Souvik Das
HBNET-GIANT: A communication-efficient accelerated Newton-type fully distributed optimization algorithm
Nov 17, 2025Abstract:This article presents a second-order fully distributed optimization algorithm, HBNET-GIANT, driven by heavy-ball momentum, for $L$-smooth and $μ$-strongly convex objective functions. A rigorous convergence analysis is performed, and we demonstrate global linear convergence under certain sufficient conditions. Through extensive numerical experiments, we show that HBNET-GIANT with heavy-ball momentum achieves acceleration, and the corresponding rate of convergence is strictly faster than its non-accelerated version, NETWORK-GIANT. Moreover, we compare HBNET-GIANT with several state-of-the-art algorithms, both momentum-based and without momentum, and report significant performance improvement in convergence to the optimum. We believe that this work lays the groundwork for a broader class of second-order Newton-type algorithms with momentum and motivates further investigation into open problems, including an analytical proof of local acceleration in the fully distributed setting for convex optimization problems.
Beyond Discrete Personas: Personality Modeling Through Journal Intensive Conversations
Dec 15, 2024Abstract:Large Language Models (LLMs) have significantly improved personalized conversational capabilities. However, existing datasets like Persona Chat, Synthetic Persona Chat, and Blended Skill Talk rely on static, predefined personas. This approach often results in dialogues that fail to capture human personalities' fluid and evolving nature. To overcome these limitations, we introduce a novel dataset with around 400,000 dialogues and a framework for generating personalized conversations using long-form journal entries from Reddit. Our approach clusters journal entries for each author and filters them by selecting the most representative cluster, ensuring that the retained entries best reflect the author's personality. We further refine the data by capturing the Big Five personality traits --openness, conscientiousness, extraversion, agreeableness, and neuroticism --ensuring that dialogues authentically reflect an individual's personality. Using Llama 3 70B, we generate high-quality, personality-rich dialogues grounded in these journal entries. Fine-tuning models on this dataset leads to an 11% improvement in capturing personality traits on average, outperforming existing approaches in generating more coherent and personality-driven dialogues.
Mitigating Clickbait: An Approach to Spoiler Generation Using Multitask Learning
May 07, 2024Abstract:This study introduces 'clickbait spoiling', a novel technique designed to detect, categorize, and generate spoilers as succinct text responses, countering the curiosity induced by clickbait content. By leveraging a multi-task learning framework, our model's generalization capabilities are significantly enhanced, effectively addressing the pervasive issue of clickbait. The crux of our research lies in generating appropriate spoilers, be it a phrase, an extended passage, or multiple, depending on the spoiler type required. Our methodology integrates two crucial techniques: a refined spoiler categorization method and a modified version of the Question Answering (QA) mechanism, incorporated within a multi-task learning paradigm for optimized spoiler extraction from context. Notably, we have included fine-tuning methods for models capable of handling longer sequences to accommodate the generation of extended spoilers. This research highlights the potential of sophisticated text processing techniques in tackling the omnipresent issue of clickbait, promising an enhanced user experience in the digital realm.
Entropy Guided Extrapolative Decoding to Improve Factuality in Large Language Models
Apr 14, 2024



Abstract:Large language models (LLMs) exhibit impressive natural language capabilities but suffer from hallucination -- generating content ungrounded in the realities of training data. Recent work has focused on decoding techniques to improve factuality during inference by leveraging LLMs' hierarchical representation of factual knowledge, manipulating the predicted distributions at inference time. Current state-of-the-art approaches refine decoding by contrasting early-exit distributions from a lower layer with the final layer to exploit information related to factuality within the model forward procedure. However, such methods often assume the final layer is the most reliable and the lower layer selection process depends on it. In this work, we first propose extrapolation of critical token probabilities beyond the last layer for more accurate contrasting. We additionally employ layer-wise entropy-guided lower layer selection, decoupling the selection process from the final layer. Experiments demonstrate strong performance - surpassing state-of-the-art on multiple different datasets by large margins. Analyses show different kinds of prompts respond to different selection strategies.
Improving Dialog Safety using Socially Aware Contrastive Learning
Feb 01, 2024Abstract:State-of-the-art conversational AI systems raise concerns due to their potential risks of generating unsafe, toxic, unethical, or dangerous content. Previous works have developed datasets to teach conversational agents the appropriate social paradigms to respond effectively to specifically designed hazardous content. However, models trained on these adversarial datasets still struggle to recognize subtle unsafe situations that appear naturally in conversations or introduce an inappropriate response in a casual context. To understand the extent of this problem, we study prosociality in both adversarial and casual dialog contexts and audit the response quality of general-purpose language models in terms of propensity to produce unsafe content. We propose a dual-step fine-tuning process to address these issues using a socially aware n-pair contrastive loss. Subsequently, we train a base model that integrates prosocial behavior by leveraging datasets like Moral Integrity Corpus (MIC) and ProsocialDialog. Experimental results on several dialog datasets demonstrate the effectiveness of our approach in generating socially appropriate responses.
Diving Deep into Modes of Fact Hallucinations in Dialogue Systems
Jan 11, 2023



Abstract:Knowledge Graph(KG) grounded conversations often use large pre-trained models and usually suffer from fact hallucination. Frequently entities with no references in knowledge sources and conversation history are introduced into responses, thus hindering the flow of the conversation -- existing work attempt to overcome this issue by tweaking the training procedure or using a multi-step refining method. However, minimal effort is put into constructing an entity-level hallucination detection system, which would provide fine-grained signals that control fallacious content while generating responses. As a first step to address this issue, we dive deep to identify various modes of hallucination in KG-grounded chatbots through human feedback analysis. Secondly, we propose a series of perturbation strategies to create a synthetic dataset named FADE (FActual Dialogue Hallucination DEtection Dataset). Finally, we conduct comprehensive data analyses and create multiple baseline models for hallucination detection to compare against human-verified data and already established benchmarks.
Using Multi-Encoder Fusion Strategies to Improve Personalized Response Selection
Aug 30, 2022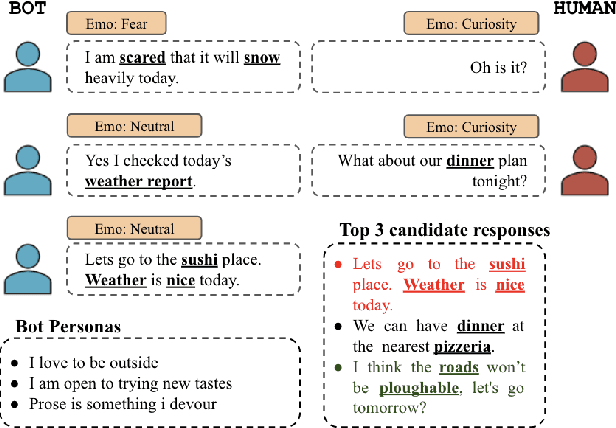

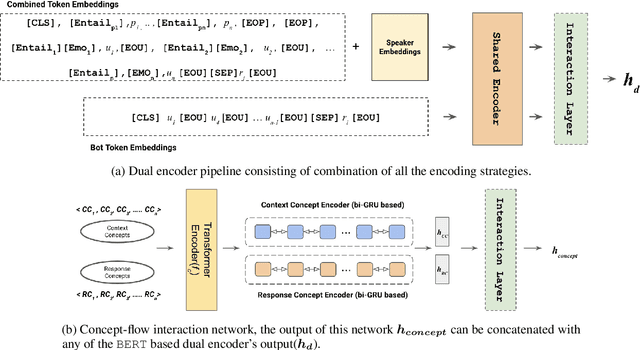
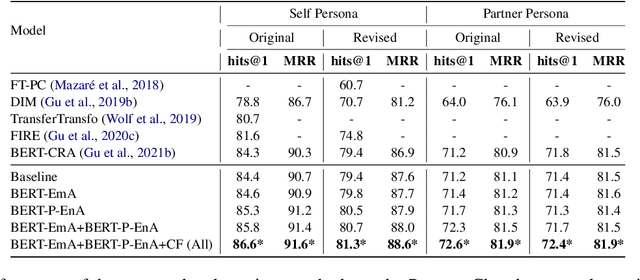
Abstract:Personalized response selection systems are generally grounded on persona. However, there exists a co-relation between persona and empathy, which is not explored well in these systems. Also, faithfulness to the conversation context plunges when a contradictory or an off-topic response is selected. This paper attempts to address these issues by proposing a suite of fusion strategies that capture the interaction between persona, emotion, and entailment information of the utterances. Ablation studies on the Persona-Chat dataset show that incorporating emotion and entailment improves the accuracy of response selection. We combine our fusion strategies and concept-flow encoding to train a BERT-based model which outperforms the previous methods by margins larger than 2.3 % on original personas and 1.9 % on revised personas in terms of hits@1 (top-1 accuracy), achieving a new state-of-the-art performance on the Persona-Chat dataset.
Proto: A Neural Cocktail for Generating Appealing Conversations
Sep 06, 2021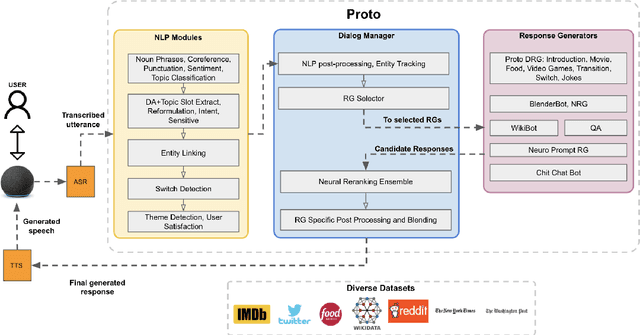
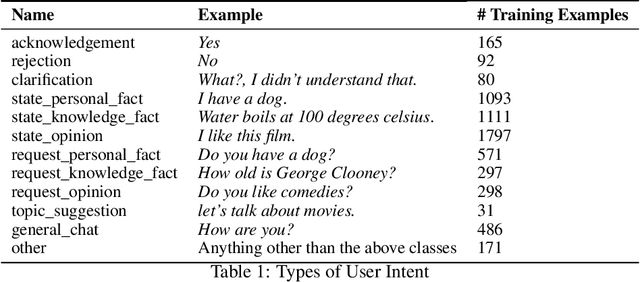
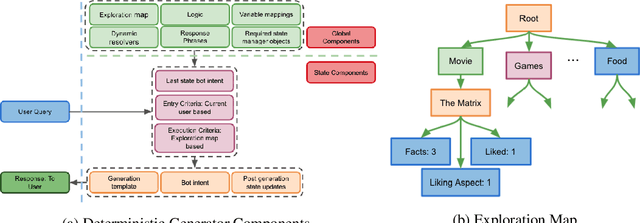
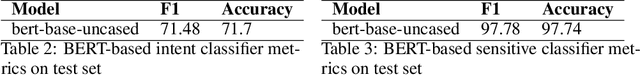
Abstract:In this paper, we present our Alexa Prize Grand Challenge 4 socialbot: Proto. Leveraging diverse sources of world knowledge, and powered by a suite of neural and rule-based natural language understanding modules, state-of-the-art neural generators, novel state-based deterministic generators, an ensemble of neural re-rankers, a robust post-processing algorithm, and an efficient overall conversation strategy, Proto strives to be able to converse coherently about a diverse range of topics of interest to humans, and provide a memorable experience to the user. In this paper we dissect and analyze the different components and conversation strategies implemented by our socialbot, which enables us to generate colloquial, empathetic, engaging, self-rectifying, factually correct, and on-topic response, which has helped us achieve consistent scores throughout the competition.
Similarity Based Label Smoothing For Dialogue Generation
Jul 23, 2021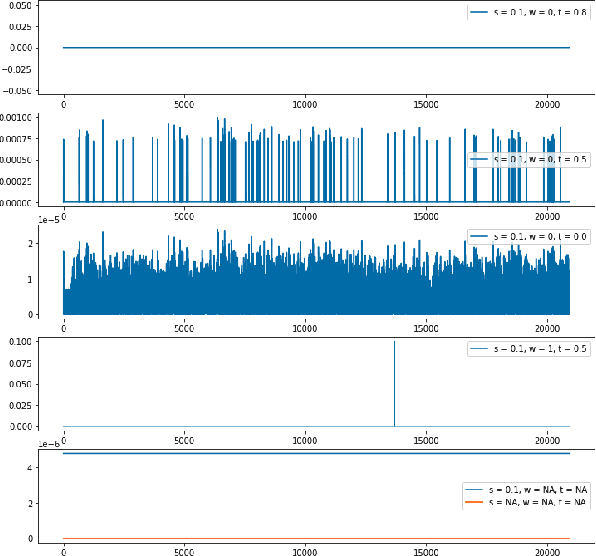
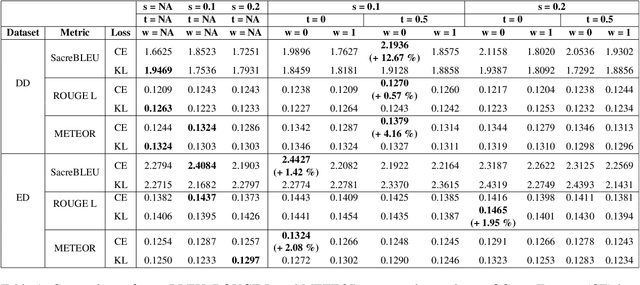
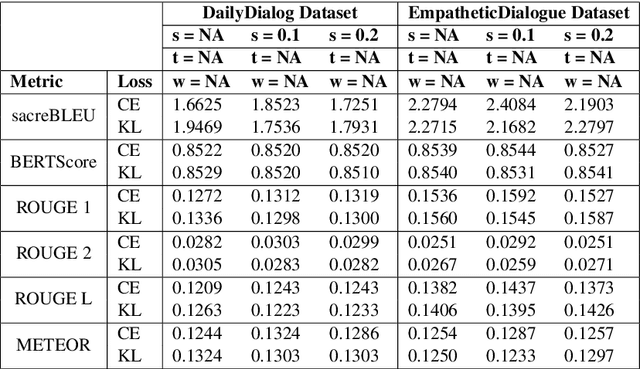
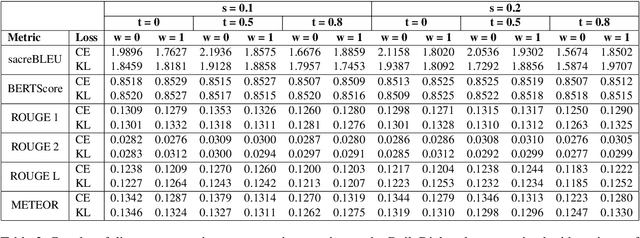
Abstract:Generative neural conversational systems are generally trained with the objective of minimizing the entropy loss between the training "hard" targets and the predicted logits. Often, performance gains and improved generalization can be achieved by using regularization techniques like label smoothing, which converts the training "hard" targets to "soft" targets. However, label smoothing enforces a data independent uniform distribution on the incorrect training targets, which leads to an incorrect assumption of equi-probable incorrect targets for each correct target. In this paper we propose and experiment with incorporating data dependent word similarity based weighing methods to transforms the uniform distribution of the incorrect target probabilities in label smoothing, to a more natural distribution based on semantics. We introduce hyperparameters to control the incorrect target distribution, and report significant performance gains over networks trained using standard label smoothing based loss, on two standard open domain dialogue corpora.
Medical Literature Mining and Retrieval in a Conversational Setting
Jul 23, 2021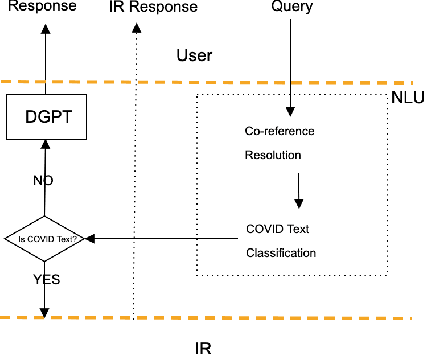
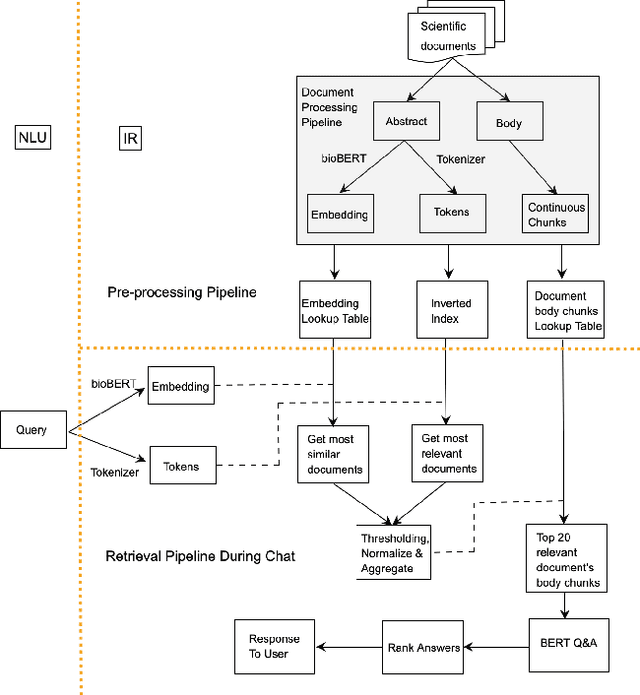

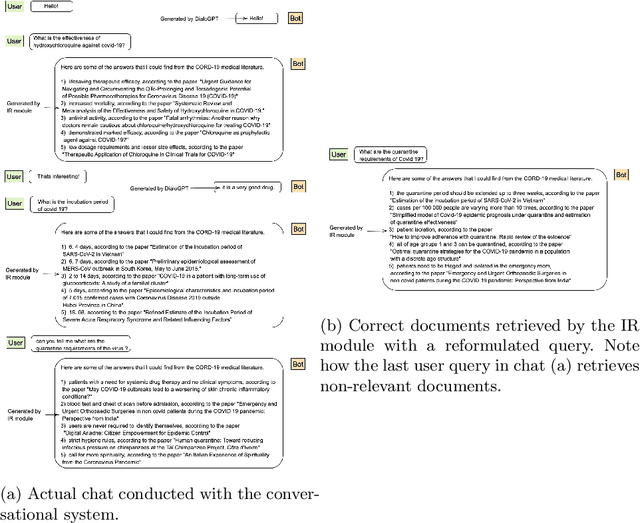
Abstract:The Covid-19 pandemic has caused a spur in the medical research literature. With new research advances in understanding the virus, there is a need for robust text mining tools which can process, extract and present answers from the literature in a concise and consumable way. With a DialoGPT based multi-turn conversation generation module, and BM-25 \& neural embeddings based ensemble information retrieval module, in this paper we present a conversational system, which can retrieve and answer coronavirus-related queries from the rich medical literature, and present it in a conversational setting with the user. We further perform experiments to compare neural embedding-based document retrieval and the traditional BM25 retrieval algorithm and report the results.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge