Sujoy Roychowdhury
Knowledge Distillation of Domain-adapted LLMs for Question-Answering in Telecom
Apr 28, 2025



Abstract:Knowledge Distillation (KD) is one of the approaches to reduce the size of Large Language Models (LLMs). A LLM with smaller number of model parameters (student) is trained to mimic the performance of a LLM of a larger size (teacher model) on a specific task. For domain-specific tasks, it is not clear if teacher or student model, or both, must be considered for domain adaptation. In this work, we study this problem from perspective of telecom domain Question-Answering (QA) task. We systematically experiment with Supervised Fine-tuning (SFT) of teacher only, SFT of student only and SFT of both prior to KD. We design experiments to study the impact of vocabulary (same and different) and KD algorithms (vanilla KD and Dual Space KD, DSKD) on the distilled model. Multi-faceted evaluation of the distillation using 14 different metrics (N-gram, embedding and LLM-based metrics) is considered. Experimental results show that SFT of teacher improves performance of distilled model when both models have same vocabulary, irrespective of algorithm and metrics. Overall, SFT of both teacher and student results in better performance across all metrics, although the statistical significance of the same depends on the vocabulary of the teacher models.
Static Program Analysis Guided LLM Based Unit Test Generation
Mar 07, 2025



Abstract:We describe a novel approach to automating unit test generation for Java methods using large language models (LLMs). Existing LLM-based approaches rely on sample usage(s) of the method to test (focal method) and/or provide the entire class of the focal method as input prompt and context. The former approach is often not viable due to the lack of sample usages, especially for newly written focal methods. The latter approach does not scale well enough; the bigger the complexity of the focal method and larger associated class, the harder it is to produce adequate test code (due to factors such as exceeding the prompt and context lengths of the underlying LLM). We show that augmenting prompts with \emph{concise} and \emph{precise} context information obtained by program analysis %of the focal method increases the effectiveness of generating unit test code through LLMs. We validate our approach on a large commercial Java project and a popular open-source Java project.
Evaluation of Table Representations to Answer Questions from Tables in Documents : A Case Study using 3GPP Specifications
Aug 30, 2024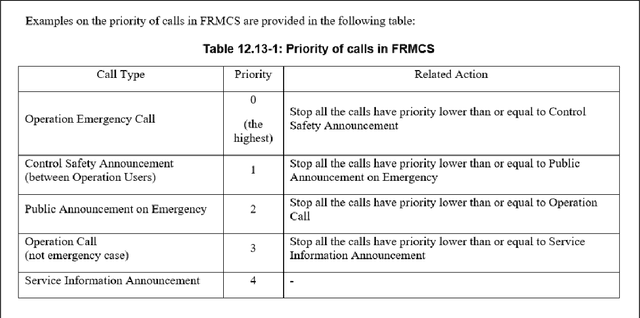
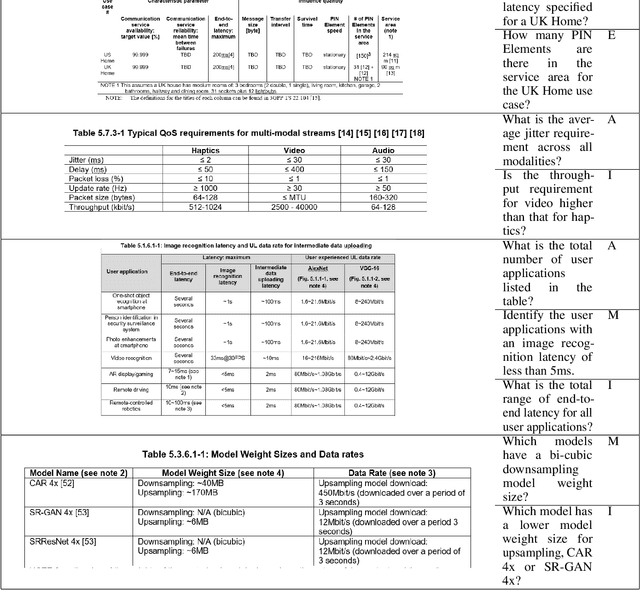
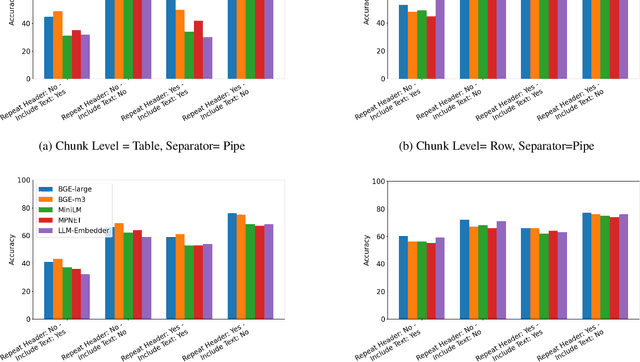
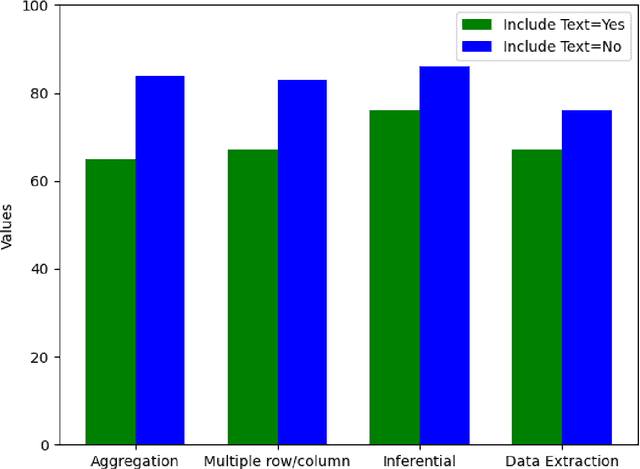
Abstract:With the ubiquitous use of document corpora for question answering, one important aspect which is especially relevant for technical documents is the ability to extract information from tables which are interspersed with text. The major challenge in this is that unlike free-flow text or isolated set of tables, the representation of a table in terms of what is a relevant chunk is not obvious. We conduct a series of experiments examining various representations of tabular data interspersed with text to understand the relative benefits of different representations. We choose a corpus of $3^{rd}$ Generation Partnership Project (3GPP) documents since they are heavily interspersed with tables. We create expert curated dataset of question answers to evaluate our approach. We conclude that row level representations with corresponding table header information being included in every cell improves the performance of the retrieval, thus leveraging the structural information present in the tabular data.
Icing on the Cake: Automatic Code Summarization at Ericsson
Aug 19, 2024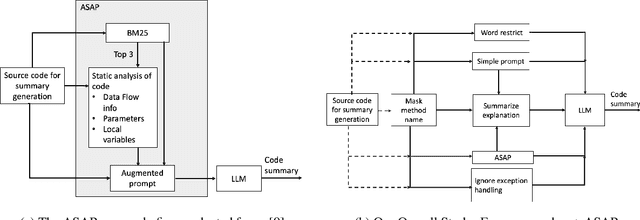
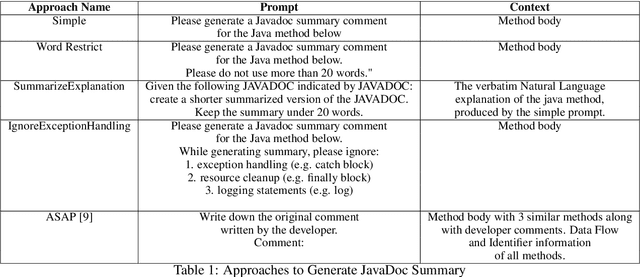
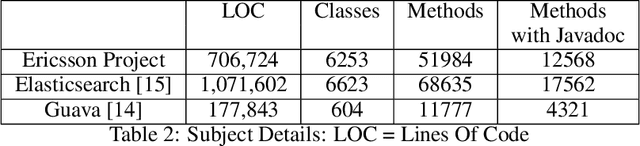
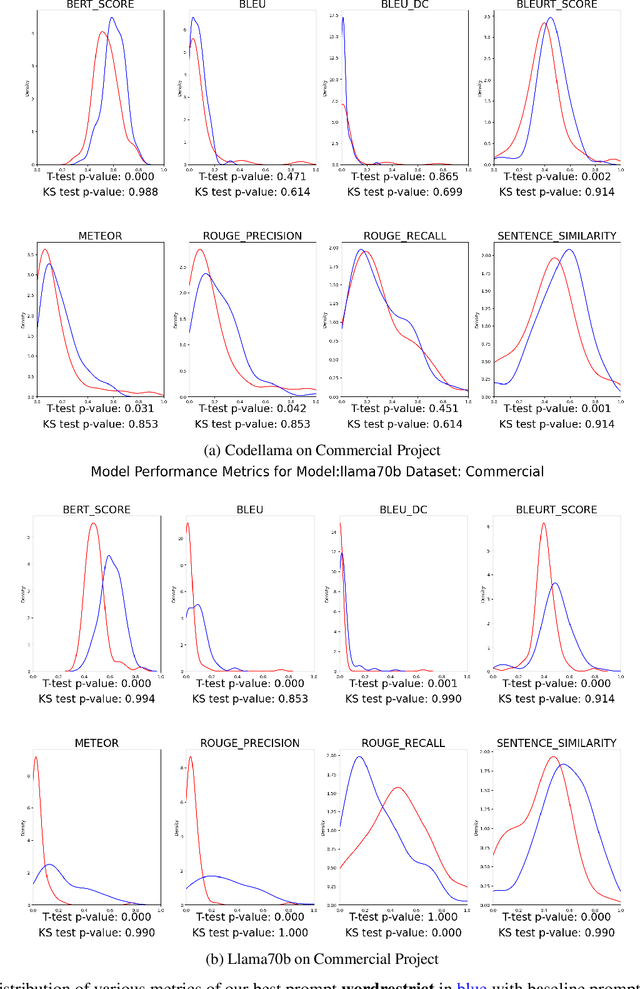
Abstract:This paper presents our findings on the automatic summarization of Java methods within Ericsson, a global telecommunications company. We evaluate the performance of an approach called Automatic Semantic Augmentation of Prompts (ASAP), which uses a Large Language Model (LLM) to generate leading summary comments for Java methods. ASAP enhances the $LLM's$ prompt context by integrating static program analysis and information retrieval techniques to identify similar exemplar methods along with their developer-written Javadocs, and serves as the baseline in our study. In contrast, we explore and compare the performance of four simpler approaches that do not require static program analysis, information retrieval, or the presence of exemplars as in the ASAP method. Our methods rely solely on the Java method body as input, making them lightweight and more suitable for rapid deployment in commercial software development environments. We conducted experiments on an Ericsson software project and replicated the study using two widely-used open-source Java projects, Guava and Elasticsearch, to ensure the reliability of our results. Performance was measured across eight metrics that capture various aspects of similarity. Notably, one of our simpler approaches performed as well as or better than the ASAP method on both the Ericsson project and the open-source projects. Additionally, we performed an ablation study to examine the impact of method names on Javadoc summary generation across our four proposed approaches and the ASAP method. By masking the method names and observing the generated summaries, we found that our approaches were statistically significantly less influenced by the absence of method names compared to the baseline. This suggests that our methods are more robust to variations in method names and may derive summaries more comprehensively from the method body than the ASAP approach.
Evaluation of RAG Metrics for Question Answering in the Telecom Domain
Jul 15, 2024



Abstract:Retrieval Augmented Generation (RAG) is widely used to enable Large Language Models (LLMs) perform Question Answering (QA) tasks in various domains. However, RAG based on open-source LLM for specialized domains has challenges of evaluating generated responses. A popular framework in the literature is the RAG Assessment (RAGAS), a publicly available library which uses LLMs for evaluation. One disadvantage of RAGAS is the lack of details of derivation of numerical value of the evaluation metrics. One of the outcomes of this work is a modified version of this package for few metrics (faithfulness, context relevance, answer relevance, answer correctness, answer similarity and factual correctness) through which we provide the intermediate outputs of the prompts by using any LLMs. Next, we analyse the expert evaluations of the output of the modified RAGAS package and observe the challenges of using it in the telecom domain. We also study the effect of the metrics under correct vs. wrong retrieval and observe that few of the metrics have higher values for correct retrieval. We also study for differences in metrics between base embeddings and those domain adapted via pre-training and fine-tuning. Finally, we comment on the suitability and challenges of using these metrics for in-the-wild telecom QA task.
A Compass for Navigating the World of Sentence Embeddings for the Telecom Domain
Jun 18, 2024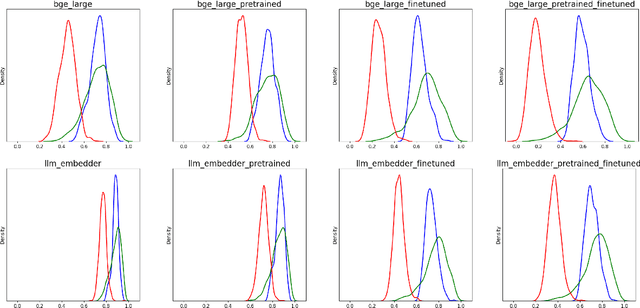
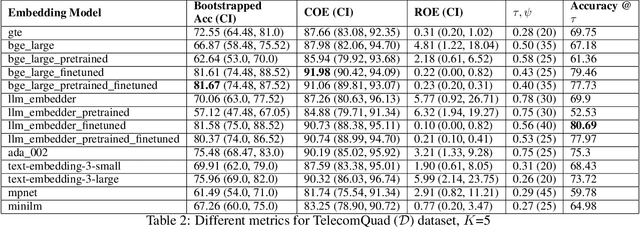
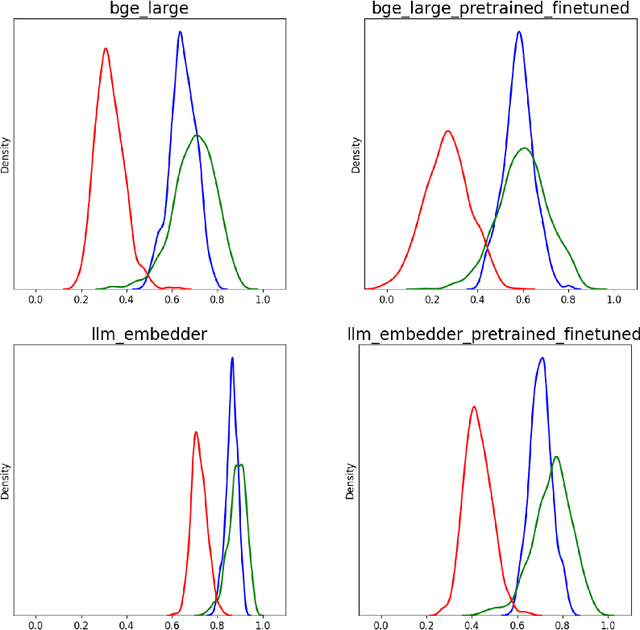
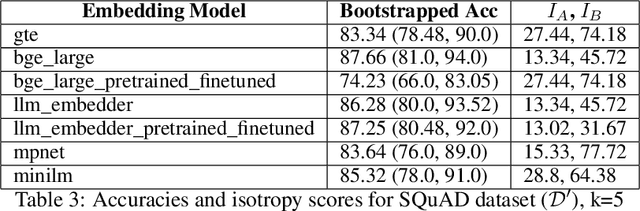
Abstract:A plethora of sentence embedding models makes it challenging to choose one, especially for domains such as telecom, rich with specialized vocabulary. We evaluate multiple embeddings obtained from publicly available models and their domain-adapted variants, on both point retrieval accuracies as well as their (95\%) confidence intervals. We establish a systematic method to obtain thresholds for similarity scores for different embeddings. We observe that fine-tuning improves mean bootstrapped accuracies as well as tightens confidence intervals. The pre-training combined with fine-tuning makes confidence intervals even tighter. To understand these variations, we analyse and report significant correlations between the distributional overlap between top-$K$, correct and random sentence similarities with retrieval accuracies and similarity thresholds. Following current literature, we analyze if retrieval accuracy variations can be attributed to isotropy of embeddings. Our conclusions are that isotropy of embeddings (as measured by two independent state-of-the-art isotropy metric definitions) cannot be attributed to better retrieval performance. However, domain adaptation which improves retrieval accuracies also improves isotropy. We establish that domain adaptation moves domain specific embeddings further away from general domain embeddings.
Observations on Building RAG Systems for Technical Documents
Mar 31, 2024



Abstract:Retrieval augmented generation (RAG) for technical documents creates challenges as embeddings do not often capture domain information. We review prior art for important factors affecting RAG and perform experiments to highlight best practices and potential challenges to build RAG systems for technical documents.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge