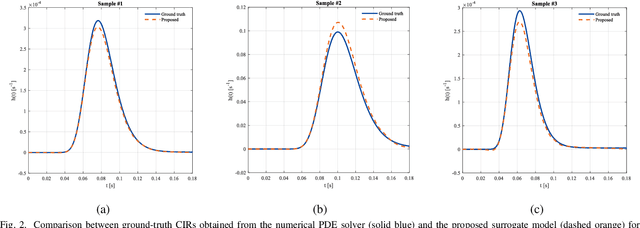
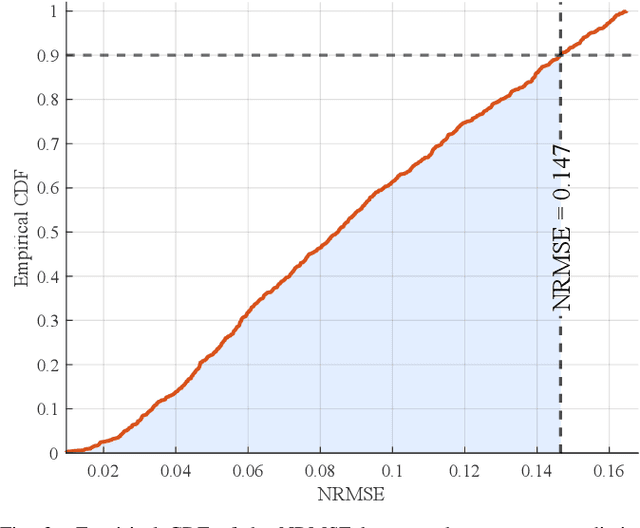
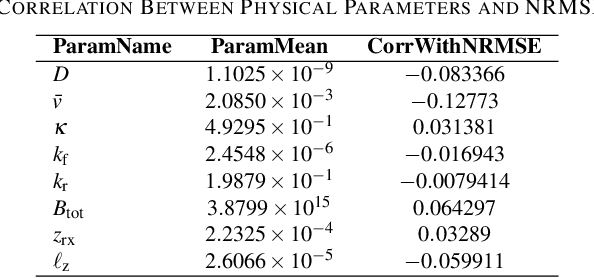
Abstract:Accurate channel impulse response (CIR) modeling in molecular communication (MC) often requires solving coupled reactive diffusion-advection equations, which is computationally expensive for large parameter sweeps or design loops. We develop a deep-learning surrogate for a three-dimensional duct MC channel with reactive diffusion-advection transport and reversible ligand-receptor binding on a finite ring receiver. Using a physics-based partial differential equation (PDE)-ordinary differential equation (ODE) model, we generate a large CIR dataset across broad transport, reaction, and geometric ranges and train a neural network that maps these parameters directly to the CIR. On an independent test set, the surrogate closely matches reference CIRs both qualitatively and quantitatively: the empirical cumulative distribution function (CDF) of the normalized root mean square error (NRMSE) shows that 90% of test channels are predicted with error below 0.15, with only weak dependence on individual parameters. The surrogate therefore offers an accurate and computationally efficient replacement for repeated PDE-based CIR evaluations in MC system analysis and design.
Brain Tumor Synthetic Data Generation with Adaptive StyleGANs
Dec 04, 2022Abstract:Generative models have been very successful over the years and have received significant attention for synthetic data generation. As deep learning models are getting more and more complex, they require large amounts of data to perform accurately. In medical image analysis, such generative models play a crucial role as the available data is limited due to challenges related to data privacy, lack of data diversity, or uneven data distributions. In this paper, we present a method to generate brain tumor MRI images using generative adversarial networks. We have utilized StyleGAN2 with ADA methodology to generate high-quality brain MRI with tumors while using a significantly smaller amount of training data when compared to the existing approaches. We use three pre-trained models for transfer learning. Results demonstrate that the proposed method can learn the distributions of brain tumors. Furthermore, the model can generate high-quality synthetic brain MRI with a tumor that can limit the small sample size issues. The approach can addresses the limited data availability by generating realistic-looking brain MRI with tumors. The code is available at: ~\url{https://github.com/rizwanqureshi123/Brain-Tumor-Synthetic-Data}.
Social Network Analysis of Hadith Narrators from Sahih Bukhari
Feb 03, 2021



Abstract:The ahadith, prophetic traditions for the Muslims around the world, are narrations originating from the sayings and the deeds of Prophet Muhammad (pbuh). They are considered one of the fundamental sources of Islamic legislation along with the Quran. The list of persons involved in the narration of each hadith is carefully scrutinized by scholars studying the hadith, with respect to their reputation and authenticity of the hadith. This is due to the its legislative importance in Islamic principles. There were many narrators who contributed to this responsibility of preserving prophetic narrations over the centuries. But to date, no systematic and comprehensive study, based on the social network, has been adapted to understand the contribution of early hadith narrators and the propagation of hadith across generations. In this study, we represented the chain of narrators of the hadith collection from Sahih Bukhari as a social graph. Based on social network analysis (SNA) on this graph, we found that the network of narrators is a scale-free network. We identified a list of influential narrators from the companions as well as the narrators from the second and third-generation who contribute significantly in the propagation of hadith collected in Sahih Bukhari. We discovered sixteen communities from the narrators of Sahih Bukhari. In each of these communities, there are other narrators who contributed significantly to the propagation of prophetic narrations. We also found that most narrators were centered in Makkah and Madinah in the era of companions and, then, gradually the center of hadith narrators shifted towards Kufa, Baghdad and central Asia over a period of time. To the best of our knowledge, this the first comprehensive and systematic study based on SNA, representing the narrators as a social graph to analyze their contribution to the preservation and propagation of hadith.
COVID-19Base: A knowledgebase to explore biomedical entities related to COVID-19
May 12, 2020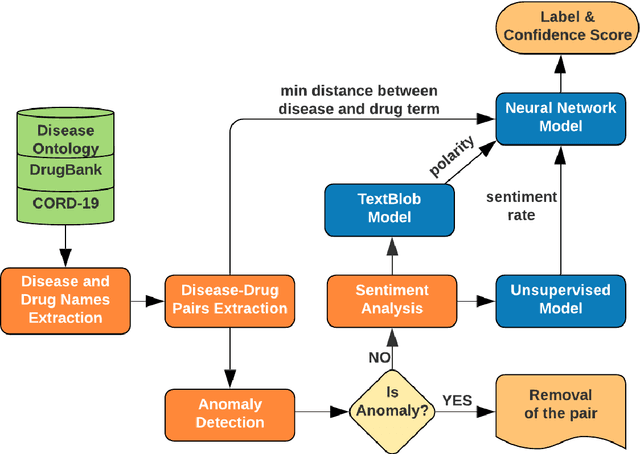
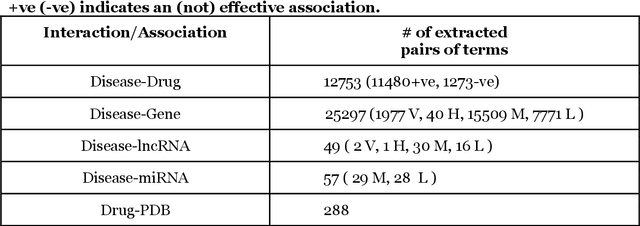
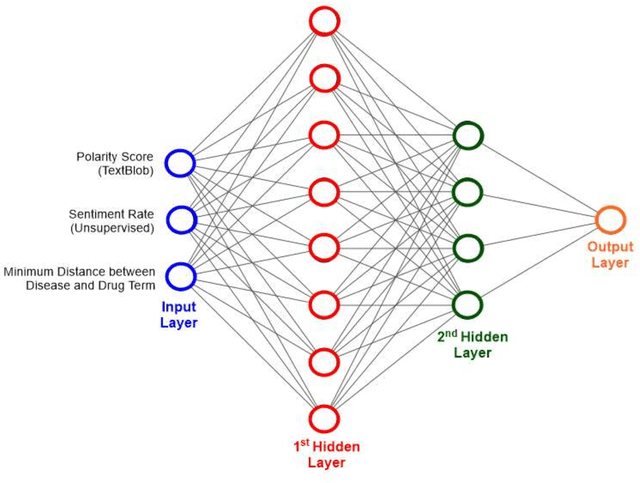
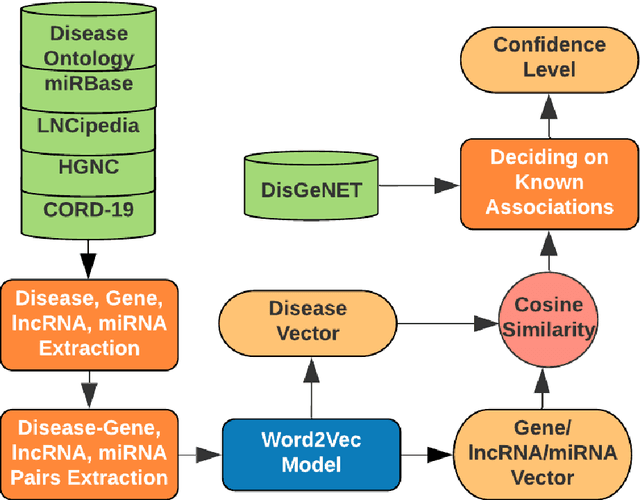
Abstract:We are presenting COVID-19Base, a knowledgebase highlighting the biomedical entities related to COVID-19 disease based on literature mining. To develop COVID-19Base, we mine the information from publicly available scientific literature and related public resources. We considered seven topic-specific dictionaries, including human genes, human miRNAs, human lncRNAs, diseases, Protein Databank, drugs, and drug side effects, are integrated to mine all scientific evidence related to COVID-19. We have employed an automated literature mining and labeling system through a novel approach to measure the effectiveness of drugs against diseases based on natural language processing, sentiment analysis, and deep learning. To the best of our knowledge, this is the first knowledgebase dedicated to COVID-19, which integrates such large variety of related biomedical entities through literature mining. Proper investigation of the mined biomedical entities along with the identified interactions among those, reported in COVID-19Base, would help the research community to discover possible ways for the therapeutic treatment of COVID-19.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge